Abstract
Study design: Multicenter, open, prospective, before-after study.
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of sildenafil therapy for erectile dysfunction in patients with spinal cord injury, and the association between the response to sildenafil and factors such as causes and levels of spinal cord injury, grade of ASIA deficit, time since injury, orgasmic perception, and degree of baseline erection.
Setting: Homes of outpatients of 16 spinal cord injury units in Spain.
Method: One hundred and seventy patients with erectile dysfunction secondary to spinal cord injury, from whom baseline data were collected on their sexual function, and who started treatment with sildenafil 50 mg. An efficacy assessment was made by the patient and his partner, and the score of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) was recorded.
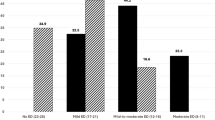
Results: It was reported by 88.2% of the patients and 85.3% of their partners that treatment with sildenafil had improved their erections, regardless of the baseline characteristics of the spinal cord injury and erectile function. In responders, this improvement was confirmed by an increase from 12.5 to 24.8 points (P<0.001) of the Erectile Function Domain of IIEF. A significant improvement was also seen in patients' satisfaction with sexual activity and general satisfaction derived from sexual life. Preservation of orgasmic perception and a baseline degree of erection of 3 or 4 (P=0.006) were predictors of therapeutic success. No serious adverse events occurred.
Conclusion: Sildenafil is an effective, well-tolerated treatment for erectile dysfunction caused by spinal cord injury, regardless of the cause, neurological level, ASIA grade, and time since injury.
Sponsorship: Spanish Society of Paraplegia.
Spinal Cord (2001) 39, 637–643.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence . Impotence JAMA 1993 270: 83–90
Courtois F et al. Clinical approach to erectile dysfunction in spinal cord injury men. A review of clinical experimental data Paraplegia 1995 33: 628–635
François N, Maury M . Sexual aspects in paraplegic patients Paraplegia 1987 25: 289–292
Andersson K-E, Wargner G . Physiology of penile erection Physiol Rev 1995 75: 191–236
Burnett AL . The role of nitric oxide in the physiology of erection Biol Reprod 1995 52: 485–489
Boolell M et al. Sildenafil: an orally active type 5 cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of penile erectile dysfunction Int J Impotence Res 1996 8: 47–52
Rosen RC et al. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): A multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction Urology 1997 49: 822–830
Maynard Jr FM et al. International Standards for Neurological and Functional Classification of Spinal Cord Injury. American Spinal Injury Association Spinal Cord 1997 35: 266–274
Giuliano F, Hultling C, El Masry E, for the Sildenafil Study Group . Randomized trial of sildenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in spinal cord injury Ann Neurol 1999 46: 15–21
Giuliano F et al. Sildenafil citrate (Viagra®): a novel oral treatment for erectile dysfunction caused by traumatic spinal cord injury IJCP 1999 Supplement 102
Derry F et al. Efficacy and safety of oral sildenafil (Viagra®) in men with erectile dysfunction caused by spinal cord injury Neurology 1998 51: 1629–1633
Mayton M et al. A two part pilot study of sildenafil (Viagra®) in men with erectile dysfunction caused by spinal cord injury Spinal Cord 1999 37: 110–116
Acknowledgements
To Drs F Casaus, N Cruz, V Forner, C Arechaga, ML López, T Usabiaga, A García and L García for their help in the study design and collection of the study date; to I Álvarez, M Mas and JL Sánchez for their participation in the statistical analysis and revision of the manuscript; to F del Moral and JC Checa for co-ordinating the study; and to all of them, our recognition for their valuable participation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez Ramos, A., Vidal, J., Jáuregui, M. et al. Efficacy, safety and predictive factors of therapeutic success with sildenafil for erectile dysfunction in patients with different spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord 39, 637–643 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101210
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101210
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sexual Health in the Neurogenic Patient
Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports (2020)
-
Erectile Dysfunction and Neurological Comorbidities: a Contemporary Review
Current Sexual Health Reports (2020)
-
Sexual Dysfunction After Spinal Cord Injury
Current Sexual Health Reports (2020)
-
Orgasm and SCI: what do we know?
Spinal Cord (2018)
-
A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial assessing the effect of tadalafil (Cialis) on the cardiovascular response in men with complete spinal cord injury above the sixth thoracic level: A Pilot Study
Spinal Cord Series and Cases (2018)