Abstract
Study design: To study the short- and long-term medical complications encountered in tetraplegic spinal cord injured persons (TSCI) and to give prominence to both the medical and socio-economic factors with which they are respectively associated.
Methods: The Tetrafigap Study is a multicentre epidemiological survey carried out using self-administered questionniares studying the global long-term outcome of TSCI patients after the initial phase of rehabilitation.
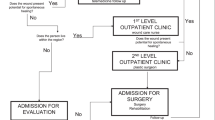
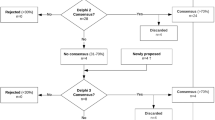
Results: The data for 1668 patients were analyzed. The rate of rehospitalisations was 74.4% with on average three stays per patient and as reported causes, in descending order: urinary complications, systematic follow-up, pressure sores, respiratory complications, contractures, bowel complications, pains and secondary fractures of the lower limbs. At the time of the survey, 84.7% of patients mentioned awkward contractures, 73.8% pains, 55.9% embarrassing urinary leakage and 14.1% pressure sores. With regard to persons suffering from complete motor lesion, urinary complications and pressure sores were more frequently reported, whereas for persons suffering from incomplete motor lesions, awkward contractures and pains were more frequent. In the elderly, pains were more often mentioned, and pressure sores and pain were also the most common in patients coming from lower socio-professional status. Contractures and pain decreased with time. All these complications but pressure sores and pain are statistically interrelated.
Conclusion: The medical complications of spinal cord injured persons are frequent, they are linked to biological, psychological and environmental factors, and are interrelated. Therefore, seeking mid- and long-term risk factors must be given priority in order to better adapt attempts at increasing secondary prevention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
De Vivo MJ et al. Seven-year survival following spinal cord injury Arch Neurol 1987 44: 872–875
De Vivo MJ et al. A cross-sectional study of the relationship between age and current health status for persons with spinal cord injuries Paraplegia 1992 30: 820–827
Le CT, Price M . Survival from Spinal Cord Injury J Chron Dis 1982 35: 487–492
De Vivo MJ, Richards JS, Stover SL, Go BK . Spinal Cord Injury: Rehabilitation adds life to years West J Med 1991 154: 602–606
De Vivo MJ et al. The influence of age at time of spinal cord injury on rehabilitation outcome Arch Neurol 1990 47: 687–691
De Vivo MJ et al. Outcomes of the older patient with spinal cord injury Paraplegia ASIA Meeting 1987
Shingu H et al. A nationwide epidemiological survey of spinal cord injuries in Japan from January 1990 to December 1992 Paraplegia 1995 33: 183–188
Frankel HL et al. Long-term survival in spinal cord injury: a fifty year investigation Spinal Cord 1998 36: 266–274
Nakajima A, Honda S . Physical and social condition of rehabilited spinal cord injury patients in Japan: a long term review Paraplegia 1988 26: 165–176
Mesard L et al. Survival after spinal cord trauma. A life table analysis Arch Neurol 1978 35: 78–83
Dincer F, Oflazer A, Beyazova M . Traumatic spinal cord injuries in Turkey Paraplegia 1992 30: 641–646
Hartkopp A et al. Survival and cause of death after traumatic spinal cord injury. A long-term epidemiological survey from Denmark Spinal Cord 1997 35: 76–85
Minaire P et al. Life expectancy following spinal cord injury: a ten-years survey in the Rhone-Alpes region, France, 1969–1980 Paraplegia 1983 21: 11–15
Whiteneck GG et al. Mortality, morbidity, and psychosocial outcomes of persons spinal cord injured more than 20 years ago Paraplegic 1992 30: 617–630
Harvey C et al. New estimates of the direct costs of traumatic spinal cord injuries: results of a nationwide survey Paraplegia 1992 30: 834–850
Acton A et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury in Arkansas, 1980 to 1989 Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1993 74: 1035–1040
Kraus JF et al. Incidence of traumatic spinal cord lesions J Chron Dis 1975 28: 471–492
Hart C, Williams E . Epidemiology of spinal cord injuries: a reflection of changes in South African society Paraplegia 1994 32: 709–714
Daverat P, Gagnon M, Dartigues JF . Initial factors predicting survival in patients with a spinal cord injury J Neurol, Neurosurg Psych 1989 52: 403–406
Berkowitz M, Harvey C, Greene CG, Wilson SE . The economic consequences of traumatic spinal cord injury New York: Demos Publications 1992
Ravaud JF et al. The Tetrafigap survey on the long-term outcome of tetraplegic spinal cord injured individuals: Part I. Protocol and methodology Spinal Cord 1998 36: 117–124
Ravaud JF, Delcey M, Desert JF the TETRAFIGAP Group. The Tetrafigap Survey on the long-term outcome of tetraplegic spinal cord injured persons, Part III: Demographic characteristics and initial cause of injury Spinal Cord 2000 38: 164–172
De Jong G . Physical disability and public policy SCI Am 1983 248: 40–49
Davidoff G et al. Rehospitalization after initial rehabilitation for acute spinal cord injury: incidence and risk factors Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1990 71: 121–124
Ivie CS, De Vivo MJ . Predicting unplanned hospitalizations in persons with spinal cord injury Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1994 75: 1182–1188
Young JS, Northrup RE . Rehospitalization in year 2 and 3 following spinal cord injury Model system's SCI 1980 1: 21–26
Savic G, Short DJ, Weitzenkamp D, Charlifue S, Gardner BP . Hospital readmissions in people with chronic spinal cord injury Spinal Cord 2000 38: 371–377
Anderson TP . Psychosocial factors associated with pressure sores Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1979 60: 341–346
Swanson ED . Relationship between locus-of-control expectancy and successful rehabilitation of spinal cord injured Tempe, AZ: Arizona State University 1976
Meyers AR et al. Rehospitalization and spinal cord injury: cross-sectional survey of adults living independently Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1985 66: 704–708
Byrne DW, Salzberg CA . Major risk factors for pressure ulcers in the spinal cord disabled: a literature review Spinal Cord 1996 34: 255–263
Garber SL, Rintala DH, Don Rossi C . Reported pressure ulcer prevention and management techniques by persons with spinal cord injury Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1996 77: 744–749
Salzberg CA, Byrne DW, Cayten CG . A new pressure ulcer risk assessment scale for individuals with spinal cord injury Am J Phys Med Rehabil 1996 4: 96–104
Sumiya T et al. A survey of wheelchair use by paraplegic individuals in Japan. Part 2: Prevalence of pressure sores Spinal Cord 1997 35: 595–598
Vidal J, Sarrias M . An analysis of the diverse factors concerned with the development of pressure sores in spinal cord injured patients Paraplegia 91 29: 261–267
Stone JM et al. Chronic gastrointestinal problems in spinal cord injury patients: a prospective analysis Am J Gastroenterol 1990 85: 1114–1119
Demirel G et al. Pain following spinal cord injury Spinal Cord 1998 36: 25–28
Fenollosa P et al. Chronic pain in the spinal cord injured: statistical approach and pharmacological treatment Paraplegia 1993 31: 722–729
Stormer S et al. Chronic pain/dysaesthesiae in spinal cord injury patients: results of a multicentre study Spinal Cord 1997 35: 446–455
Krause JS, Crewe NM . Long term prediction of self-reported problems following spinal cord injury Paraplegia 1990 28: 186–202
Lin K et al. Quality of life of spinal cord injured patients in Taiwan: a subgroup study Spinal Cord 1997 35: 841–849
Little JW, Michlesen P, Umlauf R . Lower extremity manifestations of spasticity in chronic spinal cord injury Am J Phys Med Rehabil 1989 68: 32–36
Maynard FM, Karunas RS, Waring WP . Epidemiology of spasticity following traumatic spinal cord injury Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1990 71: 566–569
Dimitrijevic MR, Dimitrijevic MM, Fragenel J . Suprasegmentally induced motor unit activity in paralyzed muscles of patients with established spinal cord injury Ann Neurol 1984 16: 216–221
Nepomuceno C et al. Pain in patients with spinal cord injury Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1979 60: 605–608
Ien H et al. Upper extremity pain in the postrehabilitation spinal cord injured patient Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1992 73: 44–48
Woolsley RM . Chronic pain following spinal cord injury J Am Paraplegia Soc 1986 9: 39–41
Lamid S et al. Chronic pain in spinal cord injury: comparison between inpatients and outpatients Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1985 66: 777–778
Britell CW, Mariano AJ . Chronic pain in spinal cord injury Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: State of the Art Reviews Philadelphia: Philadelphia, Hanley & Belfus Inc 1991 pp. 71–81
Wagner-Anke AG, Stenehjem AE, Kvalvik Stanghelle J . Pain and life quality within 2 years of spinal cord injury Paraplegia 1995 33: 555–559
Christensen FL, Jensen TS . Disturbances of sensation and pain in patients with spinal cord lesions (Danish) Ugeskr Loeger 1991 153: 3466–3469
Mariano AJ . Chronic pain and spinal cord injury Clin J Pain 1992 8: 87–92
Rintala DH, Loubser PG, Castro J, Hart KA et al. Chronic pain in a community-based sample of men with spinal cord injury: prevalence, severity, and relationship with impairment, disability, handicap, and subjective well-being Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1998 79: 604–614
Levi R, Hulting C, Seiger A . The Stockholm Spinal Cord Injury Study: 2. Associations between clinical patients characteristics and post-acute medical problems Paraplegia 1995 33: 585–594
Richards JS . Chronic pain and spinal cord injury: review and comment Clin J Pain 1992 8: 119–122
Knutsdottir S . Spinal cord injuries in Iceland 1973–1989. A follow up study Paraplegia 1993 31: 68–72
Subbarao JU, Klopfstein J, Turpin R . Prevalence and impact of wrist and shoulder pains in patients with spinal cord injury Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1979 60: 605–609
Summers JD et al. Psychosocial factors in chronic spinal cord injury pain Pain 1991 47: 183–189
Dew MA et al. A causal analysis of factors affecting adjustment to spinal cord injury Rehabilitation Psychology 1985 30: 39–46
Kennedy P et al. Factors associated with acute and chronic pain following traumatic spinal cord injuries Spinal Cord 1997 35: 814–817
McKinley WO et al. Long-term medical complications after traumatic spinal cord injury: a regional model systems analysis Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1999 80: 1402–1410
Krausse JS . Secondary conditions and spinal cord injury: a model for prediction and prevention Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil 1996 2: 58–70
Berkley LR, Dilustro JF, Salazar AM . Spinal cord injury: a 25-year morbidity and mortality study Military Medicine 1997 2: 141–147
Rodriguez GP, Garber SL . Prospective study of pressure risk in spinal cord injured patients Paraplegia 1994 34: 150–158
Krause JS . Skin sores after spinal cord injury: relationship to life adjustment Spinal Cord 1998 36: 51–56
Sapountzi-Krepia D et al. Post traumatic paraplegics living in Athens: The impact of pressure sores and UTIs on everyday life activities Spinal Cord 1999 36: 432–437
Shea JD, Sepulveda JA . Pressure sore profile Proc Am Spinal Injury Assoc 1985 1: 1–2
Acknowledgements
The TETRAFIGAP Survey was carried out thanks to grants from the following organisations which we wish to thank: HANDITEC the ‘Association de Gestion de fonds pour l'Insertion Professionnelle Des Personnes Handicapes’, (AGEFIPH), the ‘Association des Paralyses de France’ (APF) the ‘Fondation des Mutuelles Du Mans-Fondation de France, the ‘Fondation Suisse de la paraplegie’, the ‘Centre European d'analyses des Risques (CEESAR), the ‘Institut pour la Recherche sur la moelle Epiniere’, (IRME). The authors also wish to thank Papa Abdou (APF) for carrying out statistical analyses and Karine Traverse and Françoise Marchand (INSERM/RFRH) for their assistance with translation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Additional information
See Appendix
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Appendix
The Tetrafigap survey, carried out under the aegis of the ‘Association Francophone Internationale des Groupes d'Animation de la Paraplégie’ (AFIGAP), was achieved thanks to the participation of the Tetrafigap group which involves a steering committee including D Boulongne, M Delcey, JF Desert, M Maury, JP Pedelucq, JF Ravaud and M Tramblay and the 35 associated teams mentioned below:
1 Berck-Hôpital franco-américain (Dr Allas)
2 Berck-Centre Hélio-marin (Dr Chikhi)
3 Bichat (Pr Bedoiseau)
4 Bois-Guillaume (Pr Beuret-Blanquart)
5 Bordeaux (Pr Barat, Dr Petit)
6 Bouffémont (Dr Thévenin-Lemoine)
7 Bourbon-Lancy (Drs Malier, Estéve)
8 Bruxelles (Drs Heilporn, Biefnot)
9 Cerbère (Dr Enjalbert, M. Rosebande)
10 Charleville Mézières (Drs Delrez, Skoda)
11 Club de loisirs et d'entraide de Garches
12 Coubert (Dr Désert)
13 Garches (Prs Bussel et Dizien, Dr Lortat-Jacob et Tramblay)
14 Genève-Hôpital Cantonal Universitaire, (Pr Chantraine, Dr Castagnier)
15 Giens (Drs Boucand et Tournebise)
16 Invalides (INI, Dr Dumurgier, Dr Barouti)
17 Kerpape (Drs Busnel, Cormerais, Pédelucq)
18 La Membrolle sur Choisille (Dr Chauvet)
19 L'Arche (Drs Egon, Isambert)
20 La Tour-de-Gassies (Dr N'Guyen Van Tam, Dr Wiart)
21 Lay-Saint-Christophe (Dr Grugerolle, Dr Thisse)
22 L'Hospitalet-Montoire (Dr Simon)
23 Limoges (Prs Labrusse et Dudognon, Dr Munoz)
24 Lyon-Henry Gabrielle (Pr Boisson)
25 Lyon-Henry Gabrielle (Pr Eyssette, Dr Frenay)
26 Marseille-Clinique St-Martin (Dr Chapuis-Ducoffre)
27 Marseille-Valmante (Drs Benezet et Allovon)
28 Montpellier-Propara (Dr. O'Hanna, Dr Rouays-Mabit)
29 Mulhouse (Dr Jacob-Chia)
30 Nantes (Pr Mathé, Drs Perrouin-Verbe et Rome)
31 Neufmoutiers-en-Brie-Les Lycéens (Dr François)
32 Pen-Bron (Dr Tanguy)
33 Rennes Beaulieu (Pr Brissot, Dr Gallien)
34 Saint-Hilaire du Touvet (Dr Pauget)
35 Strasbourg (Dr Pinelli)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klotz, R., Joseph, P., Ravaud, J. et al. The Tetrafigap Survey on the long-term outcome of tetraplegic spinal cord injured persons: Part III. Medical complications and associated factors. Spinal Cord 40, 457–467 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101317
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101317
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
International spinal cord injury socio-demographic basic data set (version 1.0)
Spinal Cord (2023)
-
Utilization of health care providers by individuals with chronic spinal cord injury
Spinal Cord (2021)
-
Prevalence and associated factors of pain in the Swiss spinal cord injury population
Spinal Cord (2017)
-
Should sperm be cryopreserved after spinal cord injury?
Basic and Clinical Andrology (2013)
-
Frequency and age effects of secondary health conditions in individuals with spinal cord injury: a scoping review
Spinal Cord (2013)