Abstract
Study design: A case report.
Objectives: To report a case of cervical amyotrophy caused by hypertrophy of the posterior longitudinal ligament (HPLL).
Setting: Department of Neurological Surgery, Aichi Medical University, Aichi, Japan.
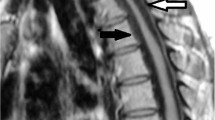
Methods: The patient had severe muscular atrophy in the deltoid and triceps with slight localized hypesthesia in the C5 area and severely unstable gait due to diminished vibration sense in the knees and ankles. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed expanded cord compression from C4 to C6 with intramedullary high-signal intensity due to HPLL. Transverse image MRI was useful to identify the HPLL.
Results: Resection of HPLL was achieved by an anterior approach. Histological findings of the surgical specimens showed thickening of the ligamentous tissue with proliferation of chondrocytes.
Conclusions: HPLL should be included as a causative pathology of cervical spondylotic amyotrophy. Careful neurological examination including sensory examination of the lower limbs should be performed to avoid confusion with motor neuron disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Brain WR, Northfield D, Wilkinson M . The neurological manifestations of cervical spondylosis Brain 1952 75: 187–225
Crandall PH, Batzdorf U . Cervical spondylotic myelopathy J Neurosurg 1966 25: 57–66
Dorsen M, Ehni G . Cervical spondylotic radiculopathy producing motor manifestations mimicking primary muscular atrophy Neurosurgery 1979 5: 427–431
Epstein NE . Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Diagnosis and surgical treatment Neurosurg Q 1992 2: 223–241
Epstein NE . Advanced cervical spondylosis with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and resultant neurological sequelae J Spinal Disord 1996 9: 477–484
Ito T et al. The clinical consideration of the dissociated motor loss syndrome (Keegan) in disease of the cervical spine Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi 1980 54: 135–151 in Japanese
Keegan JJ . The cause of dissociated motor loss in the upper extremity with cervical spondylosis J Neurosurg 1965 23: 528–536
Liversedge LA, Hutchinson EC, Lyons JB . Cervical spondylosis simulating motor-neuron disease Lancet 1953 2: 652–655
Mizuno J, Nakagawa H . Analysis of hypertrophy of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine, on the basis of clinical and experimental studies Neurosurgery 2001 49: 1091–1098
Ramanauskas WL et al. MR imaging of compressive myelomalacia J Comput Assist Tomogr 1989 13: 399–404
Mizuno J et al. Pathological study of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) with special reference to mechanism of ossification and spinal cord damage Spinal Surgery 1988 2: 81–87 in Japanese
Yanagi T, Kato K, Sobue I . Cervical spondylotic amyotrophy simulating motor neuron disease Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1976 16: 520–528 in Japanese
Iwasaki Y et al. CT myelography with intramedullary enhancement in cervical spondylosis J Neurosurg 1985 63: 363–366
Kameyama T et al. Spinal cord morphology and pathology in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament Brain 1995 118: 263–278
Wada E, Okudera M, Yonenobu K . Intramedullary changes of the spinal cord in cervical spondylotic myelopathy Spine 1995 20: 2226–2232
Hashizume Y et al. Pathology of spinal cord lesions caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1984 63: 123–130
Kamikozuru M, Yamaura I . Hypertrophy of the cervical posterior longitudinal ligament (a provisional name) causing myelopathy A case report. Presented at the Second Annual Meeting of the Japan Spine Research Society, Tokyo, Japan, November 9, 1974 (in Japanese
Hase H et al. Severe cervical myelopathy of the cervical posterior longitudinal ligament: A case report Spine 1992 17: 1417–1421
Mizuno J et al. Compression myelopathy due to hypertrophy of the posterior longitudinal ligament with herniated intervertebral discs. Case report Neuro-Orthopedics 1992 13: 113–120
Motegi H et al. Proliferation cell nuclear antigen in hypertrophied spinal ligaments: immunohistological localization of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in hypertrophied posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine Spine 1998 23: 305–310
Sakamoto R . Comparative study between MRI and histological findings in the area of ossification and calcification of the ligaments. Investigation Committee Report on the Ossification of the Spinal Ligaments of the Japanese Ministry of Public Health and Welfare in 1989 Edited by T. Kurokawa Tokyo, Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare 1990 pp. 180–182 in Japanese
Yamaura I . Degeneration of intervertebral disc and change of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Microscopic findings of the specimen obtained in the biopsy Investigation Committee Report on the Ossification of the Spinal Ligaments of the Japanese Ministry of Public Health and Welfare in 1989 Edited by T. Kurokawa Tokyo, Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare 1990 pp 180–182 in Japanese
Yamazaki A et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and histologic study of hypertrophic cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. A case report Spine 1992 16: 1262–1266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizuno, J., Nakagawa, H. & Hashizume, Y. Cervical amyotrophy caused by hypertrophy of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spinal Cord 40, 484–488 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101321
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101321
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cervical spondylotic amyotrophy: a systematic review
European Spine Journal (2019)