Abstract
Study design: Cross-sectional study comparing trained spinal cord injured (SCI) subjects (lesion level: L1∼T6) with healthy young subjects (CONT).
Objective: To investigate the kinetics of response in oxygen uptake (V̇O2) in human upper-body skeletal muscles, nine trained SCI subjects underwent submaximal supine arm exercises.
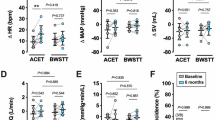
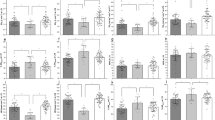
Method: The SCI subjects underwent an incremental arm exercise test until exhaustion. The days after this first round of testing, breath-by-breath V̇O2 and beat-by-beat heart rate (HR) on- and off-kinetics were determined during three repetitions of constant exercise at 50% of V̇O2peak. The overall time course of response was determined from the half time (t1/2). Increased capillary blood lactate production (Δ[La]b) at the onset of exercise was defined as the difference between at rest and at the end of exercise. Cardiac output (Q̇) was measured using the acetylene rebreathing method during the steady state of exercise. In accordance with the Fick principle, the difference in arterial-venous O2 content (Ca-\(\overline{v}\)O2) was defined as V̇O2/Q̇.
Results: During the steady state of the submaximal arm exercise, a more significant increase in the steady state of Q̇ was obtained in the CONT subjects than in the trained SCI subjects: respectively, 14.9±1.4 l/min versus (12.7±0.8 l/min). There was no difference in the steady state of V̇O2 between the two groups; as a result, SCI subjects had the greater Ca-\(\overline{v}\)2. Meanwhile,V̇O2 on- and off-kinetics became much faster in the trained SCI subjects than in the CONT subjects. In addition, t1/2 HR on-kinetics was not significantly different between the SCI and CONT groups. Increased Δ[La]b was closely related to larger t1/2 V̇O2 on-kinetics (r=0.624, P<0.05).
Conclusion: It is concluded that the acceleration of V̇O2 on- and off-kinetics in the trained SCI subjects was observed even though there was no difference in HR on- and off-kinetics between the SCI and CONT groups and a lower steady state of Q̇ in the trained SCI subjects. V̇O2 kinetics would therefore be the limiting factor in oxidative phosphorylation in the upper skeletal muscles, thereby providing a lower lactic O2-deficit (ie Δ[La]b).
Sponsorship: This study was partly supported by the grant from Frontier Science Promotion in Kumamoto, Japan (1997, 1998).
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Davis GM et al. Cardiovascular responses to arm cranking and FNS-induced leg exercise in paraplegics J Appl Physiol 1990 69: 671–674
Glaser RM . Arm exercise training for wheelchair users Med Sci Sports Exerc 1989 21: S149–S157
Hooker SPS et al. Physiologic responses to prolonged electrically stimulated leg-cycle exercise in spinal cord injured Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1990 71: 863–869
Hopman MT et al. Blood redistribution and circulation responses to submaximal arm exercise in persons with spinal cord injury Scand J Rehabil Med 1998 30: 167–174
Koga S et al. Kinetics of oxygen uptake and cardiac output at onset of arm exercise Respir Physiol 1995 103: 195–202
Cerretelli P et al. Oxygen uptake transients at the onset and offset of arm and leg work Respir Physiol 1977 30: 81–97
Casaburi R, Barstow TJ, Robinson T, Wasserman K . Dynamic and steady-state ventilatory and gas exchange responses to arm exercise Med Sci Sports Exerc 1992 24: 1365–1374
Barstow TJ et al. Peak and kinetic cardiorespiratory responses during arm and leg exercise in patients with spinal cord injury Spinal Cord 2000 38: 340–345
Cerretelli P, Rennie DW, Pendergast DP . Kinetics of metabolic transient during exercise In: Cerretelli P and Whipp BJ (eds) Exercise Bioenergetics and Gas Exchange Amsterdam: Elsevier Press 1980 pp 187–209
Cerretelli P, Pendergast DP, Paganelli WC, Rennie DW . Effects of specific muscle training on V̇O2 on-response and early blood lactate J Appl Physiol 1979 47: 761–769
Fukuoka Y et al. Early effects of exercise training on V̇O2 on- and off-kinetics in 50-year-old subjects Pflugers Arch 2002 443: 690–697
Hopman MT, Peseburg B, Binkhorst RA . Cardiovascular responses in paraplegic subjects during arm exercise Eur J Appl Physiol 1992 65: 73–78
Hopman MT, Pistorius M, Kamerbeek IC, Binkhorst RA . Cardiac output in paraplegic subjects at high exercise intensities Eur J Appl Physiol 1993 66: 531–535
Gaeeser GA, Poole DC . The slow component of oxygen uptake kinetics in humans In: Holloszy JO (ed) Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews Vol 24: Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins 1996 pp 35–71
Triebwasser JH, Johnson RL, Burpos RP . Noninvasive determination of cardiac output by a modified acetylene rebreathing procedure using mass spectrometer Aviat Space Environ Med 1997 48: 203–210
Grassi B et al. Gas exchange and cardiovascular kinetics with different exercise protocols in heart transplants recipients J Appl Physiol 1997 82: 1952–1962
Hughson RL, Shoemaker JK, Tschakovsky ME, Kowalchuk JM . Dependence of muscle V̇O2 on blood flow dynamics at onset of forearm exercise J Appl Physiol 1996 81: 1619–1626
Davis GM, Shephard RJ . Cardiorespiratory fitness in highly-active versus inactive paraplegics Med Sci Sports Exerc 1988 20: 463–468
Hjeltnes N . Oxygen uptake and cardiac in graded arm exercise in paraplegics with low level spinal lesions J Rehabil Med 1977 9: 107–113
Hughson RL, Cochrane JE, Butler GC . Faster O2 uptake kinetics at onset of supine exercise with than without lower body negative pressure J Appl Physiol 1993 75: 1962–1967
Koga S et al. Kinetics of oxygen uptake during supine and upright heavy exercise J Appl Physiol 1999 87: 253–260
Leyk D et al. Postural effect on cardiac output, oxygen uptake and lactate during cycle exercise of varying intensity Eur J Appl Physiol 1994 68: 30–35
Barstow TJ et al. Gas exchange kinetics during functional electrical stimulation in subjects with spinal cord injury Med Sci Sports Exerc 1995 27: 1284–1291
Levy M, Kushnir J, Mizrahi J, Itzchzk Y . In vivo31P NMR studies of paraplegics muscles activated by functional electrical stimulation Magn Reson Med 1993 29: 53–58
Gollnick PD . Metabolism of substrates: energy substrate metabolism during exercise and as modified by training Fed Proc 1985 44: 353–357
Taylor AW, McDonell E, Brassard L . The effects of an arm ergometer training programme on wheelchair subjects Paraplegia 1986 24: 105–114
Taylor AW et al. Skeletal muscle analysis of wheelchair athletes Paraplegia 1979 17: 457–460
Barstow TJ et al. Changes in gas exchange kinetics with training in patients with spinal cord injury Med Sci Sports Exerc 1996 28: 1222–1228
Convertino VA, Goldwater DJ, Sandler H . V̇O2 kinetics of constant-load exercise following bed rest-induced deconditioning J Appl Physiol 1984 57: 1545–1550
Tuner DL et al. Effects of endurance training on oxidative capacity and structural composition of human arm and leg muscles Acta Physiol Scand 1997 161: 459–464
di Prampero PE, Mahler PB, Giezendanner D, Cerretelli P . Effects of priming exercise on V̇O2 kinetics and O2 deficit at the onset of stepping and cycling J Appl Physiol 1989 66: 2023–2031
Pendergast DR, Shindell D, Cerretelli P, Rennie D . Role of central and peripheral circulatory adjustments in oxygen transport at the onset of exercise Int J Sports Med 1980 1: 160–170
Grassi B et al. Faster adjustment of O2 delivery does not affect V̇O2 on-kinetics in isolated in situ canine muscle J Appl Physiol 1998 84: 1394–1403
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the critical comments of Dr Shynsaku Koga, Kobe Design University, Japan. We gratefully acknowledge the expert technical assistance of Miss Y Nakamura, Miss C Murakami and Miss M Iwamizu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuoka, Y., Endo, M., Kagawa, H. et al. Kinetics and steady-state of V̇O2 responses to arm exercise in trained spinal cord injury humans. Spinal Cord 40, 631–638 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101383
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101383
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Characteristics of cardiovascular responses to an orthostatic challenge in trained spinal cord-injured individuals
Journal of Physiological Anthropology (2018)
-
The physiological responses to repeated upper-body sprint exercise in highly trained athletes
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2015)
-
Cardiac Acceleration at the Onset of Exercise: A Potential Parameter for Monitoring Progress During Physical Training in Sports and Rehabilitation
Sports Medicine (2014)