Abstract
Study design: Case report with a review of scientific literature.
Objective: To describe the course of tuberculous spinal disease (Pott's disease) complicated by pyogenic and tuberculous empyema, and chylothorax as there has been an increase in the numbers of notified cases of tuberculosis in the UK1. To the best of our knowledge, a similar case has not been reported previously in the UK, although there has been a report of bilateral chylothorax associated with Pott's disease.
Setting: A national spinal injuries unit in a Scottish university teaching hospital.
Methods: Review of literature on the chemotherapy of spinal tuberculosis and the role of streptokinase in the treatment of empyema and the relation between spinal tuberculosis, empyema and chylothorax.
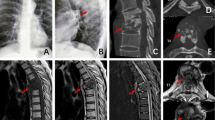
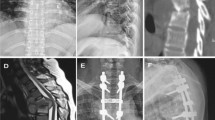
Results: Although spinal tuberculosis was recognised and treated appropriately with chemotherapy, the patient sustained pleural involvement with later development of both empyema and chylothorax.
Conclusion: The case highlights the difficulties in the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine inspite of the presence of fully sensitive organisms and early institution of appropriate chemotherapy. In the absence of surgical debridement, the duration and dosage of chemotherapy as practised in the initial period may have to be prolonged into the continuation phase. The thoracic duct can be damaged either because of extension of the tuberculosis itself or because of instillation of intrapleural streptokinase for treatment of pleural empyema leading to chylothorax. There is a need for randomised trials of intrapleural streptokinase treatment in tuberculous empyema.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hayword AC, Watson JM . Tuberculosis in England and Wales 1982–93; notifications exceeded predictions. Comm Dis Rep. 1995; 5: R29–R33.
Task force of the European Respiratory Society, World Health Organisation and the Europe region of the International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung disease. Tuberculosis management in Europe. Eur Respir J 1999; 14: 978–992.
Joint Tuberculosis Committee of the British Thoracic Society. Chemotherapy and management of tuberculosis in the United Kingdom: recommendations 1998. Thorax 1998; 53: 536–548.
Moon MS . Tuberculosis of the spine – controversies and a new challenge. Spine 1997; 22: 1791–1797.
Anonymous. Case no. 1. Pott's disease with a large psoas abscess. Tech Urol 1998; 4: 99–100.
Strange C, Sahn SA . Management of parapneumonic pleural effusions and empyema. In: Wallace RJ (ed). Infections Disease Clinics of North America. Saunders: Philadelphia, 1991, pp 539–559.
Tillet WS, Sherry S . The effect in patients of streptococcal fibrinolysin (streptokinase) and streptococcal des-oxyribonuclease on fibrinous, purulent and sanguinous pleural exudations. J Clin Invest 1949; 28: 173–190.
Godley PJ, Bell RC . Major haemorrhage following administration of intrapleural streptokinase. Chest 1984; 86: 486–487.
Aye RW, Froese DP, Hill LD . Use of purified streptokinase in empyema and haemothorax. Am J Surg 1991; 161: 560–562.
Davies RJO, Traill ZC, Gleeson FV . Randomised controlled trial of intrapleural streptokinase in community acquired pleural infection. Thorax 1997; 52: 416–421.
Barletta JF . Streptokinase and urokinase for the treatment of pleural effusions and empyema [Review]. Ann Pharm 1999; 33: 495–498.
Yater WM . Nontraumatic chylothorax and chylopericardium: review and report of a case due to carcinomatous thomboangitis obliterans of the duct and upper great veins. Ann Intern Med 1935; 9: 600–616.
Menzies R, Hidvegi R . Chylothorax associated with tuberculous spondylitis. Can Assoc Radiol J 1988; 39: 238–241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Funding was from departmental sources
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, R., Fraser, M., Urquhart, G. et al. Rupture of tuberculous spinal abscess resulting in tuberculous empyema and chylothorax. Spinal Cord 41, 410–412 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101449
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101449
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Successful surgical intervention for acute pyothorax caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus thoracic pyogenic spondylitis: a case report
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Cases (2024)
-
Does computed tomography-guided percutaneous catheter drainage is effective for spinal tuberculous abscess: a midterm results
Spinal Cord Series and Cases (2022)
-
Late-onset post-diskectomy tuberculosis at the same operated lumbar level: case report and review of literature
European Spine Journal (2010)
-
Chylothorax due to tuberculosis lymphadenopathy: Report of a case
Surgery Today (2008)