Abstract
Study design: Randomized controlled trial of physical exercise and dopaminergic agonist in persons with spinal cord injury and periodic leg movement (PLM).
Objective: The objective of the present study was to compare the effectiveness of physical exercise and of a dopaminergic agonist in reducing the frequency of PLM.
Setting: Centro de Estudos em Psicobiologia e Exercício. Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil.
Methods: A total of 13 volunteers (mean age: 31.6±8.3 years) received L-DOPA (200 mg) and benserazide (50 mg) 1 h before sleeping time for 30 days and were then submitted to a physical exercise program on a manual bicycle ergometer for 45 days (3 times a week).
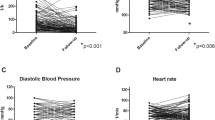
Results: Both L-DOPA administration (35.11–19.87 PLM/h, P<0.03) and physical exercise (35.11–18.53 PLM/h, P<0.012) significantly reduced PLM; however, no significant difference was observed between the two types of treatment.
Conclusions: The two types of treatment were found to be effective in the reduction of PLM; however, physical exercise is indicated as the first treatment approach, while dopaminergic agonists or other drugs should only be recommended for patients who do not respond to this type of treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ekbom KA . Restless legs syndrome. Neurologym 1960; 10: 868–873.
Ekbom KA . Restless legs. Acta Med Scand 1945; 158(Suppl): 123 (abstract).
Hening WA, Walters A, Kavey N, Gidro-Frank S, Côte L, Fahn S . Dyskinesias while awake and periodic movements in sleep in restless legs syndrome: treatment with opioids. Neurology 1986; 36: 1363–1366.
Montplaisir J, Lorrain D, Godbout R . Restless legs syndrome and periodic leg movements in sleep: the primary role of dopaminergic mechanism. Eur Neurol 1991; 31: 41–43.
Yokota T, Hirose K, Tanabe H, Tsukagoshi H . Sleep-related periodic leg movements (nocturnal myoclonus) due to spinal cord lesion. J Neurol Sci 1991; 104: 13–18.
Lee MS, Choi YC, Lee SH, Lee SB . Sleep-related periodic leg movement associated with spinal cord lesions. Mov Disord 1996; 11: 719–722.
De Mello MT, Lauro FA, Silva AC, Tufik S . Incidence of periodic leg movements and of the restless legs syndrome during sleep following acute physical activity in spinal cord injury subjects. Spinal Cord 1996; 34: 294–296.
De Mello MT, Silva AC, Rueda AD, Poyares D, Tufik S . Correlation between K complex, periodic leg movements (PLM), and myoclonus during sleep in paraplegic adults before and after an acute physical activity. Spinal Cord 1997; 35: 248–252.
O'Keeffe ST . Restless legs syndrome. A review. Arch Intern Med 1996; 156: 243–248.
Williams DC . Periodic limb movements of sleep and the restless legs syndrome. VA Med Q 1996; 123: 260–265.
Inami Y et al. A polysomnographic study on periodic limb movements in patients with restless legs syndrome and neuroleptic-induced akathisia. Hiroshima J Med Sci 1997; 46: 133–141.
Montplaisir J, Boucher S, Gosselin A, Poirier G, Lavigne G . Persistence of repetitive EEG arousals (K–alpha complexes) in RLS patients treated with L-DOPA. Sleep 1996; 19: 196–199.
Montplaisir J, Boucher S, Poirier G, Lavigne G, Lapierre O, Lesperance P . Clinical, polysomnographic, and genetic characteristics of restless legs syndrome: a study of 133 patients diagnosed with new standard criteria. Mov Disord 1997; 12: 61–65.
Chokroverty S, Jankovic J . Restless legs syndrome: a disease in search of identity. Neurology 1999; 52: 907–910.
Glausauer FE . Restless legs syndrome. Spinal Cord 2001; 39: 125–133.
Staed J et al. Dopamine D2 receptor alteration in patients with periodic movements in sleep (nocturnal myoclonus). J Neural Trans Gen Sect 1993; 93: 71–74.
Montplaisir J, Godbout R, Pellether G, Warnes H . Restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movements during sleep. In: Kryger MH, Rath T, Dement WC (eds). Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine, 2nd edn WB Saunders Company: Philadelphia, 1994, P. 589.
Schwarz L, Kindermann W . Changes in β-endorphin levels in response to aerobic and anaerobic exercise. Sports Med 1992; 13: 25–36.
Kavey N, Walters AS, Hening W, Gidro-Frank S . Opioid treatment of periodic movements in sleep in patients without restless legs. Neuropeptides 1988; 11: 181–184.
Maynard FM et al. International Standards for Neurological and Functional Classification of Spinal Cord Injury. Spinal Cord 1997; 35: 266–274.
Vuori I, Urponen H, Hasan J, Partinen M . Epidemiology of exercise effects on sleep. Acta Physiol Scand 1988; 574: 3–7.
Driver HS, Meintjes AF, Rogers GG, Shapiro CM . Submaximal exercise effects on sleep patterns in young women before and after an aerobic training programme. Acta Physiol Scand 1988; 574: 8–13.
Trinder J, Montgomery I, Paxton SJ . The effect of exercise on sleep: the negative view. Acta Physiol Scand 1988; 574: 14–20.
Meeusen R, De Meirleir K . Exercise and brain neurotransmission. Sports Med 1995; 20: 160–188.
Bulbulian R, Darabos BL . Motor neuron excitability: the Hoffmann reflex following exercise of low and high intensity. Med Sci Sports Exer 1986; 18: 697–702.
Ferreira SH, Lorenzetti BB, Corrêa FMA . Central and peripheral antialgesic action of aspirin-like drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 1978; 53: 39–48.
Ferreira SH . Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nature N Biol 1972; 240: 200.
Ferreira SH, Moncada S, Vane JR . Prostaglandins and the mechanism of analgesia produced by aspirin-like drugs. Br J Pharmacol 1973; 49: 86.
De Mello MT, Poyares DL, Tufik S . Treatment of periodic leg movements with a dopaminergic agonist in subjects with total spinal cord lesion. Spinal Cord 1999; 37: 634–637.
Acknowledgements
We thank AFIP, CEPID (FAPESP Proc. no. 98/143033), Federal Government and the Sleep Institute/UNIFESP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Mello, M., Esteves, A. & Tufik, S. Comparison between dopaminergic agents and physical exercise as treatment for periodic limb movements in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 42, 218–221 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101575
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101575
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Accelerometer-measured physical activity and its impact on sleep quality in patients suffering from restless legs syndrome
BMC Neurology (2021)
-
Non-pharmacological methods used in coping with restless leg syndrome (RLS): A systematic review
Sleep and Biological Rhythms (2021)
-
Dopaminergic treatment of restless legs syndrome in spinal cord injury patients with neuropathic pain
Spinal Cord Series and Cases (2016)
-
Using REBT in the Treatment of Restless Leg Syndrome: A Case-Study
Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy (2014)
-
Obesity, diabetes and OSAS induce of sleep disorders: Exercise as therapy
Lipids in Health and Disease (2011)