Abstract
Study design:
Case report.
Objective:
To evaluate the functional recovery of chronic complete idiopathic transverse myelitis (ITM) after administration of acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF).
Methods:
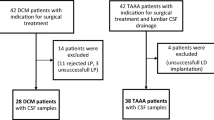
A 28-year-old woman presented with a 4-year history of spastic paralysis, sensory level at T10, urinary retention and constipation due to ITM. In all, 20 μg aFGF bolus injection was applied via intradural lumbar puncture, which was repeated every 5 months for 15 months.
Results:
At 3 weeks after first injection, the patient experienced vague sensation at approximately T12–L1 dermatomes. At 2 months after the second injection, muscle activities and gait pattern were recorded in bilateral gluteus and hip abductors as she ambulated with long leg brace and axillary crutches. Increased walking speeds, reduced pelvic tilting and reduced compensatory trunk rotation during the swing phase were also demonstrated as compared to the initial gait analysis. At 18 months after injection, motor evoked potentials were obtained in hip abductors of both legs.
Conclusions:
aFGF may increase the efficacy of spinal reactivation/regeneration and is a potential remedy for chronic transverse myelitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Transverse Myelitis Consortium Working Group. Proposed diagnostic criteria and nosology of acute transverse myelitis. Neurology 2002; 59: 499–505.
Kerr DA, Ayetey H . Immunopathogenesis of acute transverse myelitis. Curr Opin Neurol 2002; 15: 339–347.
Stock A et al. Localization of acidic fibroblast growth factor in specific subcortical neuronal populations. J Neurosci 1992; 12: 4688–4700.
Guest JD et al. Influence of IN-1 antibody and acidic FGF-fibrin glue on the response of injured corticospinal tract axons to human Schwann cell grafts. J Neurosci Res 1997; 50: 888–905.
Cuevas P, Carceller F, Gimenez-Gallego G . Acidic fibroblast growth factor prevents death of spinal cord motoneurons in newborn rats after nerve section. Neurol Res 1995; 17: 396–399.
Javerzat S, Auguste P, Bikfalvi A . The role of fibroblast growth factors in vascular development. Trends Mol Med 2002; 8: 483–489.
Kelley CE, Mathews J, Noskin GA . Acute transverse myelitis in the emergency department: a case report and review of the literature. J Emerg Med 1991; 9: 417–420.
Webster HD . Growth factors and myelin regeneration in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 1997; 3: 113–120.
Albrecht PJ et al. Astrocytes produce CNTF during the remyelination phase of viral-induced spinal cord demyelination to stimulate FGF-2 production. Neurobiol Dis 2003; 13: 89–101.
Thorne RG, Frey II WH . Delivery of neurotrophic factors to the central nervous system: pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet 2001; 40: 907–946.
Cheng H et al. Characterization of a fibrin glue-GDNF slow-release preparation. Cell Transplant 1998; 7: 52–61.
Cheng H, Cao Y, Olson L . Spinal cord repair in adult paraplegic rats: partial restoration of hind limb function. Science 1996; 273: 510–513.
Basso DM . Neuroanatomical substrates of functional recovery after experimental spinal cord injury: implications of basic science research for human spinal cord injury. Phys Ther 2000; 80: 808–817.
McDonald JW, Sadowsky C . Spinal cord injury. Lancet 2002; 359: 417–425.
Li XK et al. Pharmacokinetic study of recombinant human acidic fibroblast growth factor in rabbits by skin external use. Yao Hsueh Hsueh Pao – Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 2002; 37: 424–427.
Thorne RG, Frey II WH . Delivery of neurotrophic factors to the central nervous system: pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet 2001; 40: 907–946.
Cheng H, Cao Y, Olson L . Spinal cord repair in adult paraplegic rats: partial restoration of hindlimb function. Science 1996; 273: 510–513.
Chuang TY et al. Forelimb muscle activity following nerve graft repair of ventral roots in the rat cervical spinal cord. Life Sci 2002; 71: 487–496.
Lee YS et al. aFGF promotes axonal growth in rat spinal cord organotypic slice co-cultures. J Neurotraum 2002; 19: 357–367.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the contribution of Professor Lars Olson at Department of Neuroscience, Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, Sweden, for his assistance in the laboratory work. This work was supported by Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Grant number: VGH 93-371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, PH., Chuang, TY., Liao, KK. et al. Functional recovery of chronic complete idiopathic transverse myelitis after administration of neurotrophic factors. Spinal Cord 44, 254–257 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101809
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101809
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Functional improvement in chronic human spinal cord injury: Four years after acidic fibroblast growth factor
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2009)