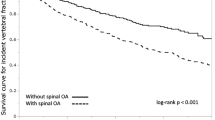
Abstract
Study design:
Retrospective case series.
Objectives:
To assess the efficacy of posterior spinal shortening for paraparetic patients following vertebral collapse owing to osteoporosis, especially on instrumentation loosening.
Setting:
Department of orthopaedic surgery, Jichi Medical University Hospital and Omiya Medical Center in Japan.
Methods:
The clinical records and radiographs of 13 patients with paraparesis following vertebral collapse owing to osteoporosis treated with posterior spinal shortening were retrospectively reviewed to evaluate the usefulness of this method. Assessment of the clinical course was done by direct examination in all cases. Ambulatory ability was divided into four categories.
Results:
Upon final observation, nine cases were able to walk with a cane or crutch, one case remained in gait training, two cases remained unable to stand and one case with urinary incontinence improved in urinary function. In one case, paralysis deteriorated. Vertebral compression fracture of the end vertebrae that were fixed occurred in three cases complicated with rheumatoid arthritis.
Conclusion:
The posterior spinal shortening can be a choice for treating delayed paraparesis following vertebral collapse owing to osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ross PD, Fujiwara S, Huang C, Davis JW, Epstein RS, Wasnich RD et al. Japanese women in Hiroshima have greater vertebral fracture prevalence than Caucasian or Japanese in the US. Int J Epidemiol 1995; 24: 1171–1177.
Yoshimura N, Kinoshita H, Danjoh S, Yamada H, Tamaki T, Morioka S et al. Prevalence of vertebral fracture in a rural Japanese population. J Epidemiol 1995; 5: 171–175.
Lee YL, Yip KM . The osteoporotic spine. Clin Orthop 1996; 323: 91–97.
Kempinsky WH, Morgan PP, Boniface WR . Osteoporotic kyphosis with paraplegia. Neurology 1958; 8: 181–186.
Baba H, Maezawa Y, Kamitani K, Furusawa N, Imura S, Tomita K . Osteoporotic vertebral collapse with late neurological complications. Paraplegia 1995; 33: 281–289.
Kaneda K, Asano S, Hashimoto T, Satoh S, Fujiya M . The treatment of osteoporotic-posttraumatic vertebral collapse using the Kaneda device and a bioactive ceramic vertebral prosthesis. Spine 1992; 17: S295–S303.
Salomon C, Chopin D, Benoist M . Spinal cord compression: an exceptional complication of spinal osteoporosis. Spine 1988; 13: 222–324.
Shikata J, Yamamuro T, Iida H, Shimizu K, Yoshikawa J . Surgical treatment for paraplegia resulting from vertebral fractures in senile osteoporosis. Spine 1990; 15: 485–489.
Maruo S, Tatekawa F, Nakano K . Paraplegia caused by vertebral compression fractures in senile osteoporosis. Z Orthop 1987; 125: 320–323.
Nguyen HV, Ludwig S, Gelb D . Osteoporotic vertebral burst fractures with neurologic compromise. J Spinal Disord Tech 2003; 16: 10–19.
Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Widell EH, Thomas JC, Holland WR, Field BT et al. A biomechanical study of intrapeduncular screw fixation in the lumbosacral spine. Clin Orthop 1986; 203: 99–112.
Saita K, Hoshino Y, Kikkawa I, Nakamura H . Posterior spinal shortening for paraplegia after vertebral collapse caused by osteoporosis. Spine 2000; 25: 2832–2835.
Hu SS . Internal fixation in the osteoporotic spine. Spine 1997; 22: S43–S48.
Lotz JC, Hu SS, Chiu FM, Yu M, Colliou O, Poser RD . Carbonated apatite cement augmentation of pedicle screw fixation. Spine 1997; 22: 2716–2723.
Soshi S, Shiba R, Kondo H, Murota K . An experimental study on transpedicular screw fixation in relation to osteoporosis of the lumbar spine. Spine 1991; 16: 1335–1341.
Wittenberg RH, Lee KS, Shea M, White AA, Hayes WC . Effect of screw diameter, insertion technique, and bone cement augmentation of pedicular screw fixation strength. Clin Orthop 1993; 296: 278–287.
Thiranont N, Netawichien P . Transpedicular decancellation closed wedge vertebral osteotomy for treatment of fixed flexion deformity of spine in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine 1993; 18: 2517–2522.
Thomasen E . Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop 1985; 194: 142–152.
Wu SS, Hwa SY, Lin LC, Pai WM, Chen PQ, Au MK . Management of rigid post-traumatic kyphosis. Spine 1996; 21: 2260–2267.
Kawaguchi Y, Matsuno H, Kanamori M, Ishihara H, Ohmori K, Kimura T . Radiologic findings of the lumbar spine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a review of pathologic mechanisms. J Spinal Disord Tech 2003; 16: 38–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saita, K., Hoshino, Y., Higashi, T. et al. Posterior spinal shortening for paraparesis following vertebral collapse due to osteoporosis. Spinal Cord 46, 16–20 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3102052
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3102052
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vertebral mobility is a valuable indicator for predicting and determining bone union in osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a conventional observation study
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2020)
-
Surgical outcomes of spinal fusion for osteoporotic thoracolumbar vertebral fractures in patients with Parkinson’s disease: what is the impact of Parkinson’s disease on surgical outcome?
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019)
-
Stabilisierung der osteoporotischen Wirbelsäule unter biomechanischen Gesichtspunkten
Der Orthopäde (2010)
-
One-stage posterior instrumentation surgery for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral collapse with neurological deficits
European Spine Journal (2010)
-
Behandlungsmöglichkeiten bei thorakalen und lumbalen osteoporotischen Problemfrakturen
Der Orthopäde (2008)