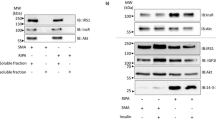
Abstract
The protein products of several transforming retroviruses as well as the receptors for several hormones and growth factors, including insulin, have been shown to possess a protein kinase activity in vitro specific for tyrosine residues in protein substrates, including themselves (see ref. 1 for a review). In the case of pp60src and the insulin receptor, autophosphorylation activates the tyrosine kinase activity towards exogenous substrates2–4. Experiments indicate that, in vivo, many of these viruses or growth factors induce an increase in cellular phosphotyrosine, as well as an increase in the phosphorylation of serine residues on proteins, including ribosomal protein S6. It seems likely that some of the effects of insulin might be mediated by phosphorylation of intracellular substrates by its receptor. As the β subunit of the receptor is a transmembrane protein5, such phosphorylation could occur either while the receptor is still in the membrane or after its internalization. In various cell systems, internalized receptors are degraded, reshuttled back to the plasmalemma or maintained in a separate compartment before reinsertion in the membrane6,7; shuttling of the insulin receptor could provide the opportunity for it to phosphorylate various intracellular components as part of its mechanism of signal trans-duction. To approach directly the question of whether the receptor can elicit a signal while acting at an intracellular location, we have microinjected Xenopus oocytes with the insulin receptor kinase. The results indicate that an S6 protein-serine kinase is stimulated or an S6 protein-serine phosphatase inhibited by the activity of the insulin receptor, supporting the concept that the insulin receptor acting within the cell can elicit a biological response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sefton, B. M. & Hunter, T. Adv. Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 18, 195–226 (1984).
Rosen, O. M., Herrera, R., Olowe, Y., Petruzelli, L. M. & Cobb, M. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 3237–3240 (1983).
Yu, K.-T. & Czech, M. P. J. biol. Chem. 259, 5277–5286 (1984).
Purchio, A. F., Wells, S. K. & Collett, M. S. Molec. cell. Biol. 3, 1589–1597 (1983).
Ullrich, A. et al. Nature. 313, 756–761 (1985).
Heidenreich, K. A. & Olefsky, J. M. in Molecular Basis of Insulin Action (ed. Czech, M. P.) 45–65 (Plenum, New York, 1985).
Simpson, I. A., Hedo, J. A. & Cushman, S. W. Diabetes 33, 13–18 (1984).
Maller, J. L. & Koontz, J. W. Devl Biol. 85, 309–316 (1981).
Stith, P. J. & Maller, J. L. Devl Biol. 102, 72–89 (1984).
Stith, B. J. & Maller, J. L. Devl Biol. 107, 460–469 (1985).
Maller, J. L. & Smith, D. S. Devl Biol. 109, 150–156 (1985).
Spivack, J. G., Erikson, R. L. & Mailer, J. L. Molec. cell Biol. 4, 1631–1634 (1984).
Maller, J. L., Foulkes, J. G., Erikson, E. & Baltimore, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 272–276 (1985).
Pike, L. J., Eakes, A. T. & Krebs, E. G. J. biol. Chem. 261 (in the press).
Brandenburg, D., Draconescu, C., Saunders, D. & Thamm, P. Nature 286, 821–822 (1980).
Heidenreich, K., Berhanu, P., Brandenburg, D. & Olesfsky, J. M. Diabetes 32, 1001–1009 (1983).
Fehlmann, M. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 5921–5925 (1982).
Fehlmann, M. et al. J. Cell Biol. 93, 82–87 (1982).
Martin-Perez, J. & Thomas, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 926–930 (1983).
Nielsen, P. J., Thomas, G. & Maller, J. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 2937–2941 (1982).
Thomas, G., Martin-Perez, J., Siegmann, M. & Otto, A. M. Cell 30, 235–242 (1982).
Wettenhall, R. E. H., Cohen, P., Caudwell, B. & Holland, R. FEBS Lett. 148, 207–213 (1982).
Smith, C. J., Wejksnora, P. J., Warner, J. R., Rubin, C. S. & Rosen, O. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 76, 2725–2729 (1979).
Perrotti, N. et al. Science 227, 761–763 (1985).
Finidori, J., Hanoune, J. & Baulieu, E. E. Molec. cell. Endocr. 28, 211–227 (1982).
Petruzelli, L. M. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6792–6796 (1982).
Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y., Choi, S., Sakamoto, Y. & Itakura, K. J. biol. Chem. 258, 5045–5049 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mailer, J., Pike, L., Freidenberg, G. et al. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 following microinjection of insulin receptor-kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Nature 320, 459–461 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/320459a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/320459a0