Abstract
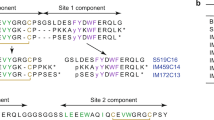
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone of major physiological importance in the regulation of fuel homeostasis in animals (reviewed in refs 1, 2). It is synthesized by the β-cells of pancreatic islets, and circulating insulin levels are regulated by several small molecules, notably glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and certain pharmacological agents. Insulin consists of two polypeptide chains (A and B, linked by disulphide bonds) that are derived from the proteolytic cleavage of proinsulin, generating equimolar amounts of the mature insulin and a connecting peptide (C-peptide). Humans, like most vertebrates, contain one proinsulin gene3,4, although several species, including mice5 and rats6,7, have two highly homologous insulin genes. We have studied the regulation of serum insulin levels and of insulin gene expression by generating a series of transgenic mice containing the human insulin gene. We report here that the human insulin gene is expressed in a tissue-specific manner in the islets of these transgenic mice, and that serum human insulin levels are properly regulated by glucose, amino acids and tolbutamide, an oral hypoglycaemic agent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steiner, D. F. & Tager, H. S. in Endocrinology Vol. 2 (eds DeGroot, L. J. et al.) 921–934 (Grune & Stratton, New York, 1979).
Rubenstein, A. H. in Endocrinology Vol. 2 (eds DeGroot, L. J. et al.) 951–957 (Grune & Stratton, New York, 1979).
Tager, H. et al. Nature 281, 122–125 (1979).
Bell, G. I. et al. Nature 284, 26–32 (1980).
Lally, P. A. & Chirgwin, J. M. Cytogenet. cell. Genet. 37, 515 (1984).
Cordell, B. et al. Cell 18, 533–543 (1979).
Lomedico, P. et al. Cell 18, 545–558 (1979).
Moskalewski, S. Gen. comp. Endocr. 5, 342–353 (1965).
Lacy, P. E. & Kostianovsky, M. Diabetes 16, 35–39 (1967).
Ganda, O. P. et al. Diabetes 24, 354–361 (1975).
Fajans, S. S. & Conn, J. W. J. Lab. clin. Med. 54, 811 (1959).
Walker, M. D., Edlund, T., Boulet, A. M. & Rutter, W. J. Nature 306, 557–561 (1983).
Edlund, T., Walker, M. D., Barr, P. J. & Rutter, W. J. Science 230, 912–916 (1985).
Hanahan, D. Nature 315, 115–122 (1985).
Bell, G. I. et al. Nature 282, 525–527 (1979).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Wagner, T. E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 6376–6380 (1981).
Rogol, A. D. et al. Pediat. Res. 19, 489–492 (1985).
Southern, E. M. J. molec. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975).
Chirgwin, J. M., Przybyla, A. E., MacDonald, R. J. & Rutter, W. J. Biochemistry 18, 5294–5299 (1979).
Sobel, R. A., Blanchette, B. W., Bhan, A. B. & Colvin, R. B. J. Immun. 132, 2402–2403 (1984).
Larkins, R. G. Diabetes 22, 251–255 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selden, R., Skośkiewicz, M., Howie, K. et al. Regulation of human insulin gene expression in transgenic mice. Nature 321, 525–528 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/321525a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/321525a0
This article is cited by
-
TrackingH-2 alleles in transgenic mice by RFLP and heteroduplex analysis
Transgenic Research (1996)
-
Transcription of the insulin gene: towards defining the glucosesensitive cis-element and trans-acting factors
Diabetologia (1994)
-
Neuropeptide gene expression and neural activity: Assessing a working hypothesis in nucleus caudalis and dorsal horn neurons expressing preproenkephalin and preprodynorphin
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1990)