Abstract
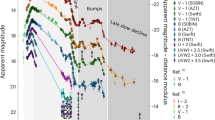
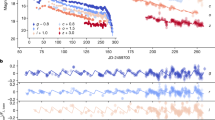
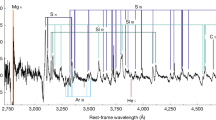
Optical study of late-time nebular emission provided the first direct evidence for the presence of radioactive 56Co in the ejecta of Type Ia supernovae1 and yielded conclusive evidence that Type Ib events constitute a physically distinct class of supernovae2. Hydrogen-rich Type II supernovae have not been studied in detail in the nebular phase, but SN1987A provides an unprecedented opportunity to probe the structure and composition of the ejecta by modelling the nebular spectrum. Here we investigate the late-time nebular spectra of SN1987A by computing the emergent spectra from model atmospheres. The new features of this calculation are the inclusion of a complex model hydrogen atom and the self-consistent treatment of an opaque lower boundary which approximates the observed continuum. We adopt hydrodynamic models reported in the literature, which are known to reproduce the observed light curve and γ-ray and X-ray spectra, and we obtain qualitative agreement with observed optical spectra. By examining the effect of mixing core material into the envelope, we conclude that the metals in the hydrogen-rich envelope make a substantial contribution to the optical nebular lines even for models with no outward mixing of the core material; however, a significant fraction of the energy emitted in 56Co decay must be deposited in the envelope to produce the observed linewidths and hydrogen line strengths.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod, T. S. in Type I Supernova (ed. Wheeler, J. C.) 80–95 (University of Texas, Austin, 1980).
Gaskell, C. M. et al. Astrophys. J. 306, L77–L80 (1987).
Fransson, C. & Chevalier, R. A. Astrophys. J. 322, L15–L20 (1987).
Shigeyama, T., Nomoto, K. & Hashimoto, M. Astr. Astrophys. 196, 141–151 (1988).
Woosley, S. E. Astrophys. J. 330, 218–253 (1988).
Nomoto, K., Shigeyama, T. & Hashimoto, M. in Proc. IAU Colloq. 108: Atmospheric Diagnostics of Stellar Evolution (ed. Nomoto, K.) 319–334 (Springer, Berlin, 1988).
Saio, H., Kato, M. & Nomoto, K. Astrophys. J. 331, 388–393 (1988).
Woosley, S. E. in Proc. IAU Colloq. 108: Atmospheric Diagnostics of Stellar Evolution (ed. Nomoto, K.) 361–374 (Springer, Berlin, 1988).
Woosley, S. E. in Proc. 4th George Mason Astrophysics Workshop (eds Kafatos, M. & Michalitsianos, A.) 289–299 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1988).
Itoh, M., Kumgai, S., Shigeyama, T., Nomoto, K. & Nishimura, J. Nature 330, 233–235 (1987).
Pinto, P. A. & Woosley, S. E. Nature 333, 534–537 (1988).
Kumagai, S., Itoh, M., Shigeyama, T., Nomoto, K. & Nishimura, J. Astr Astrophys 197, L7–L10 (1988)
Pinto, P A & Woosley, S E Astrophys J. 329, 820–830 (1988).
Leising, M. D. Nature 332, 516–518 (1988).
Shibazaki, N. & Ebisuzaki, T. Astrophys J. 327, L9–L12 (1988).
Ebisuzaki, T. & Shibazaki, N. Astrophys J. 327, L5–L8 (1988).
Axelrod, T. S. thesis, Univ Calif Santa Cruz (1980).
Fransson, C. & Chevalier, R. A. Astrophys J. (in the press).
Sobolev, V. V. Moving Envelopes of Stars (Harvard Univ, Cambridge, 1960).
Castor, J. I. Mon. Not. R. astr Soc. 149, 111–127 (1970).
Rybicki, G. B. & Hummer, D. G. Astrophys J. 219, 654–675 (1978).
Olson, G. L. Astrophys J. 255, 267–277 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swartz, D., Harkness, R. & Wheeler, J. Late-time optical spectra of SN1987A. Nature 337, 439–442 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/337439a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/337439a0
This article is cited by
-
The evolution of massive stars to explosion
Space Science Reviews (1994)