Abstract
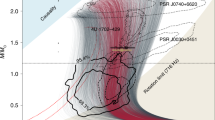
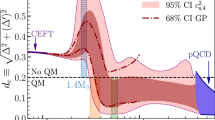
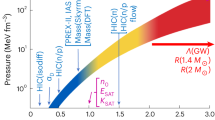
IF THE recently reported 0.5-ms optical pulsar in the remnant of SN1987A1,2 is indeed a rotating neutron star, then its very existence may be used to rule out many previously viable equations of state of nuclear matter (ref. 3). We demonstrated3 that it may be impossible to spin up an initially non-rotating neutron star to a spin period Prot≲0.5ms for any currently proposed nuclear equation of state. Here, we reverse the argument: a uniformly rotating neutron star with Prot≲ 0.5ms may be unable to spin down to become a slowly rotating neutron star, if any of the proposed equations of state is correct. Assuming that the neutron star in SN1987A is 'typical' and does not collapse to a black hole as it spins down to Prot» 0.5 ms, then its existence may actually invalidate all previously viable nuclear equations of state. We propose an approximate, analytical test that can be used to identify untenable equations of state in the future.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Middleditch, J. et al. IAU Circ. No. 4735 (1989).
Kristian, J. et al. Nature 338, 234–236 (1989).
Shapiro, S. L., Teukolsky, S. A. & Wasserman, I. Astrophys. J. 272, 702–707 (1983).
Butterworth, E. M. & Ipser, J. R. Astrophys. J. 204, 200–223 (1976).
Butterworth, E. M. Astrophys. J. 204, 561–572 (1976).
Butterworth, E. M. Astrophys. J. 231, 219–223 (1979).
Friedman, J. L., Ipser, J. R. & Parker, L. Astrophys. J. 304, 115–139 (1986).
Lightman, A. P. et al. Problem Book in Relativity and Gravitation (Princeton University Press, 1975).
Hartle, J. B. & Thorne, K. S. Astrophys. J. 153, 807–834 (1968).
Chandrasekhar, S. Ellipsoidal Figures of Equilibrium (Dover, New York, 1987).
Bondi, H. in Lectures on General Relativity (eds S. Deser & Ford, K. W.) 379–459 (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1964).
Weinberg, S. Gravitation and Cosmology 330–335 (Wiley, New York, 1972).
Baym, G. & Pethick, C. J. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 17, 415–443 (1979).
Shapiro, S. L. & Teukolsky, S. A. Black Holes, White Dwarfs, and Neutron Stars: The Physics of Compact Objects (Wiley, New York, 1983).
Arnett, W. D. Astrophys. J. 319, 136–142 (1987).
Maxwell, O. & Weise, W. Phys. Lett. 62B, 159–161 (1976).
Fechner, W. B. & Joss, P. C. Nature 274, 347–348 (1978).
Friedman, J. L. & Schutz, B. F. Astrophys. J. 222, 281–296 (1978).
Wang, Q. et al. Nature 338, 319–320 (1989).
Pandharipande, V. R. & Smith, R. A. Phys. Lett. B59, 15–18 (1975).
Pandharipande, V. R. & Smith, R. A. Nucl. Phys. A237, 507–532 (1975).
Bethe, H. A. & Johnson, M. B. Nucl. Phys. A230, 1–58 (1974).
Friedman, B. & Pandharipande, V. R. Nucl. Phys. A361, 502–520 (1981).
Pandharipande, V. R. Nucl. Phys. A178, 123–144 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shapiro, S., Teukolsky, S. & Wasserman, I. Testing nuclear theory using the 0.5 ms pulsar. Nature 340, 451–452 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/340451a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/340451a0
This article is cited by
-
Numerical solutions of general-relativistic field equations for rapidly rotating neutron stars
Science in China Series A: Mathematics (1997)
-
Static massive configurations with constant local adiabatic exponents
Astrophysics and Space Science (1991)
-
Relativistic polytropic spheres in general relativity
Astrophysics and Space Science (1991)
-
Rotating black holes in neutron and quark stars: Phenomenon of pulsars
Astrophysics and Space Science (1991)
-
Pulsar puzzles for astronomers
Nature (1989)