Abstract
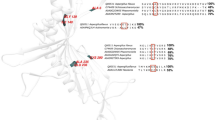
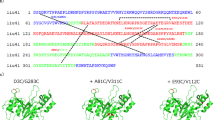
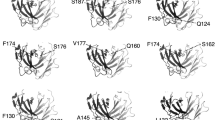
DISULPHIDE bonds can significantly stabilize the native structures of proteins1–3. The effect is presumed to be due mainly to a decrease in the configurational chain entropy of the unfolded polypeptide4–7. In phage T4 lysozyme, a disulphide-free enzyme, engineered disulphide mutants that crosslink residues 3–97, 9–164 and 21–142 are significantly more stable than the wild-type protein8–11. To investigate the effect of multiple-disulphide bonds on protein stability, mutants were constructed in which two or three stabilizing disulphide bridges were combined in the same protein. Reversible thermal denaturation shows that the increase in melting temperature resulting from the individual disulphide bonds is approximately additive. The triple-disulphide variant unfolds at a temperature 23.4 °C higher than wild-type lysozyme. The results demonstrate that a combination of disulphide bonds, each of which contributes to stability, can achieve substantial overall improvement in the stability of a protein.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creighton, T. E. BioEssays 8, 57–63 (1988).
Thornton, J. M. J. molec. Biol. 151, 261–287 (1981).
Pace, C. N., Grimsley, G. R., Thomson, J. A. & Barnett, B. J. J. biol. Chem. 263, 11820–11825 (1988).
Schellman, J. A. C. R. Trav. Lab. Carlsberg Ser. Chim. 29, 230–259 (1955).
Flory, P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 78, 5222–5235 (1956).
Poland, D. C. & Scheraga, H. A. Biopolymers 3, 379–399 (1965).
Chan, H. S. & Dill, K. A. J. chem. Phys. 90, 492–509 (1988).
Perry, L. J. & Wetzel, R. Science 226, 555–557 (1984).
Wetzel, R., Perry, L. J., Baase, W. A. & Becktel, W. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 401–405 (1988).
Matsumura, M., Becktel, W. J. & Matthews, B. W. Nature 334, 406–410 (1988).
Matsumura, M., Becktel, W. J., Levitt, M. & Matthews, B. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 6562–6566 (1989).
Perry, L. J. & Wetzel, R. Biochemistry 25, 733–739 (1986).
Matsumura, M., & Matthews, B. W. Science 243, 792–794 (1989).
Lin, S. H., Konishi, Y., Denton, M. E. & Scheraga, H. A. Biochemistry 23, 5504–5512 (1984).
Johnson, R. E., Adams, P. & Rupley, J. A. Biochemistry 17, 1479–1484 (1978).
Signor, G., Matsumura, M., Schellman, J. A. & Matthews, B. W. in Current Research in Protein Chemistry (ed. Villafranca, J. J.) (Academic, in the press).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Kunkel, T. A., Roberts, J. D. & Zakour, R. A. Meth. Enzym. 154, 367–382 (1987).
Messing, J. Meth. Enzym. 101, 20–78 (1983).
Sanger, F., Nickelsen, S. & Coulson, A. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Zoller, M. J. & Smith, M. Meth. Enzym. 100, 468–500 (1983).
Muchmore, D. C. McIntosh, L. P., Russell, C. B., Anderson, D. E. & Dahlquist, F. W. Meth. Enzym. 177, 44–73 (1989).
Habeeb, A. F. S. A. Meth. Enzym. 25, 457–464 (1972).
Tsugita, A., Inouye, M., Terzaghi, E. & Streisinger, G. J. biol. Chem. 243, 391–397 (1968).
Matthews, B. W., Nicholson, H. & Becktel, W. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 6663–6667 (1987).
Elwell, M. & Schellman, J. biochem. biophys. Acta 386, 309–323 (1975).
Hawkes, R., Grütter, M. G. & Schellman, J. J. molec. Biol. 175, 195–212 (1984).
Becktel, W. J. & Baase, W. A. Biopolymers 26, 619–623 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumura, M., Signor, G. & Matthews, B. Substantial increase of protein stability by multiple disulphide bonds. Nature 342, 291–293 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/342291a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/342291a0
This article is cited by
-
Evolution of antimicrobial cysteine-rich peptides in plants
Plant Cell Reports (2023)
-
To cleave or not—disulfide bond of cystine on nanocopper: a computational approach
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2023)
-
A comprehensive analysis of novel disulfide bond introduction site into the constant domain of human Fab
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Prediction of disulfide bond engineering sites using a machine learning method
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Engineering of a thermo-alkali-stable lipase from Rhizopus chinensis by rational design of a buried disulfide bond and combinatorial mutagenesis
Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (2020)