Abstract
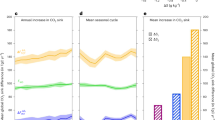
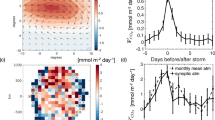
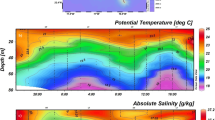
THE transfer of dissolved atmospheric gases across the air/sea interface is a strong function of wind speed and state of the sea surface. The form of the dependence on wind velocities is needed to calculate oceanic sources and sinks of climatically significant gases, particularly carbon dioxide1 and dimethylsulphide2,3. Previous measurements at sea have used techniques that reveal this dependence only when averaged over weeks or months4,5, making it impossible to study the effects of high winds, which are generally episodic. Here we report first results from the application of a tracer technique which enables accurate measurements to be made over periods of 24–72 hours, including the first determination of gas exchange in storm conditions. Our results support the wind-speed dependence suggested by Liss and Merlivat6 on the basis of lake and wind-tunnel experiments, and are consistent with most measurements made by the radon-deficit technique. They suggest slower rates for CO2exchange than those obtained by 14C budgeting, and favour recent lower estimates1,7 of the global oceanic sink for anthropogenic CO2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Etcheto, J. & Merlivat, L. J. geophys. Res. 93, 15669–15678 (1988).
Andreae, M. O. in The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling (ed. Buat-Menard, P.) 331–362 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1986).
Charlson, R. J., Lovelock, J. E., Andreae, M. O. & Warren, S. G. Nature 326, 655–661 (1987).
Roether, W. in Dynamic Processes in the Chemistry of the Upper Ocean (eds Burton, J. D., Brewer, P. G. & Chesselet, R.) 117–128 (Plenum, New York, 1986).
Roether, W. & Kromer, B. in Gas Transfer at Water Surfaces (eds Brutsaert, W. & Jirka, G. H.) 447–457 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1984).
Liss, P. S. & Merlivat, L. in The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling (ed. Buat-Menard, P.) 113–127 (Reidel, Doredrecht, 1986).
Tans, P. P., Fung, I. Y. & Takahashi, T. Science 247, 1431–1438 (1990).
Holmen, K. & Liss, P. S. Tellus B36, 92–100 (1984).
Ledwell, J. R. in Gas Transfer at Water Surfaces (eds Brutsaert, W. & Jirka, G. H.) 243–302 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1984).
Jähne, B. et al. J. geophys. Res. 92, 1937–1949 (1987).
Upstill-Goddard, R. C., Watson, A. J., Liss, P. S. & Liddicoat, M. I. Tellus B 42, 364–377 (1990).
Broecker, H. C., Petermann, J. & Siems, W. in Gas Transfer at Water Surfaces (eds Brutsaert, W. & Jirka, G. H.) 229–236 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1984).
Wanninkhof, R., Ledwell, J. R. & Broecker, W. S. Science 227, 1224–1226 (1985).
Broecker, W. S., Peng, T-H., Ostlund, G. & Stuiver, M. J. geophys. Res. 90, 6953–6970 (1986).
Hayduk, W. & Laudie, H. J. Am. Inst. chem. Engnr 20, 611–615 (1974).
Jähne, B., Heinz, G. & Dietrich, W. J. geophys. Res. 92, 10767–10776 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watson, A., Upstill-Goddard, R. & Liss, P. Air–sea gas exchange in rough and stormy seas measured by a dual-tracer technique. Nature 349, 145–147 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/349145a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/349145a0
This article is cited by
-
Optimized methods for diffusive greenhouse gas flux analyses in inland waters
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2020)
-
Highly cited articles in wind tunnel-related research: a bibliometric analysis
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2018)
-
Methods for Estimating Air–Sea Fluxes of CO2 Using High-Frequency Measurements
Boundary-Layer Meteorology (2012)
-
On Factors Controlling Air–Water Gas Exchange in a Large Tidal River
Estuaries and Coasts (2011)
-
Estimating of gas transfer velocity using triple isotopes of dissolved oxygen
Journal of Oceanography (2010)