Abstract
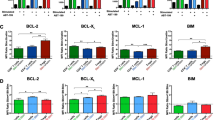
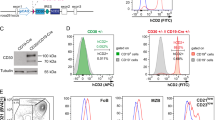
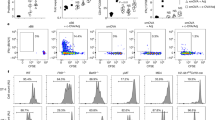
IN mice transgenic for an autoantibody, self-reactive B cells have been shown to be eliminated upon interaction with membrane-bound self-antigens in the periphery1,2as well as in the bone marrow3–5, suggesting that both immature and mature B cells are eliminated by multimerization of surface immunoglobulins (sIg). Activation of mature B cells by antigens may thus require a second signal that inhibits sIg-mediated apoptosis. Such a second signal is likely to be provided by T helper cells, because B-cell tolerance is more easily induced in the absence of T helper cells6–9. To assess the molecular nature of the signal that inhibits slg-mediated apoptosis, we used anti-IgM-induced apoptotic death of WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells10,11 as a model system. Here we report that the signal for abrogating sIg-mediated apoptosis is generated by association of the CD40L molecule on T cells with the CD40 molecule on WEHI-231 cells. T-cell help through CD40 may thus determine whether B cells are eliminated or activated upon interaction with antigens.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murakami, M. et al. Nature 357, 77–80 (1992).
Russell, D. M. et al. Nature 354, 308–311 (1991).
Nemazee, D. A. & Bürki, K. Nature 337, 562–566 (1989).
Hartley, S. B. et al. Nature 353, 765–769 (1991).
Okamoto, M. et al. J. exp. Med. 175, 71–79 (1992).
Nossal, G. J. V. A. Rev. Immun. 1, 33–62 (1983).
Goodnow, C. C. A. Rev. Immun. 10, 489–518 (1992).
Metcalf, E. S. & Klinman, N. R. J. exp. Med. 143, 1327–1340 (1976).
Metcalf, E. S. & Klinman, N. R. J. Immun. 118, 2111–2116 (1977).
Benhamou, L. E., Cazenave, P. A. & Sarthou, P. Eur. J. Immun. 20, 1405–1407 (1990).
Hasbold, J. & Klaus, G. G. B. Eur. J. Immun. 20, 1685–1690 (1990).
Ozaki, S., Durum, S. K., Muegge, K., York-Jolley, J. & Berzofsky, J. A. J. Immun. 141, 71–78 (1988).
Ogasawara, K., Maloy, W. L., Beverly, B. & Schwartz, R. H. J. Immun. 142, 1448–1456 (1989).
Ashwell, J. D., Cunningham, R. E., Noguchi, P. D. & Hernandez, D. J. exp. Med. 165, 173–194 (1987).
Odaka, C., Kizaki, H. & Tadakuma, T. J. Immun. 144, 2096–2101 (1990).
Armitage, R. J. et al. Nature 357, 80–82 (1992).
Van de Velde, H., von Hoegen, I., Luo, W., Parnes, J. R. & Thielemans, K. Nature 351, 662–664 (1991).
Clark, E. A. & Ledbetter, J. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 4494–4498 (1986).
Paulie, S. et al. J. Immun. 142, 590–595 (1989).
Rousset, F., Garcia, E. & Banchereau, J. J. exp. Med. 173, 705–710 (1991).
Subbarao, B. & Mosier, D. E. J. Immun. 130, 2033–2037 (1983).
Subbarao, B. & Mosier, D. E. J. exp. Med. 159, 1796–1801 (1984).
Noelle, R. J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 6550–6554 (1992).
Liu, Y.-J. et al. Nature 342, 929–931 (1989).
Nicoletti, I., Migliorati, M. C., Grignani, F. & Riccardi, C. J. Immun. Meth. 139, 271–279 (1991).
Mond, J. J., Seghal, E., Kung, J. & Finkelman, F. D. J. Immun. 127, 881–888 (1981).
Armitage, R. J. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 22, 2071–2176 (1992).
Cuende, E. et al. EMBO J. 12, 1555–1560 (1993).
Hartley, S. B. et al. Cell 72, 325–335 (1993).
Noell, R. J., Ledbetter, J. A. & Aruffo, A. Immun. Today 13, 431–433 (1992).
Robb, R. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3992–3996 (1986).
Karasuyama, H. & Melchers, F. Eur. J. Immun. 18, 97–104 (1988).
Shimizu, A., Nussenzweig, M. C., Mizuta, T.-R., Leder, P. & Honjo, T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 8020–8023 (1989).
Matsunami, N. et al. Nature 342, 934–937 (1989).
Stamenkovic, I., Clark, E. A. & Seed, B. EMBO J. 8, 1403–1410 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsubata, T., Wu, J. & Honjo, T. B-cell apoptosis induced by antigen receptor crosslinking is blocked by a T-cell signal through CD40. Nature 364, 645–648 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/364645a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/364645a0
This article is cited by
-
HAX1 deletion impairs BCR internalization and leads to delayed BCR-mediated apoptosis
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2016)
-
HAX1 deletion impairs BCR internalization and leads to delayed BCR-mediated apoptosis
Cellular and Molecular Immunology (2015)
-
Biallelic loss-of-function mutation in NIK causes a primary immunodeficiency with multifaceted aberrant lymphoid immunity
Nature Communications (2014)
-
MicroRNAs regulate B-cell receptor signaling-induced apoptosis
Genes & Immunity (2012)
-
Induction of high-dose tolerance to the rat anti-mouse IL-6 receptor antibody in NZB/NZW F1 mice
Rheumatology International (2011)