Abstract
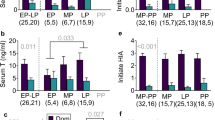
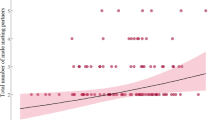
THE intrauterine position relative to members of the same or opposite sex that a rodent fetus occupies affects both its morphology and behaviour when adult1–14. Female fetuses that mature between males are androgenized by testosterone crossing fetal membranes15,16, and their phenotypes as adults differ significantly from those of sisters that received less intrauterine exposure to exogenous testosterone17–20. We report here that adult female Mongolian gerbils that gestated between male fetuses produce litters containing a significantly greater proportion of sons than the litters produced by those that gestated between female fetuses. Consequently, daughters delivered by dams that gestated between male fetuses are more likely to have gestated between male fetuses and be androgenized in utero than are daughters of dams that gestated between female fetuses. Female gerbils thus tend to inherit the phenotype (either androgenized or not androgenized) of their respective mothers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, M. J., Schultz, G. S. & Hilton, F. K. Endocrinology 115, 2318–2323 (1984).
Clark, M. M., Malenfant, S. A., Winter, D. A. & Galef, B. G. Jr Physiol. Behav. 47, 301–305 (1990).
Clemens, L. G. in Reproductive Behavior (eds Montagna, W. & Sadler, W. A.) 25–53 (Plenum, New York, 1974).
Clemens, L. G., Gladue, B. A. & Coniglio, L. P. Horm. Behav. 10, 40–53 (1978).
Gandelman, R., vom Saal F. S. & Reinisch, J. M. Nature 266, 722–724 (1977).
Kinsley, C., Konen, C., Miele, J., Ghiraldi, L. & Svare, B. Physiol. Behav. 36, 793–799 (1986).
Kinsley, C., Miele, J., Konen, C., Ghiraldi, L. & Svare, B. Horm. Behav. 20, 7–12 (1986).
Kinsley, C. et al. Horm. Behav. 20, 201–211 (1986).
Meisel, R. L. & Ward, I. L. Science 213, 239–241 (1981).
Vornachka, A. J. & Lisk, R. D. Horm. Behav. 20, 181–193 (1986).
vom Saal, F. S. J. Anim. Sci. 67, 1824–1840 (1991).
Wechman, R. Jr, Brown, M. & Hilton, F. Biol. Reprod. 33, 803–807 (1985).
Zielinski, W. J., vom Saal, F. S. & Vandenbergh, J. G. Behavl Ecol. Sociobiol. 30, 185–191 (1992).
Tobet, S. A. Dunlap, J. L. & Gerall, A. A. Horm. Behav. 16, 251–258 (1982).
vom Saal, F. S. & Dahr, M. Physiol. Behav. 52, 163–171 (1992).
Even, M. D., Dahr, M. & vom Saal, F. S. J. Reprod. Fertil. 96, 709–716 (1992).
vom Saal, F. S. & Bronson, F. H. Biol. Reprod. 19, 842–853 (1978).
vom Saal, F. S. & Bronson, F. H. Science 208, 597–599 (1980).
vom Saal, F. S., Grant, W. M., McMullen, C. W. & Laves, K. S. Science 220, 1306–1309 (1983).
Clark, M. M., Robertson, R. K. & Galef, B. G. Jr Dev. Psychobiol. 26, 185–194 (1993).
Clark, M. M., Crews, D. & Galef, B. G. Jr Physiol. Behav. 49, 239–243 (1991).
Clark, M. M. & Galef, B. G. Jr Physiol. Behav. 42, 15–18 (1988).
Clark, M. M., Spencer, C. A. & Galef, B. G. Jr Anim. Behav. 34, 551–560 (1986).
Clark M. M., Malenfant, S. A. Winter, D. A. & Galef, B. G. Jr Physiol. Behav. 47, 301–305 (1989).
Clark, M. M. & Galef, B. G. Jr Dev. Psychobiol. 23, 29–37 (1990).
Clark, M. M., Galef, B. G. Jr & vom Saal, F. S. Devl Psychobiol. 24, 81–90 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, M., Karpiuk, P. & Galef, B. Hormonally mediated inheritance of acquired characteristics in Mongolian gerbils. Nature 364, 712 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/364712a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/364712a0
This article is cited by
-
Hazards inherent in interdisciplinary behavioral research
Frontiers in Zoology (2015)
-
On books
The Behavior Analyst (2007)
-
Epigenesis: The Missing Beat in Biotechnology?
Nature Biotechnology (1994)
-
Sex-ratio and inheritance
Nature (1994)
-
Embryonic growth and the evolution of the mammalian Y chromosome. I. The Y as an attractor for selfish growth factors
Heredity (1994)