Abstract
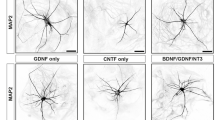
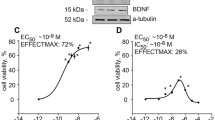
DURING vertebrate development, many neurons depend for survival and differentiation on their target cells1–3. The best documented mediator of such a retrograde trophic action is the neurotrophin nerve growth factor (NGF)1. NGF and the other known members of the neurotrophin family, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5) are conserved as distinct genes over large evolutionary distances4–6. Here we report the cloning of neurotrophin-6 (NT-6), a new mem-ber of this family from the teleost fish Xiphophorus. NT-6 dis-tinguishes itself from the other known neurotrophins in that it is not found as a soluble protein in the medium of producing cells. The addition of heparin (but not chondroitin) effects the release of NT-6 from cell surface and extracellular matrix molecules. Recombinant purified NT-6 has a spectrum of actions similar to NGF on chick sympathetic and sensory neurons, albeit with a lower potency. NT-6 is expressed in the embryonic valvulla cerebelli; expression persists in some adult tissues. The interaction of NT-6 with heparin-binding molecules may modulate its action in the nervous system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levi-Montalcini, R. Science 237, 1154–1162 (1987).
Purves, D. Body and Brain: A Tropic Theory of Neural Connection (Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1988).
Barde, Y.-A. Neuron 2, 1525–1534 (1989).
Götz, R., Raulf, F. & Schartl, M. J. Neurochem. 59, 432–442 (1992).
Götz, R. & Schartl, M. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 108C, 1–10 (1994).
Hallböök, F., Ibán̄ez, C. F. & Persson, H. Neuron 6, 845–858 (1991).
Hosaka, M. et al. J. biol. Chem. 266, 12127–12130 (1991).
McDonald, N. Q. et al. Nature 354, 411–414 (1991).
Crawford, J. L., Lipscomb, W. N. & Schellman, C. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 538–542 (1973).
Meek, J. Eur. J. Morphol. 1, 37–51 (1992).
Ruoslahti, E. & Yamaguchi, Y. Cell 64, 867–869 (1991).
LaRochelle, W. J., May-Siroff, M., Robbins, K. C. & Aaronson, S. A. Genes Dev. 5, 1191–1199 (1991).
Lee, B. A. & Donoghue, D. J. J. Cell Biol. 113, 361–370 (1991).
Östman, A., Andersson, M., Betsholtz, C., Westermark, B. & Heldin, C.-H. Cell Reg. 2, 503–512 (1991).
Higashiyama, S., Lau, K., Besner, G. E., Abraham, J. A. & Klagsbrun, M. J. biol. Chem. 267, 6205–6212 (1992).
Yayon, A., Klagsbrun, M., Esko, J. D., Leder, P. & Ornitz, D. M. Cell 64, 841–848 (1991).
Nurcombe, V., Ford, M. D., Wildschut, J. A. & Bartlett, P. F. Science 260, 103–106 (1993).
Rifkin, D. B. & Moscatelli, D. J. Cell Biol. 109, 1–6 (1989).
Vlodavsky, I., Bar-Shavit, R., Ishai-Michaeli, R., Bashkin, P. & Fuks, Z. Trends biochem. Sci. 168, 268–271 (1991).
Marcey, D. & Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Nature 321, 380–381 (1986).
Powers, D. A. Science 246, 352–358 (1989).
Rossant, J. & Hopkins, N. Genes Dev. 6, 1–13 (1992).
Tavolga, W. N. Bull. Am. Mus. nat. Hist. 94, 161–230 (1949).
Okayama, H. et al. Meth. Enzym. 154, 3–28 (1987).
Krumlauf, R. in Gene Transfer and Expression Protocols (ed. Murray, E. J.) 307–323 (Humana, Clifton, 1991).
Wilkinson, D. G. & Green, J. in Postimplantation Mammalian Embryos: A Practical Approach (eds Copp, A. J. & Cockroft, D. L) 155–171 (IRL, Oxford, 1990).
Götz, R., Kolbeck, R., Lottspeich, F. & Barde, Y.-A. Eur. J. Biochem. 204, 745–749 (1992).
Laemmli, U. K. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Barde, Y.-A., Edgar, D. & Thoenen, H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 77, 1199–1203 (1980).
Lindsay, R. M., Thoenen, H. & Barde, Y.-A. Devl Biol. 112, 319–328 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Götz, R., Köster, R., Winkler, C. et al. Neurotrophin-6 is a new member of the nerve growth factor family. Nature 372, 266–269 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/372266a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/372266a0
This article is cited by
-
The evolution of nerve growth factor inhibition in clinical medicine
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2021)
-
A C-terminal cysteine residue is required for peptide-based inhibition of the NGF/TrkA interaction at nM concentrations: implications for peptide-based analgesics
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Synthesis and In Vitro Neuroprotector Activity of Diastereoisomers of a Dimeric Dipeptide Mimetic of Nerve Growth Factor GK-2
Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal (2018)
-
Neurotrophin Signaling and Stem Cells—Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases and Stem Cell Therapy
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)