Abstract
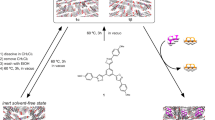
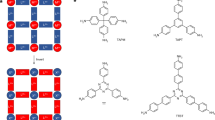
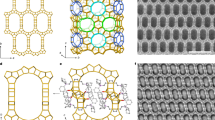
MICROPOROUS inorganic materials such as zeolites find widespread application in heterogeneous catalysis, adsorption and ion-exchange processes. The rigidity and stability of such frameworks allow for shape- and size-selective inclusion of organic molecules and ions1–4. Analogous microporous structures based on organic building blocks have the potential for more precise rational design, through control of the shape, size and functionalization of the pores5–8. Here we report the synthesis of a metal–organic framework designed to bind aromatic guest molecules selectively. The basic building block is a symmetric organic molecule, which binds metal ions9,10 to form layers of the metal–organic compound alternating with layers whose composition is determined by the functionalization of the starting molecules. The layers create channels in which guest aromatic molecules may be selectively bound. We show that the crystal lattice thus formed is thermally stable up to 350 °C, even after removal of included guest molecules, and that the inclusions can be selectively readsorbed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Komarneni, S., Smith, D. M. & Beck, J. S. (eds) Advances in Porous Materials (Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, 1995).
Ribeiro, F. R., Rodrigues, A. E., Rollmann, L. D. & Naccache, C. (eds) Zeolites: Science and Technology (Nijhoff, The Hague, 1984).
Dyer, A. An Introduction to Zeolite Molecular Sieves (Wiley, Chichester, 1988).
Hölderich, W., Hesse, M. & Näumann, F. Angew. Chem. int. Edn engl. 27, 226–246 (1988).
Yaghi, O. M. & Li, G. Angew. Chem. int. Edn engl. 34, 207–209 (1995).
Gardner, G. B., Venkataraman, D., Moore, J. S. & Lee, S. Nature 374, 792–795 (1995).
Abrahams, B. F., Hoskins, B. F., Michall, D. M. & Robson, R. Nature 369, 727–729 (1994).
MacGillivray, L. R., Subramanian, S. & Zaworotko, M. J. J. chem. Soc., chem. Commun. 1325–1326 (1994).
Yaghi, O. M., Sun, Z., Richardson, D. A. & Groy, T. L. J. Am. chem.Soc. 116, 807–808 (1994).
Hoskins, B. F. & Robson, R. J. Am. chem. Soc. 112, 1546–1554 (1990).
Wilkinson, G., Gillard, R. D. & McCleverty, J. A. Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry: The Synthesis, Reactions, Properties and Applications of Coordination Compounds 5; Late Transition Elements (Pergamon, Oxford, 1987).
Johnson, J. W. et al. J. Am. chem. Soc. 111, 381–383 (1989).
Calabrese, J. et al. J. Am. chem. Soc. 113, 2328–2330 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaghi, O., Li, G. & Li, H. Selective binding and removal of guests in a microporous metal–organic framework. Nature 378, 703–706 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/378703a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/378703a0
This article is cited by
-
Porous isoreticular non-metal organic frameworks
Nature (2024)
-
Light-induced MOF synthesis enabling composite photothermal materials
Nature Communications (2024)
-
A functional FeIII-based NH2-MOF as an electrochemical sensor for Cu2+ detection in ethanol fuel
Ionics (2024)
-
Mechanistic investigations of the disproportionation reaction catalyzed by AlCl3/NH2-MIL-53(Al) to produce dimethyldichlorosilane
Silicon (2024)
-
Enhancing catalytic activity of UiO-66 through CuO nanoparticles incorporation: a study on Henry reaction and one-pot allylic C-H bond oxidation of olefins
Journal of Chemical Sciences (2024)