Abstract
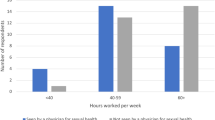
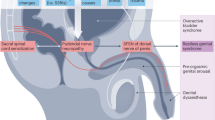
Erectile dysfunction affects 31–52% of American men. Although considerable advances have been made in the diagnosis and treatment of erectile dysfunction in the past decade, more than 80% of men with erectile dysfunction are not treated because they do not seek medical attention or their physicians do not initiate a dialogue about sexual problems during their visits. This despite patients' desires to confront sexual problems and receive treatment. Most subgroups of men can now be effectively treated for sexual dysfunction. Although men with severe cardiac disease may require stabilization of their cardiac condition before treatment, most can successfully return to an active sex life. Some men, however, do not respond to the use of oral agents. These men can be treated with second- and third-line treatment modalities or with the newer concept of combined-modality treatment. Despite excellent treatment alternatives, many men have low libido or hypoactive sexual desire disorder. In the ultimate resolution of a patient's sexual dysfunction, physicians must open a free and sympathetic dialogue and offer a full spectrum of treatment modalities tailored to the individual patient and partner. If initial treatment modalities fail, more invasive alternatives or combination therapy should be offered to cure the patient's erectile dysfunction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carson, C. Erectile dysfunction in the 21st century: whom we can treat, whom we cannot treat and patient education. Int J Impot Res 14 (Suppl 1), S29–S34 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900804
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900804
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The impact of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on lower urinary tract symptoms
Current Prostate Reports (2008)
-
The evolving relationship of erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms
Current Sexual Health Reports (2008)
-
Lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: Epidemiology and treatment in the aging man
Current Urology Reports (2005)
-
Topical application of a Rho-kinase inhibitor in rats causes penile erection
International Journal of Impotence Research (2004)