Abstract
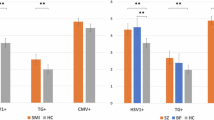
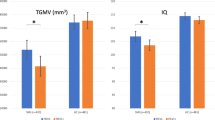
Infectious agents have been proposed as one of the risk factors for schizophrenia. However, the data on the association of infectious agents with in vivo brain changes are scant. We evaluated the association of serological evidence of exposure to herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV1) with in vivo brain structural variations among first-episode antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder patients and control subjects. We assayed HSV1 immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody in serum samples from 30 patients and 44 healthy subjects and obtained structural magnetic resonance imaging scans from the same individuals. There were proportionately more patients with elevated HSV1 antibody ratios than healthy comparison subjects (χ2=3.98, 1 df, P=0.046) and patients had significantly higher HSV1 IgG antibody ratios compared with healthy subjects. Using optimized voxel-based morphometry, we examined diagnosis by HSV1 serological status interaction followed by within- and between-group comparison across the serological status. We observed a diagnosis by HSV1 serological status interaction and a significant main effect of HSV1 serological status in the prefrontal gray matter. Patients exposed to HSV1 had decreased gray matter in Brodmann area 9 (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex) and 32 (anterior cingulate cortex) compared with patients without serological evidence of exposure to HSV1. HSV1-associated differences in brain structure were not detected among healthy subjects. These findings suggest that HSV1 exposure in schizophrenia is associated with specific regional gray matter differences that may not be attributable to medications, illness chronicity or comorbid substance use. This study provides suggestive evidence for a link between HSV1 exposure and some of the cerebral morphological changes often reported in schizophrenia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torrey EF, Miller J, Rawlings R, Yolken RH . Seasonality of births in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a review of the literature. Schizophr Res 1997; 28: 1–38.
Torrey EF, Rawlings R, Waldman IN . Schizophrenic births and viral diseases in two states. Schizophr Res 1988; 1: 73–77.
Kudelova M, Rajcani J, Pogady J, Sramka M . Herpes simplex virus DNA in the brain of psychotic patients. Acta Virol 1988; 32: 455–460.
Moises HW, Ruger R, Reynolds GP, Fleckenstein B . Human cytomegalovirus DNA in the temporal cortex of a schizophrenic patient. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 1988; 238: 110–113.
Buka SL, Tsuang MT, Torrey EF, Klebanoff MA, Bernstein D, Yolken RH . Maternal infections and subsequent psychosis among offspring. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001; 58: 1032–1037.
Pelonero AL, Pandurangi AK, Calabrese VP . Serum IgG antibody to herpes viruses in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 1990; 33: 11–17.
Srikanth S, Ravi V, Poornima KS, Shetty KT, Gangadhar BN, Janakiramaiah N . Viral antibodies in recent onset, nonorganic psychoses: correspondence with symptomatic severity. Biol Psychiatry 1994; 36: 517–521.
Bartova L, Rajcani J, Pogady J . Herpes simplex virus antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid of schizophrenic patients. Acta Virol 1987; 31: 443–446.
Fux M, Sarov I, Ginot Y, Sarov B . Herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus in the serum of schizophrenic patients versus other psychosis, normal controls. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci 1992; 29: 33–35.
Delisi LE, Smith SB, Hamovit JR, Maxwell ME, Goldin LR, Dingman CW et al. Herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus antibody titres in sera from schizophrenic patients. Psychol Med 1986; 16: 757–763.
King DJ, Cooper SJ, Earle JA, Martin SJ, McFerran NV, Rima BK et al. A survey of serum antibodies to eight common viruses in psychiatric patients. Br J Psychiatry 1985; 147: 137–144.
Cleator GM, Klapper PE . The herpesviridae. In: Zuckerman AJ, Banatvala JE, Pattison JR (eds). Principles, Practice of Clinical Virology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: New York, 2002, pp 19–21.
Daheshia M, Feldman LT, Rouse BT . Herpes simplex virus latency and the immune response. Curr Opin Microbiol 1998; 1: 430–435.
Cinque P, Marenzi R, Ceresa D . Cytomegalovirus infections of the nervous system. Intervirology 1997; 40: 85–97.
Rodriguez MM, Delgado PI, Petito CK . Epstein–Barr virus-associated primary central nervous system lymphoma in a child with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1997; 121: 1287–1291.
Gray F, Belec L, Lescs MC, Chretien F, Ciardi A, Hassine D et al. Varicella-zoster virus infection of the central nervous system in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Brain 1994; 117 (Part 5): 987–999.
Sauerbrei A, Eichhorn U, Hottenrott G, Wutzler P . Virological diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. J Clin Virol 2000; 17: 31–36.
Schmutzhard E . Viral infections of the CNS with special emphasis on herpes simplex infections. J Neurol 2001; 248: 469–477.
Kimberlin DW, Whitley RJ . Human herpesvirus-6: neurologic implications of a newly-described viral pathogen. J Neurovirol 1998; 4: 474–485.
Klapper P, Cleator G, Longson M . Mild forms of herpes encephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1984; 47: 1247–1250.
Cleator GM, Klapper PE . Herpes simplex. In: Zuckerman AJ, Banatvala JE, Pattison JR (eds). Principles and Practice of Clinical Virology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: New York, 2004, pp 27–51.
Padgett DA, Sheridan JF, Dorne J, Berntson GG, Candelora J, Glaser R . Social stress and the reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 7231–7235.
Myesliwska J, Trzonkowski P, Bryl E, Lukaszuk K, Myesliwski A . Lower interleukin-2 and higher serum tumor necrosis factor-A levels are associated with perimenstrual, recurrent herpes simplex infection in young women. Eur Cytokine Netw 2000; 11: 397–406.
Ben-Hur T, Cialic R, Itzik A, Barak O, Yirmiya R, Weidenfeld J . A novel permissive role for glucocorticoids in induction of febrile and behavioral signs of experimental herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Neuroscience 2001; 108: 119–127.
Engel JA, Zhang J, Bergstrom T, Conradi N, Forkstam C, Liljeroth A et al. Neonatal herpes simplex virus type 1 brain infection affects the development of sensorimotor gating in rats. Brain Res 2000; 863: 233–240.
Braff DL, Geyer MA . Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1990; 47: 181–188.
Zuckerman L, Weiner I . Maternal immune activation leads to behavioral and pharmacological changes in the adult offspring. J Psychiatr Res 2005; 39: 311–323.
Barnett EM, Cassell MD, Perlman S . Two neurotropic viruses, herpes simplex virus type 1 and mouse hepatitis virus, spread along different neural pathways from the main olfactory bulb. Neuroscience 1993; 57: 1007–1025.
Paivarinta MA, Marttila RJ, Koulu M, Pesonen U, Roytta M, Rinne UK . Brain monoamine metabolism and rotational behaviour induced by experimental herpes simplex virus encephalitis. J Neural Trans – Gen 1991; 86: 181–190.
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A . Dopamine as the wind of the psychotic fire: new evidence from brain imaging studies. J Psychopharmacol 1999; 13: 358–371.
Girault JA, Greengard P . The neurobiology of dopamine signaling. Arch Neurol 2004; 61: 641–644.
Dickerson FB, Boronow JJ, Stallings C, Origoni AE, Ruslanova I, Yolken RH . Association of serum antibodies to herpes simplex virus 1 with cognitive deficits in individuals with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 466–472.
Schroth G, Gawehn J, Thron A, Vallbracht A, Voigt K . Early diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis by MRI. Neurology 1987; 37: 179–183.
Jubelt B, Miller JR . Viral infections. In: Rowland LP (ed). Merritt's Neurology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2000, pp 134–163.
Gaviani P, Leone M, Mula M, Naldi P, Macchiarulo E, Brustia D et al. Progression of MRI abnormalities in herpes simplex encephalitis despite clinical improvement: natural history or disease progression? Neurol Sci 2004; 25: 104–107.
Pandurangi AK, Pelonero AL, Nadel L, Calabrese VP . Brain structure changes in schizophrenics with high serum titers of antibodies to herpes virus. Schizophr Res 1994; 11: 245–250.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic & Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, 1994.
First MB . The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV for Axis I Disorders: Clinical Version, Administration Booklet. American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC, 1997.
Hollingshead AB . Four-factor Index of Social Status. Yale University: New Haven, CT, 1975.
Gilbert AR, Rosenberg DR, Harenski K, Spencer S, Sweeney JA, Keshavan MS . Thalamic volumes in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2001; 158: 618–624.
Mathworks Inc. Matlab, 7th edn. Mathworks Inc.: Natick, MA, 2005.
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS . A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 2001; 14: 21–36.
Gitelman DR, Ashburner J, Friston KJ, Tyler LK, Price CJ . Voxel-based morphometry of herpes simplex encephalitis. NeuroImage 2001; 13: 623–631.
Ashley RL . Genital herpes. Type-specific antibodies for diagnosis and management. Dermatol Clin 1998; 16: 789–793, xiii–xiv.
Zhang XY, Zhou DF, Cao LY, Wu GY, Shen YC . Cortisol and cytokines in chronic and treatment-resistant patients with schizophrenia: association with psychopathology and response to antipsychotics. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005; 30: 1532–1538.
Wang J, Dunn AJ . The role of interleukin-6 in the activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis and brain indoleamines by endotoxin and interleukin-1 beta. Brain Res 1999; 815: 337–348.
Pariante CM, Dazzan P, Danese A, Morgan KD, Brudaglio F, Morgan C et al. Increased pituitary volume in antipsychotic-free and antipsychotic-treated patients of the AEsop First-Onset Psychosis Study. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005; 30: 1923–1931.
Pariante CM, Vassilopoulou K, Velakoulis D, Phillips L, Soulsby B, Wood SJ et al. Pituitary volume in psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 2004; 185: 5–10.
Shenton ME, Dickey CD, Frumin M, McCarley RW . A review of MRI findings in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2001; 49: 1–52.
Pettegrew JW, Keshavan MS, Panchalingam K, Strychor S, Kaplan DB, Tretta MG et al. Alterations in brain high-energy phosphate and membrane phospholipid metabolism in first-episode, drug-naive schizophrenics. A pilot study of the dorsal prefrontal cortex by in vivo phosphorus 31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1991; 48: 563–568.
Barch DM, Carter CS, Braver TS, Sabb FW, MacDonald III A, Noll DC et al. Selective deficits in prefrontal cortex function in medication-naive patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001; 58: 280–288.
Weinberger DR, Berman KF, Daniel DG . Mesoprefrontal cortical dopaminergic activity and prefrontal hypofunction in schizophrenia. Clin Neuropharmacol 1992; 15: 568A–569A.
Prasad KMR, Chowdari KV, Nimgaonkar VL, Talkowski ME, Lewis DA, Keshavan MS . Polymorphism of the RGS4 gene and the DLPFC morphometry in first episode schizophrenia: a ROI study using the structural magnetic resonance imaging. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 213–219.
Prasad KMR, Chowdari KV, Talkowski ME, Keshavan MK, Nimgaonkar VL, Keshavan MS . Cerebral morphometry and COMT Val/Met polymorphism in first-episode schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004; 29: S222.
Ingi T, Aoki Y . Expression of RGS2, RGS4 and RGS7 in the developing postnatal brain. Eur J Neurosci 2002; 15: 929–936.
Tsai G, Coyle JT . Glutamatergic mechanisms in schizophrenia. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2002; 42: 165–179.
Beraki S, Aronsson F, Karlsson H, Ogren SO, Kristensson K . Influenza A virus infection causes alterations in expression of synaptic regulatory genes combined with changes in cognitive and emotional behaviors in mice. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 299–308.
DeBiasi RL, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Richardson-Burns S, Tyler KL . Central nervous system apoptosis in human herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus encephalitis. J Infect Dis 2002; 186: 1547–1557.
Gotlieb-Stematsky T, Zonis J, Arlazoroff A, Mozes T, Sigal M, Szekely AG . Antibodies to Epstein–Barr virus, herpes simplex type 1, cytomegalovirus and measles virus in psychiatric patients. Arch Virol 1981; 67: 333–339.
Leweke FM, Gerth CW, Koethe D, Klosterkotter J, Ruslanova I, Krivogorsky B et al. Antibodies to infectious agents in individuals with recent onset schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2004; 254: 4–8.
Theil D, Derfuss T, Paripovic I, Herberger S, Meinl E, Schueler O et al. Latent herpesvirus infection in human trigeminal ganglia causes chronic immune response. Am J Pathol 2003; 163: 2179–2184.
Keadle TL, Morris JL, Pepose JS, Stuart PM . CD4(+) and CD8(+) cells are key participants in the development of recurrent herpetic stromal keratitis in mice. Microb Pathog 2002; 32: 255–262.
Miles DH, Willcox MD, Athmanathan S . Ocular and neuronal cell apoptosis during HSV-1 infection: a review. Curr Eye Res 2004; 29: 79–90.
Fortunato EA, Spector DH . Viral induction of site-specific chromosome damage. Rev Med Virol 2003; 13: 21–37.
O’Neill FJ, Miles CP . Chromosome changes in human cells induced by herpes simplex, types 1 and 2. Nature 1969; 223: 851–852.
Mincheva A, Dundarov S, Bradvarova I . Effects of herpes simplex virus strains on human fibroblast and lymphocyte chromosomes and the localization of chromosomal aberrations. Acta Virol 1984; 28: 97–106.
Dickerson FB, Boronow JJ, Stallings CR, Origoni AE, Yolken RH . Reduction of symptoms by valacyclovir in cytomegalovirus-seropositive individuals with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2003; 160: 2234–2236.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by APIRE/Lilly Fellowship, NIMH MH19126 and MH72995 (KMRP), MH 63420, 66263, 56242 and Stanley Foundation (VLN) and MH45156 (MSK). We thank Drs Cameron S Carter, MD (CSC), Gretchen L Haas, PhD (GLH), Nina R Schooler, PhD (NRS) and the clinical core staff of the Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders (MH45156) for their assistance in diagnostic and psychopathological assessments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, K., Shirts, B., Yolken, R. et al. Brain morphological changes associated with exposure to HSV1 in first-episode schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 12, 105–113 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001915
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001915
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Herpes simplex virus 1 infection on grey matter and general intelligence in severe mental illness
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Classification of schizophrenia using feature-based morphometry
Journal of Neural Transmission (2012)