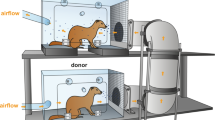
There is now a choice of animal models for testing therapies against the human virus.
Abstract
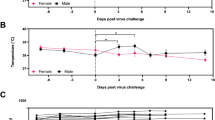
The reservoir of the coronavirus isolated from patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)1,2 is still unknown, but is suspected to have been a wild animal species. Here we show that ferrets (Mustela furo) and domestic cats (Felis domesticus) are susceptible to infection by SARS coronavirus (SCV) and that they can efficiently transmit the virus to previously uninfected animals that are housed with them. The observation that these two distantly related carnivores can so easily be infected with the virus indicates that the reservoir for this pathogen may involve a range of animal species.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ksiazek, T. G. et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1953–1966 (2003).
Peiris, J. S. M. et al. Lancet 361, 1319–1325 (2003).
Guan, Y. et al. Science 302, 276–278 (2003).
Fouchier, R. A. M. et al. Nature 423, 240 (2003).
Kuiken, T. et al. Lancet 362, 263–270 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martina, B., Haagmans, B., Kuiken, T. et al. SARS virus infection of cats and ferrets. Nature 425, 915 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/425915a
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/425915a
This article is cited by
-
Evaluation of the clinical evolution and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection in cats by simulating natural routes of infection
Veterinary Research Communications (2022)
-
Exploring COVID-19 incidence hotspot in Metropolitan area of Pakistan using geo-statistical approach: a study of Lahore city
Spatial Information Research (2022)
-
Ecology, evolution and spillover of coronaviruses from bats
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2022)
-
Screening and development of monoclonal antibodies for identification of ferret T follicular helper cells
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
COVID-19 preclinical models: human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice
Human Genomics (2020)