Abstract
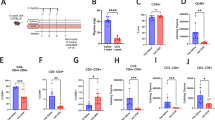
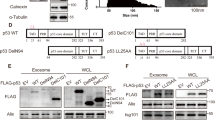
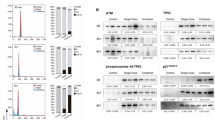
The involvement of the tumor suppressor protein, p53, in thymic epithelial cell-induced apoptosis of CD4+8+ (double positive) thymocytes, was studied in an in vitro model consisting of a thymic epithelial cell line (TEC) and thymocytes. p53 expression was not augmented in double positive (DP) thymocytes upon co-culturing with TEC, although extensive apoptosis was observed. In the same cells, p53 expression was upregulated in response to low ionizing irradiation, which was accompanied with massive apoptosis. Moreover, TEC induced apoptosis in two DP thymomas, derived from p53(−/−) mice, and in a double positive thymoma clone expressing mutant p53. The extent and kinetics of TEC-induced apoptosis was not affected by the status of p53 in the thymocytes tested. We conclude that thymic epithelial cell-induced apoptosis of immature DP thymocytes is p53-independent and apparently, involves a different apoptotic pathway than that triggered by DNA damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- TEC:
-
thymic epithelial cell line
- TE:
-
thymic epithelial cells
- RadLV:
-
radiation leukemia virus
- TcR:
-
T cell receptor
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- PE:
-
phycoerythrine
- DP:
-
double positive
- DN:
-
double negative
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- GC:
-
glucocorticoids
- WT:
-
wild type
References
Ashton-Rickardt PG, Bandeira A, Delaney JR, Van Kaer L, Pircher H-P, Zinkernagel RM and Tonegawa S . (1994) Evidence for a differential avidity model of T cell selection in the thymus. Cell 76: 651–663
Amsen D and Kruisbeek AM . (1998) Thymocyte selection: not by TcR alone. Immunol. Rev. 165: 209–229
Tolosa E and Ashwell JD . (1999) Thymus-derived glucocorticoids and the regulation of antigen specific T cell development. Neuroimmunomodulation 6: 90–96
Gutierrez JC and Palacios R . (1991) Heterogeneity of thymic epithelial cells in promoting T-lymphocyte differentiation in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 642–646
von Boehmer H and Kisielow P . (1990) Self-nonself discrimination by T cells. Science 248: 1369–1373
Sprent J, Lo D, Gao EK and Ron Y . (1988) T cell selection in the thymus. Immunol. Rev. 101: 173–190
Iwata M, Hanaoka S and Sato K . (1991) Rescue of thymocytes and T cell hybridomas from GC-induced apoptosis by stimulation via the TcR/CD3 complex: a possible in vitro model for positive selection of the T cell repertoire. Eur. J. Immunol. 21: 643–648
Vacchio MS, Papadopoulus V and Ashwell JD . (1994) Steroid production in the thymus: Implications for thymocyte selection. J. Exp. Med. 179: 1835–1846
Zacharchuk CM, Mercep M, Chakraborti PK, Simons JR SS and Ashwell JD . (1990) Programmed T lymphocytes death. Cell activation and steroid-induced pathways are mutually antagonistic. J. Immunol. 145: 4037–4045
Zilberman Y, Yefenof E, Oron E, Dorogin A and Guy R . (1996) T cell receptor-independent apoptosis of thymocyte clones induced by a thymic epithelial cell line is mediated by steroids. Cell. Immunol. 170: 78–84
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA and Jacks T . (1993b) p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature 362: 847–849
Clarke AR, Purdie CA, Harrison DJ, Morris RG, Bird CC, Hooper ML and Wyllie AH . (1993) Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature 362: 849–852
Halazonetis TD, Davis LJL and Kandil AN . (1993) Wild-type p53 adopts a ‘mutant’-like conformation when bound to DNA. EMBO J. 12: 1021–1028
Vogt Sionov R and Haupt Y . (1998) Apoptosis by p53: mechanism, regulation, and clinical implications. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 19: 345–362
Lotem J and Sachs L . (1993) Hematopoietic cells from mice deficient in wild type p53 are more resistant to induction of apoptosis by some agents. Blood 82: 1092–1096
Levine AJ . (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88: 323–331
Donehower LA and Bradley A . (1993) The tumor suppressor p53. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1155: 181–205
Jacks T, Remington L, Williams BO, Schmitt EM, Halachmi S, Bronson RT and Weinberg RA . (1994) Tumor spectrum analysis in p53 mutant mice. Curr. Biol. 4: 1–7
Purdie CA, Harrison DJ, Peter A, Dobbie L, White S, Howie SE, Salter DM, Bird CC, Wyllie AH, Hooper ML and Clarke AR . (1994) Tumor incidence, spectrum and ploidy in mice with a large deletion in the p53 gene. Oncogene 9: 603–609
Jiang D, Lenardo MJ and Zuniga-Pflucker JC . (1996) p53 prevents maturation to the CD4+8+ stage of thymocytes differentiation in the absence of TcR rearrangement. J. Exp. Med. 183: 1923–1928
Nacht M, Strasser A, Chan YR, Harris AW, Schlissel M, Bronson RT and Jacks T . (1996) Mutations in the p53 and SCID genes cooperate in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 10: 2055–2066
Guy R, Gafnovitch I, Rosenheimer N, Oron E, Dorogin A, Yefenof E and Zilberman Y . (1996) MHC non-restricted, CD95 independent apoptosis of immature thymocytes induced by thymic epithelial cells. Cell Death Differ. 3: 431–438
Zilberman Y, Katzav S, Yefenof E, Rosenheimer-Goudsmid N, Dorogin A and Guy R . (1999) Apoptosis of thymic lymphoma clones by thymic epithelial cells: a putative model for ‘death by neglect’. Immunol. Lett. 67: 95–104
Schreiber L, Sharabi Y, Schwartz D, Goldfinger N, Brodie C, Rotter V and Shoham J . (1996) Induction of apoptosis and p53 expression in immature thymocytes by direct interaction with thymic epithelial cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 44: 314–322
Reinke V and Lozano G . (1997) The p53 targets mdm2 and Fas are not required as mediators of apoptosis in vivo. Oncogene 15: 1527–1534
Nicolleti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F and Riccardi C . (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocytes apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 139: 271–279
Strasser A, Harris AW, Jaks T and Cory S . (1994) DNA damage can induce apoptosis in proliferating lymphoid cells via p53-independent mechanisms inhibitable by Bcl-2. Cell 73: 329–339
Haupt Y, Rowan S, Shaulian E, Vousden KH and Oren M . (1995) Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells by trans-activation-deficient p53. Genes Dev. 9: 2170–2183
Yewdell JW, Gannon JV and Lane DP . (1986) Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J. Virol. 59: 444–452
Ganon JV, Greaves R, Iggo R and Lane DP . (1990) Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 9: 1595–1602
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and Harris CC . (1991) p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 253: 49–53
Levine AJ, Momand J and Finlay CA . (1991) The p53 tumor suppressor gene. Nature 351: 453–456
Li R, Sutphin PD, Schwartz D, Matas D, Almog N, Wolkowicz R, Goldfinger N, Pei H, Prokocimer M and Rotter V . (1998) Mutant p53 protein expression interferes with p53-independent apoptotic pathways. Oncogene 16: 3269–3277
Aas T, Borresen A-L, Geisler S, Smith-Sorensen B, Johnsen H, Varhaug JE, Akslen LA and Lonning PE . (1996) Specific p53 mutations are associated with de novo resistance to doxorubicin in breast cancer patients. Nature Med. 2: 811–814
Blandino G, Levine AJ and Oren M . (1999) Mutant p53 gain of function: differential effects of different p53 mutants on resistance of cultured cells to chemotherapy. Oncogene 18: 477–485
Ben-David Y, Yefenof E and Kotler M . (1987) Clonal analysis of radiation leukemia virus-induced leukemic and preleukemic murine cells. Cancer Res. 47: 6590–6594
Glimcher LH, Kruisbeek AM, Paul WE and Green I . (1983) Functional activity of a transformed thymic epithelial cell line. Scand. J. Immunol. 17: 1–11
Acknowledgements
We thank A Dorogin for expert technical assistance. This study was supported by grants from The Israeli Ministry of Health and the Concern Foundation II, Los Angeles, California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by JC Reed
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenheimer-Goudsmid, N., Haupt, Y., Yefenof, E. et al. p53 and thymic ‘death by neglect’: thymic epithelial cell-induced apoptosis of CD4+8+ thymocytes is p53-independent. Cell Death Differ 7, 241–249 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400657
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400657