Abstract
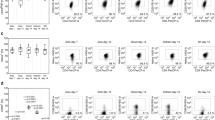
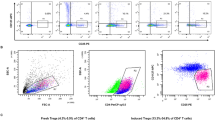
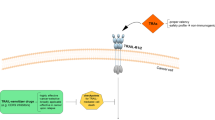
Deletion of T cells due to apoptosis induction is a regulatory mechanism in the human immune system that may be impaired in autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS). Involvement of the apoptosis-mediating CD95/CD95 ligand system in MS has been demonstrated. Here, we report that (auto)antigen-specific human T cells are not killed in vitro by soluble TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) although expressing death-inducing receptors, TRAIL receptor 1 (TRAIL-R1) and TRAIL-R2. Apoptosis was assessed by caspase activation and DNA fragmentation, receptor expression was detected by RT–PCR and flow cytometry. The (auto)antigen-specific T cells were also resistant to specific TRAIL-R1/TRAIL-R2-directed induction of apoptosis, indicating that coexpression of the truncated TRAIL-R3 and TRAIL-R4 in these T cells is not responsible for the observed resistance. Upon stimulation, levels of death-inducing TRAIL receptors decreased whereas TRAIL was up-regulated on the cell surface. In contrast to CD95, the role of TRAIL receptors in MS might not involve regulation of T cell vulnerability. Cell Death and Differentiation (2000) 7, 637–644
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- Trail-R:
-
TRAIL receptor
- MS:
-
Multiple Sclerosis
- EAE:
-
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- MBP:
-
myelin basic protein
- TT:
-
tetanus toxoid
References
Lenardo M, Ka-Ming Chan F, Hornung F, McFarland H, Siegel R, Wang J and Zheng L . (1999) Mature Lymphocyte Apoptosis–Immune Regulation in a Dynamic and Unpredictable Antigenic Environment. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17: 221–253
Pender MP . (1999) Activation-induced apoptosis of autoreactive and alloreactive T lymphocytes in the target organ as a major mechanism of tolerance. Immunol. Cell Biol 77: 216–223
Alderson MR, Tough TW, Davis-Smith T, Braddy S, Falk B, Schooley KA, Goodwin RG, Smith CA, Ramsdell F and Lynch DH . (1995) Fas ligand mediates activation-induced cell death in human T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 181: 71–77
Dhein J, Walczak H, Bèumler C, Debatin KM and Krammer PH . (1995) Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1(Fas/CD95). Nature 373: 438–441
Ju ST, Panka DJ, Cui H, Ettinger R, El-Khatib M, Sherr DH, Stanger BZ and Marshak-Rothstein A . (1995) Fas (CD95)/FasL interactions required for programmed cell death after T cell-activation. Nature 373: 444–448
D'Souza SD, Bonetti B, Balasingam V, Cashman NR, Barker PA, Troutt AB, Raine CS and Antel JP . (1996) Multiple sclerosis: Fas signaling in oligodendrocyte cell death. J. Exp. Med. 184: 2361–2370
Dowling P, Shang G, Raval S, Menonna J, Cook S and Husar W . (1996) Involvement of the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) receptor/ligand system in multiple sclerosis brain. J. Exp. Med. 184: 1513–1518
Zipp F, Krammer PH and Weller M . (1999) Immune (dys)regulation in multiple sclerosis: role of the CD95/CD95 ligand system. Immunol. Today 20: 550–554
Schmied M, Breitschopf H, Gold R, Zischler H, Rothe G, Wekerle H and Lassmann H . (1993) Apoptosis of T lymphocytes in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Evidence for programmed cell death as a mechanism to control inflammation in the brain. Am. J. Pathology 143: 446–452
Critchfield JM, Racke MK, Zuniga-Pflucker JC, Cannella B, Raine CS, Goverman J and Lenardo MJ . (1994) T cell deletion in high antigen dose therapy of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science 263: 1139–1143
Ishigami T, White CA and Pender MP . (1998) Soluble antigen therapy induces apoptosis of autoreactive T cells preferentially in the target organ rather than in the peripheral lymphoid organs. Eur. J. Immunol. 28: 1626–1635
Zhou T, Song L, Yang P, Wang Z, Lui D and Jope RS . (1999) Bisindolylmaleimide VIII faciltates Fas-mediated apoptosis and inhibits T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Nat. Med. 5: 42–48
Malipiero U, Frei K, Spanaus K-S, Agresti C, Lassmann H, Hahne M, Tschopp J, Eugster H-P and Fontana A . (1997) Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced encephalomyelitis is chronic/relapsing in perforin knockout mice, but monophasic in Fas- and Fas ligand-deficient lpr and gld mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 27: 3151–3160
Waldner H, Sobel RA, Howard E and Kuchroo VK . (1997) Fas- and FasL-deficient mice are resistant to induction of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 159: 3100–3103
Sabelko KA, Kelly KA, Nahm MH, Cross AH and Russell JH . (1997) Fas and Fas ligand enhance the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, but are not essential for immune privilege in the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 159: 3096–3099
Zipp F, Weller M, Calabresi PA, Frank JA, Bash CN, Dichgans J, McFarland H and Martin R . (1998) Increased serum levels of soluble CD95 (APO1/Fas) in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 43: 116–120
Zipp F, Otzelberger K, Dichgans J, Martin R and Weller M . (1998) Serum CD95 of multiple sclerosis patients protects from CD95-mediated apoptosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 86: 151–154
Ciusani E, Frigerio S, Gelati M, Corsini E, Dufour A, Nespolo A, La Mantia L, Milanese C, Massa G and Salmaggi A . (1998) Soluble Fas (Apo-1) levels in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 82: 5–12
Zang YCQ, Kozovska MM, Hong J, Li S, Mann S, Killian JM, Rivera VM and Zhang JZ . (1999) Impaired apoptotic deletion of myelin basic protein-reactive T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 29: 1692–1700
Macchi B, Matteucci C, Nocentini U, Caltagirone C and Mastino A . (1999) Impaired apoptosis in mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes of patients with multiple sclerosis. Neuroreport. 10: 399–402
Sabelko-Downes KA, Cross AH and Russell JH . (1999) Dual role for Fas ligand in the initiation of and recovery from experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 189: 1195–1205
Klas C, Debatin KM, Jonker RR and Krammer PH . (1993) Activation interferes with the APO-1 pathway in mature human T cells. Int. Immunol. 5: 625–630
Peter ME, Kischkel FC, Scheuerpflug CG, Medema JP, Debatin KM and Kramer PH . (1997) Resistance of cultured peripheral T cells towards activation-induced cell death involves a lack of recruitment of FLICE (MACH/caspase 8) to the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex. Eur. J. Immunol. 27: 1207–1212
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA and Goodwin RG . (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3: 673–682
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A and Ashkenazi A . (1996) Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 12687–12690
Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R, Ebner R, Ni J and Dixit VM . (1997) The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 276: 111–113
Sheridan JP, Marsters S, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray CL, Baker K, Wood WI, Goddard AD, Godowski P and Ashkenazi A . (1997) Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 277: 818–821
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, Timour MS, Gerhart MJ, Schooley KA, Smith CA, Goodwin RG and Rauch CT . (1997) TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J. 16: 5386–5397
Pan G, Ni J, Wei Y, Yu G, Gentz R and Dixit VM . (1997) An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 277: 815–818
Mongkolsapaya J, Cowper AE, Xu XN, Morris G, McMichael AJ, Bell J and Screaton GR . (1998) Lymphocyte inhibitor of TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand): a new receptor protecting lymphocyte from the death ligand TRAIL. J. Immunol. 160: 3–6
Degli-Esposti MA, Dougall WC, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Smith CA and Goodwin RG . (1997) The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kappaB and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity 7: 813–820
Marsters SA, Sheridan JP, Pitti RM, Huang A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Yuan J, Gurney A, Goddard AD, Godowski P and Ashkenzai A . (1997) A novel receptor for Apo2L/TRAIL contains a truncated death domain. Curr. Biol. 7: 1003–1006
Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K, Bodmer J-L, Hofman K, Kataoka T, Holler N and Tschopp J . (1997) TRAIL receptors 1(DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappaB. Immunity 7: 831–836
Jeremias I, Herr I, Boehler T and Debatin KM . (1998) TRAIL/Apo-2-ligand-induced apoptosis in human T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 28: 143–152
Marsters SA, Sheridan JP, Pitti RM, Huang A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Yuan J, Gurney A, Goddard AD, Godowski P and Ashkenazi A . (1996) Activation of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand is independent of FADD but blocked by CrmA. Curr. Biol. 6: 750–752
Rieger J, Naumann U, Glaser T, Ashkenazi A and Weller M . (1998) APO2 ligand: a novel lethal weapon against malignant glioma? FEBS Lett. 427: 124–128
Nagata S and Golstein P . (1995) The Fas death factor. Science 267: 1449–1456
Fisher GH, Rosenberg FJ, Straus SE, Dale JK, Middelton LA, Lin AY, Strober W, Lenardo MJ and Puck JM . (1995) Dominant interfering Fas gene mutations impair apoptosis in a human autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Cell 81: 935–946
Rieux-Laucat F, Le Deist F, Hivroz C, Roberts IAG, Debatin KM, Fischer A and de Villartay JP . (1995) Mutations in Fas associated with human lymphoproliferative syndrome and autoimmunity. Science 268: 1347–1349
Drappa J, Vaishnaw AK, Sullivan KE, Chu JL and Elkon KB . (1996) Fas gene mutations in the Canale-Smith syndrome, an inherited lymphoproliferative disorder associated with autoimmunity. N. Engl. J. Med. 335: 1643–1649
Le Deist F, Emile JF, Rieux-Laucat F, Benkerrou M, Roberts I, Brousse N and Fischer A . (1996) Clinical, immunological, and pathological consequences of Fas-deficient conditions. Lancet 348: 719–723
Hohlfeld R, Meinl E, Weber F, Zipp F, Schmidt S, Sotgiu S, Goebels N, Voltz R, Spuler S, Iglesias A and Wekerle H . (1995) The role of autoimmune T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 45: S33–S38
Martin R, McFarland HF and McFarlin DE . (1992) Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 10: 153–187
Degli-Esposti MA, Smolak PJ, Walczak H, Waugh J, Huang C-P, DuBose RF, Goodwin RG and Smith CA . (1997) Cloning and characterization of TRAIL-R3, a novel member of the emerging TRAIL receptor family. J. Exp. Med. 186: 1165–1170
Zipp F, Martin R, Lichtenfels R, Roth W, Dichgans J, Krammer PH and Weller M . (1997) Human autoreactive and foreign antigen-specific T cells resist apoptosis induced by soluble recombinant CD95 ligand. J. Immunol. 159: 2108–2115
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, Smith C, Smolak P, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT, Schuh JACL and Lynch DH . (1990) Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat. Med. 5: 157–163
Martinez LM, Alava MA, Gamen S, Kim KJ, Chuntharapai A, Pineiro A, Naval J and Anel A . (1998) Involvement of APO2 ligand/TRAIL in activation-induced death of Jurkat and human peripheral blood T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 28: 2714–2725
Mariani SM and Krammer PH . (1998) Differential regulation of TRAIL and CD95 ligand in transformed cells of the T and B lymphocyte lineage. Eur. J. Immunol. 28: 973–982
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AMJ, Matzku S, Müller P, Falk W, Debatin KM and Krammer PH . (1989) Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 245: 301–305
Riddell SR and Greenberg PD . (1990) The use of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies to clone and expand human antigen-specific T cells. J. Immunol. Methods 128: 189–201
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F and Riccardi C . (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 139: 271–279
Acknowledgements
We thank Ulrike Grieger, Heiko Stahl and Eva Rieser for expert technical assistance and Orhan Aktas for help with preparing the manuscript. F Zipp was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft ZI 448/7-1, the Gemeinnützige Hertie-Stiftung, and the Deutsche Multiple Sklerose-Gesellschaft. H Walczak received a fellowship from the Bundesministerium für Forschung und Technologie (AIDS-Stipendium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by ML Gougeon
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wendling, U., Walczak, H., Dörr, J. et al. Expression of TRAIL receptors in human autoreactive and foreign antigen-specific T cells. Cell Death Differ 7, 637–644 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400692
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400692
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Apoptosis of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes: a new immune checkpoint mechanism
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2019)
-
Immunotherapy with liposome-bound TRAIL overcomes partial protection to soluble TRAIL-induced apoptosis offered by down-regulation of Bim in leukemic cells
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2015)
-
TRAIL Death Receptor-4, Decoy Receptor-1 and Decoy Receptor-2 Expression on CD8+ T Cells Correlate with the Disease Severity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2010)
-
Tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in central nervous system inflammation
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2009)
-
The effect of TRAIL molecule on cell viability in in vitro beta cell culture
Acta Diabetologica (2007)