Abstract
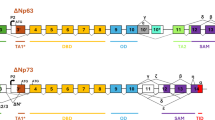
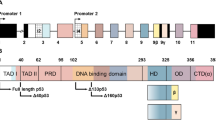
Inactivation of the tumour suppressor p53 is the most common defect in cancer cells. p53 is a sequence specific transcription factor that is activated in response to various forms of genotoxic stress to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Induction of p53 is subjected to complex and strict control through several pathways, as it will often determine cellular fate. The p73 protein shares strong structural and functional similarities with p53 such as the potential to activate p53 responsive genes and the ability to induce apoptosis. In addition to alternative splicing at the carboxyl terminus which yields several p73 isoforms, a p73 variant lacking the N-terminal transactivation domain (ΔNp73) was described in mice. In this study, we report the cloning and characterisation of the human ΔNp73 isoforms, their regulation by p53 and their possible role in carcinogenesis. As in mice, human ΔNp73 lacks the transactivation domain and starts with an alternative exon (exon 3′). Its expression is driven by a second promoter located in a genomic region upstream of this exon, supporting the idea of two independently regulated proteins, derived from the same gene. As anticipated, ΔNp73 is capable of regulating TAp73 and p53 function since it is able to block their transactivation activity and their ability to induce apoptosis. Interestingly, expression of the ΔNp73 is strongly up-regulated by the TA isoforms and by p53, thus creating a feedback loop that tightly regulates the function of TAp73 and more importantly of p53. The regulation of ΔNp73 is exerted through a p53 responsive element located on the ΔN promoter. Expression of ΔNp73 not only regulates the function of p53 and TAp73 but also shuts off its own expression, once again finely regulating the whole system. Our data also suggest that increased expression of ΔNp73, functionally inactivating p53, could be involved in tumorogenesis. An extensive analysis of the expression pattern of ΔNp73 in primary tumours would clarify this issue.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ΔN:
-
amino-terminus deleted
- TA:
-
transactivation
- DBD:
-
DNA-binding domain
- OD:
-
oligomerisation domain
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's Modified essential Medium
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
References
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC . 1991 p53 mutations in human cancers Science 253: 49–53
Hollstein M, Shomer B, Greenblatt M, Soussi T, Hovig E, Montesano R, Harris CC . 1996 Somatic point mutations in the p53 gene of human tumors and cell lines: updated compilation Nucleic Acids Res. 24: 141–146
Ko LJ, Prives C . 1996 p53: puzzle and paradigm Genes Dev. 10: 2438–2451
Levine AJ . 1997 p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division Cell 89: 1175–1184
Choisy-Rossi C, Yonish-Rouach E . 1998 Apoptosis and the cell cycle: the p53 connection Cell Death Differ. 5: 129–131
el-Deiry WS . 1998 Regulation of p53 downstream genes Semin. Cancer Biol. 8: 345–357
Prives C, Hall PA . 1999 The p53 pathway J. Pathol. 187: 112–126
Oren M . 1999 Regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein J. Biol. Chem. 274: 8371–8374
Lohrum MA, Vousden KH . 1999 Regulation and activation of p53 and its family members Cell Death Differ. 6: 1162–1168
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Lelias JM, Dumont X, Ferrara P, McKeon F, Caput D . 1997 Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers Cell 90: 809–819
Yang A, McKeon F . 2000 P63 and P73: P53 mimics, menaces and more Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1: 199–207
Levrero M, De Laurenzi V, Costanzo A, Gong J, Wang JY, Melino G . 2000 The p53/p63/p73 family of transcription factors: overlapping and distinct functions J. Cell Sci. 113: 1661–1670
Levrero M, De Laurenzi V, Costanzo A, Gong J, Melino G, Wang JY . 1999 Structure, function and regulation of p63 and p73 Cell Death Differ. 6: 1146–1153
De Laurenzi V, Catani MV, Terrinoni A, Corazzari M, Melino G, Costanzo A, Levrero M, Knight RA . 1999 Additional complexity in p73: induction by mitogens in lymphoid cells and identification of two new splicing variants epsilon and zeta Cell Death Differ. 6: 389–390
Ikawa S, Nakagawara A, Ikawa Y . 1999 p53 family genes: structural comparison, expression and mutation Cell Death Differ. 6: 1154–1161
Kaelin Jr WG . 1999 The p53 gene family Oncogene 18: 7701–7705
Yang A, Walker N, Bronson R, Kaghad M, Oosterwegel M, Bonnin J, Vagner C, Bonnet H, Dikkes P, Sharpe A, McKeon F, Caput D . 2000 p73-deficient mice have neurological, pheromonal and inflammatory defects but lack spontaneous tumours Nature 404: 99–103
De Laurenzi V, Raschella G, Barcaroli D, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Ranalli M, Catani MV, Tanno B, Costanzo A, Levrero M, Melino G . 2000 Induction of neuronal differentiation by p73 in a neuroblastoma cell line J. Biol. Chem. 275: 15226–15231
Fang L, Lee SW, Aaronson SA . 1999 Comparative analysis of p73 and p53 regulation and effector functions J. Cell Biol. 147: 823–830
Knight RA . 1999 p53 and its younger siblings Cell Death Differ. 6: 1143
Jost CA, Marin MC, Kaelin Jr WG . 1997 p73 is a simian [correction of human] p53-related protein that can induce apoptosis Nature 389: 191–194
Zhu J, Jiang J, Zhou W, Chen X . 1998 The potential tumor suppressor p73 differentially regulates cellular p53 target genes Cancer Res. 58: 5061–5065
Miller FD, Pozniak CD, Walsh GS . 2000 Neuronal life and death: an essential role for the p53 family Cell Death Differ. 7: 880–888
Strano S, Munarriz E, Rossi M, Cristofanelli B, Shaul Y, Castagnoli L, Levine AJ, Sacchi A, Cesareni G, Oren M, Blandino G . 2000 Physical and functional interaction between p53 mutants and different isoforms of p73 J. Biol. Chem. 275: 29503–29512
Ueda Y, Hijikata M, Takagi S, Chiba T, Shimotohno K . 1999 New p73 variants with altered C-terminal structures have varied transcriptional activities Oncogene 18: 4993–4998
Gong JG, Costanzo A, Yang HQ, Melino G, Kaelin Jr WG, Levrero M, Wang JY . 1999 The tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage Nature 399: 806–809
Agami R, Blandino G, Oren M, Shaul Y . 1999 Interaction of c-Abl and p73alpha and their collaboration to induce apoptosis Nature 399: 809–813
Yuan ZM, Shioya H, Ishiko T, Sun X, Gu J, Huang YY, Lu H, Kharbanda S, Weichselbaum R, Kufe D . 1999 p73 is regulated by tyrosine kinase c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage Nature 399: 814–817
Corn PG, Kuerbitz SJ, van Noesel MM, Esteller M, Compitello N, Baylin SB, Herman JG . 1999 Transcriptional silencing of the p73 gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and Burkitt's lymphoma is associated with 5′ CpG island methylation Cancer Res. 59: 3352–3356
Kawano S, Miller CW, Gombart AF, Bartram CR, Matsuo Y, Asou H, Sakashita A, Said J, Tatsumi E, Koeffler HP . 1999 Loss of p73 gene expression in leukemias/lymphomas due to hypermethylation Blood 94: 1113–1120
Stirewalt DL, Clurman B, Appelbaum FR, Willman CL, Radich JP . 1999 p73 mutations and expression in adult de novo acute myelogenous leukemia Leukemia 13: 985–990
Casciano I, Ponzoni M, Lo Cunsolo C, Tonini GP, Romani M . 1999 Different p73 splicing variants are expressed in distinct tumour areas of a multifocal neuroblastoma Cell Death Differ. 6: 391–393
De Laurenzi V, Costanzo A, Barcaroli D, Terrinoni A, Falco M, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Levrero M, Melino G . 1998 Two new p73 splice variants, gamma and delta, with different transcriptional activity J. Exp. Med. 188: 1763–1768
Chi SW, Ayed A, Arrowsmith CH . 1999 Solution structure of a conserved C-terminal domain of p73 with structural homology to the SAM domain EMBO J. 18: 4438–4445
Tschan MP, Grob TJ, Peters UR, De Laurenzi V, Huegli B, Kreuzer KA, Schmidt CA, Melino G, Fey MF, Tobler A, Cajot JF . 2000 Enhanced p73 expression during differentiation and complex p73 isoforms in myeloid leukemia Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277: 62–65
Nozaki M, Tada M, Kashiwazaki H, Hamou MF, Diserens AC, Shinohe Y, Sawamura Y, Iwasaki Y, de Tribolet N, Hegi ME . 2001 p73 is not mutated in meningiomas as determined with a functional yeast assay but p73 expression increases with tumor grade Brain Pathol. 11: 296–305
Ito Y, Takeda T, Wakasa K, Tsujimoto M, Sakon M, Matsuura N . 2001 Expression of p73 and p63 proteins in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: p73 overexpression is inversely correlated with biological aggressiveness Int. J. Mol. Med. 8: 67–71
Liu ZG, Baskaran R, Lea-Chou ET, Wood LD, Chen Y, Karin M, Wang JY . 1996 Three distinct signalling responses by murine fibroblasts to genotoxic stress Nature 384: 273–276
Senoo M, Tsuchiya I, Matsumura Y, Mori T, Saito Y, Kato H, Okamoto T, Habu S . 2001 Transcriptional dysregulation of the p73L/p63/p51/p40/KET gene in human squamous cell carcinomas: expression of Delta Np73L, a novel dominant-negative isoform, and loss of expression of the potential tumour suppressor p51 Br. J. Cancer 84: 1235–1241
El-Naggar AK, Lai S, Clayman GL, Mims B, Lippman SM, Coombes M, Luna MA, Lozano G . 2001 p73 gene alterations and expression in primary oral and laryngeal squamous carcinomas Carcinogenesis 22: 729–735
Matos P, Isidro G, Vieira E, Lacerda AF, Martins AG, Boavida MG . 2001 P73 expression in neuroblastoma: a role in the biology of advanced tumors? Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 18: 37–46
De Laurenzi V, Melino G . 2000 Evolution of functions within the p53/p63/p73 family Ann NY Acad. Sci. 926: 90–100
Scaruffi P, Casciano I, Masiero L, Basso G, Romani M, Tonini GP . 2000 Lack of p73 expression in mature B-ALL and identification of three new splicing variants restricted to pre B and C-ALL indicate a role of p73 in B cell ALL differentiation Leukemia 14: 518–519
Pozniak CD, Radinovic S, Yang A, McKeon F, Kaplan DR, Miller FD . 2000 An anti-apoptotic role for the p53 family member, p73, during developmental neuron death Science 289: 304–306
Zwahlen D, Tschan MP, Grob TJ, Peters UR, Fink D, Haenggi W, Altermatt HJ, Cajot JF, Tobler A, Fey MF, Aebi S . 2000 Differential expression of p73 splice variants and protein in benign and malignant ovarian tumours Int. J. Cancer 88: 66–70
Peters UR, Tschan MP, Kreuzer KA, Baskaynak G, Lass U, Tobler A, Fey MF, Schmidt CA . 1999 Distinct expression patterns of the p53-homologue p73 in malignant and normal hematopoiesis assessed by a novel real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay and protein analysis Cancer Res. 59: 4233–4236
Fillippovich I, Sorokina N, Gatei M, Haupt Y, Hobson K, Moallem E, Spring K, Mould M, McGuckin MA, Lavin MF, Khanna MK . 2001 Transactivation-deficient p73alpha (p73Deltaexon2) inhibits apoptosis and competes with p53 Oncogene 20: 514–522
Marchuk D, Drumm M, Saulino A, Collins FS . 1991 Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products Nucleic Acids Res. 19: 1154
Kalejta RF, Shenk T, Beavis AJ . 1997 Use of a membrane-localized green fluorescent protein allows simultaneous identification of transfected cells and cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry Cytometry 29: 286–291
Acknowledgements
The HaCaT cell line was a kind gift from N. Fusenig (Heidelberg, Germany). We would like to thank Dr. R. Kalejta and Dr. A.J. Beavis for the GFP-spectrin expression vector. This work was supported by grants from the Swiss National Foundation (3200-053596.98), from the Swiss Cancer League (KFS 156-9-1995) and the Ursula-Hecht-Stiftung. Telethon grant E872, AIRC, MURST and EU grant QLGI-1999-00739 to G Melino. Telethon grant E1224 to V De Laurenzi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by RA Knight
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grob, T., Novak, U., Maisse, C. et al. Human ΔNp73 regulates a dominant negative feedback loop for TAp73 and p53. Cell Death Differ 8, 1213–1223 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400962
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400962
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Requirement for TP73 and genetic alterations originating from its intragenic super-enhancer in adult T-cell leukemia
Leukemia (2022)
-
Hexokinase 3 enhances myeloid cell survival via non-glycolytic functions
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
p73 isoforms meet evolution of metastasis
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2022)
-
Tissue-specific expression of p73 and p63 isoforms in human tissues
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
A carbazole compound, 9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3-carbaldehyde, plays an antitumor function through reactivation of the p53 pathway in human melanoma cells
Cell Death & Disease (2021)