Abstract
Caspase-14 is a recent addition to the caspase family of aspartate proteases involved in apoptotic processes. Human caspase-14 appears to be only weakly processed during apoptosis, and it does not cleave classical caspase substrates. Post partum, caspase-14 is prominently expressed by human keratinocytes and reportedly participates in terminal differentiation of complex epithelia. Here we provide evidence challenging the view that caspase-14 expression or processing is linked exclusively to terminal keratinocyte differentiation. We demonstrate that caspase-14 expression extended to multiple cell lines derived from simple epithelia of the breast, prostate, and stomach. In keratinocytes and breast epithelial cells, caspase-14 expression was upregulated in high-density cultures and during forced suspension culture. These effects were primarily due to transcriptional activation as indicated by reporter gene assays using a 2 kb caspase-14 promoter fragment. Importantly, caspase-14 was not cleaved during forced suspension culture of either cell type although this treatment induced caspase-dependent apoptosis (anoikis). Forced expression of caspase-14 in immortalized human keratinocytes had no effect on cell death in forced suspension nor was the transfected caspase-14 processed in this setting. In contrast to postconfluent and forced suspension culture, terminal differentiation of keratinocytes induced in vitro by Ca2+ treatment was not associated with increased caspase-14 expression or promoter activity. Our results indicate that (1) caspase-14 is expressed not only in complex but also simple epithelia; (2) cells derived from complex and simple epithelia upregulate caspase-14 expression in conditions of high cell density or lack of matrix interaction and; (3) in both cell types this phenomenon is due to transcriptional regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- IL-1β:
-
interleukin-1beta
- ICE:
-
interleukin-1β converting enzyme
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulphate
- Ac-DEVD-CHO:
-
N-acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp aldehyde
- LD:
-
low density
- HD:
-
high density
- BCC:
-
basal cell carcinoma
- SCC:
-
squamous cell carcinoma
- BSA-FAF:
-
bovine serum albumin-fatty acid-free
- RLB:
-
reporter lysis buffer
References
Alnemri ES . 1997 Mammalian cell death proteases: a family of highly conserved aspartate specific cysteine proteases J. Cell Biochem. 64: 33–42
Cohen GM . 1997 Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis Biochem. J. 326: 1–16
Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC . 1997 Programmed cell death in animal development Cell 88: 347–354
Ellis HM, Horvitz HR . 1986 Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans Cell 44: 817–829
Muzio M, Stockwell BR, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM . 1998 An induced proximity model for caspase-8 activation J. Biol. Chem. 273: 2926–2930
Yamin TT, Ayala JM, Miller DK . 1996 Activation of the native 45-kDa precursor form of interleukin-1- converting enzyme J. Biol. Chem. 271: 13273–13282
Yang X, Chang HY, Baltimore D . 1998 Autoproteolytic activation of pro- caspases by oligomerization Mol. Cell 1: 319–325
Fraser A, Evan G . 1996 A license to kill Cell 85: 781–784
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM . 1997 Caspases: intracellular signaling by proteolysis Cell 91: 443–446
Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA . 1997 Caspases: killer proteases Trends Biochem. Sci. 22: 299–306
Steller H . 1995 Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide Science 267: 1445–1449
Wolf BB, Green DR . 1999 Suicidal tendencies: apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases J. Biol. Chem. 274: 20049–20052
Wilson KP, Black JA, Thomson JA, Kim EE, Griffith JP, Navia MA, Murcko MA, Chambers SP, Aldape RA, Raybuck SA, et al . 1994 Structure and mechanism of interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme Nature 370: 270–275
Wong WW . 1998 ICE family proteases in inflammation and apoptosis Agents Actions Suppl 49 5–13
Hu S, Snipas SJ, Vincenz C, Salvesen G, Dixit VM . 1998 Caspase-14 is a novel developmentally regulated protease J. Biol. Chem. 273: 29648–29653
Ahmad M, Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Mukattash R, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES . 1998 Identification and characterization of murine caspase-14, a new member of the caspase family Cancer Res. 58: 5201–5205
Van de Craen M, Van Loo G, Pype S, Van Criekinge W, Van den brande I, Molemans F, Fiers W, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P . 1998 Identification of a new caspase homologue: caspase-14 Cell Death Differ. 5: 838–846
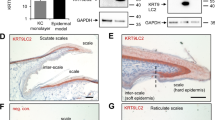
Eckhart L, Declercq W, Ban J, Rendl M, Lengauer B, Mayer C, Lippens S, Vandenabeele P, Tschachler E . 2000 Terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes and stratum corneum formation is associated with caspase-14 activation J. Invest. Dermatol. 115: 1148–1151
Gandarillas A . 2000 Epidermal differentiation, apoptosis, and senescence: common pathways? Exp. Gerontol. 35: 53–62
Candi E, Melino G, Mei G, Tarcsa E, Chung SI, Marekov LN, Steinert PM . 1995 Biochemical, structural, and transglutaminase substrate properties of human loricrin, the major epidermal cornified cell envelope protein J. Biol. Chem. 270: 26382–26390
Takahashi H, Aoki N, Nakamura S, Asano K, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Iizuka H . 2000 Cornified cell envelope formation is distinct from apoptosis in epidermal keratinocytes J. Dermatol. Sci. 23: 161–169
Weil M, Raff MC, Braga VM . 1999 Caspase activation in the terminal differentiation of human epidermal keratinocytes Curr. Biol. 9: 361–364
Bright RK, Vocke CD, Emmert-Buck MR, Duray PH, Solomon D, Fetsch P, Rhim JS, Linehan WM, Topalian SL . 1997 Generation and genetic characterization of immortal human prostate epithelial cell lines derived from primary cancer specimens Cancer Res. 57: 995–1002
Jost M, Gasparro FP, Jensen PJ, Rodeck U . 2001 Keratinocyte apoptosis induced by ultraviolet B radiation and CD95 ligation–differential protection through epidermal growth factor receptor activation and Bcl-x(L) expression J. Invest. Dermatol. 116: 860–866
Jost M, Huggett TM, Kari C, Rodeck U . 2001 Matrix-independent Survival of Human Keratinocytes through an EGF Receptor/MAPK-Kinase-dependent Pathway Mol. Biol. Cell 12: 1519–1527
Lippens S, Kockx M, Knaapen M, Mortier L, Polakowska R, Verheyen A, Garmyn M, Zwijsen A, Formstecher P, Huylebroeck D, Vandenabeele P, Declercq W . 2000 Epidermal differentiation does not involve the pro-apoptotic executioner caspases, but is associated with caspase-14 induction and processing Cell Death Differ. 7: 1218–1224
Poumay Y, Herphelin F, Smits P, De Potter IY, Pittelkow MR . 1999 High-cell-density phorbol ester and retinoic acid upregulate involucrin and downregulate suprabasal keratin 10 in autocrine cultures of human epidermal keratinocytes Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun. 2: 138–144
Vicanova J, Boelsma E, Mommaas AM, Kempenaar JA, Forslind B, Pallon J, Egrud T, Koerten HK, Ponec M . 1998 Normalization of epidermal calcium distribution profile in reconstructed human epidermis is related to improvement of terminal differentiation and stratum corneum barrier formation J. Invest. Dermatol. 111: 97–106
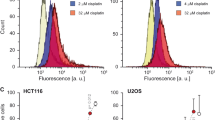
Mueller S, Cadenas E, Schonthal AH . 2000 p21WAF1 regulates anchorage-independent growth of HCT116 colon carcinoma cells via E-cadherin expression Cancer Res. 60: 156–163
Poumay Y, Pittelkow MR . 1995 Cell density and culture factors regulate keratinocyte commitment to differentiation and expression of suprabasal K1/K10 keratins J. Invest. Dermatol. 104: 271–276
Hague A, Hicks DJ, Bracey TS, Paraskeva C . 1997 Cell-cell contact and specific cytokines inhibit apoptosis of colonic epithelial cells: growth factors protect against c-myc-independent apoptosis Br. J. Cancer 75: 960–968
Schon M, Klein CE, Hogenkamp V, Kaufmann R, Wienrich BG, Schon MP . 2000 Basal-cell adhesion molecule (B-CAM) is induced in epithelial skin tumors and inflammatory epidermis, and is expressed at cell-cell and cell-substrate contact sites J. Invest. Dermatol. 115: 1047–1053
McNeill H, Jensen PJ . 1990 A high-affinity receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator on human keratinocytes: characterization and potential modulation during migration Cell Regul. 1: 843–852
Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE . 1988 Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line J. Cell Biol. 106: 761–771
Rodeck U, Herlyn M, Menssen HD, Furlanetto RW, Koprowsk H . 1987 Metastatic but not primary melanoma cell lines grow in vitro independently of exogenous growth factors Int. J. Cancer 40: 687–690
Simmen RC, Chung TE, Imataka H, Michel FJ, Badinga L, Simmen FA . 1999 Trans-activation functions of the Sp-related nuclear factor, basic transcription element-binding protein, and progesterone receptor in endometrial epithelial cells Endocrinology 140: 2517–2525
Baffa R, Gomella LG, Vecchione A, Bassi P, Mimori K, Sedor J, Calviello CM, Gardiman M, Minimo C, Strup SE, McCue PA, Kovatich AJ, Pagano F, Huebner K, Croce CM . 2000 Loss of FHIT expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder Am. J. Pathol. 156: 419–424
Ritter PM, Marti A, Blanc C, Baltzer A, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Jaggi R . 2000 Nuclear localization of procaspase-9 and processing by a caspase-3-like activity in mammary epithelial cells Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 79: 358–364
Lechardeur D, Drzymala L, Sharma M, Zylka D, Kinach R, Pacia J, Hicks C, Usmani N, Rommens JM, Lukacs GL . 2000 Determinants of the nuclear localization of the heterodimeric DNA fragmentation factor (ICAD/CAD) J. Cell. Biol. 150: 321–334
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant AG14357 (to ES Alnemri), and CA81008 (to U Rodeck). SM Srinivasula is a special fellow of the Leukemia & Limphoma Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by G Nunez
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pistritto, G., Jost, M., Srinivasula, S. et al. Expression and transcriptional regulation of caspase-14 in simple and complex epithelia. Cell Death Differ 9, 995–1006 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401061
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401061
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A Review on Caspases: Key Regulators of Biological Activities and Apoptosis
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Role of syntaxin3 an apical polarity protein in poorly polarized keratinocytes: regulation of asymmetric barrier formations in the skin epidermis
Cell and Tissue Research (2023)
-
Transcriptome changes in undifferentiated Caco-2 cells exposed to food-grade titanium dioxide (E171): contribution of the nano- and micro- sized particles
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Phytoconstituents as apoptosis inducing agents: strategy to combat cancer
Cytotechnology (2016)
-
Caspase 14 does not influence intestinal epithelial cell differentiation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2013)