Abstract
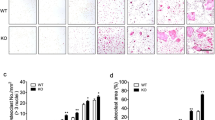
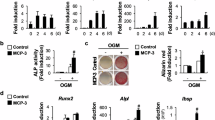
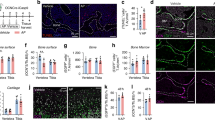
Recent evidence indicates that the decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) of the TNF receptor superfamily, which initially though prevents cytokine responses of FasL, LIGHT and TL1A by binding and neutralization, can modulate monocyte function through reverse signaling. We show in this work that DcR3 can induce osteoclast formation from human monocytes, murine RAW264.7 macrophages, and bone marrow cells. DcR3-differentiated cells exhibit characteristics unique for osteoclasts, including polynuclear giant morphology, bone resorption, TRAP, CD51/61, and MMP-9 expression. Consistent with the abrogation of osteoclastogenic effect of DcR3 by TNFR-Fc, DcR3 treatment can induce osteoclastogenic cytokine TNF-α release through ERK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. We conclude that DcR3 via coupling reverse signaling of ERK and p38 MAPK and stimulating TNF-α synthesis is a critical regulator of osteoclast formation. This action of DcR3 might play an important role in significant osteoclastic activity in osteolytic bone metastases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- DcR3:
-
decoy receptor 3
- M-CSF:
-
macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- RANKL:
-
receptor for activation of NF-κB ligand
- TRAP:
-
tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase
- DCs:
-
dendritic cells
References
Quinn JM, McGee JO and Athanasou NA (1998) Human tumour-associated macrophages differentiate into osteoclastic bone-resorbing cells. J. Pathol. 184: 31–36
Kobayashi K, Takahashi N, Jimi E, Udagawa N, Takami M, Kotake S, Nakagawa N, Kinosaki M, Yamaguchi K, Shima N, Yasuda H, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Martin TJ and Suda T (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-α stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL–RANK interaction. J. Exp. Med. 191: 275–285
Suda T, Takahashi N and Martin TJ (1992) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation. Endocr. Rev. 13: 66–80
Udagawa N, Takahashi N and Akatsu T (1990) Origin of osteoclasts: mature monocytes and macrophages are capable of differentiating into osteoclasts under a suitable microenvironment prepared by bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 7260–7264
Hofbauer LC, Khosla S, Dunstan CR, Lacey DL, Boyle WJ and Riggs L (2000) The roles of osteoprotegerin and osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone resorption. J. Bone Miner. Res. 15: 2–12
Li X, Udagawa N, Itoh K, Suda K, Murase Y, Nishihara T, Suda T and Takahashi N (2002) p38 MAPK-mediated signals are required for inducing osteoclast differentiation but not for osteoclast function. Endocrinology 143: 3105–3113
Hsu H, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Solovyev I, Colombero A, Timms E, Tan HL, Elliott G, Kelley MJ, Sarosi I, Wang L, Xia XZ, Elliott R, Chiu L, Black T, Scully S, Capparelli C, Morony S, Shimamoto G, Bass MB and Boyle WJ (1999) Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 3540–3545
Teitelbaum SL (2000) Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science 289: 1504–1508
Roodman GD (1999) Cell biology of the osteoclast. Exp. Hematol. 27: 1229–1241
Uy HL, Dallas M, Calland JW, Boyce BF, Mundy GR and Roodman GD (1995) Use of an in vivo model to determine the effects of interleukin-1 on cells at different stages in the osteoclast lineage. J. Bone Miner. Res. 10: 295–301
Tamura T, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Miyaura C, Tanaka S, Yamada Y, Koishihara Y, Ohsugi Y, Kumaki K, Taga T, Kishimoto T and Suda T (1993) Soluble interleukin-6 receptor triggers osteoclast formation by interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 11924–11928
Fujikawa Y, Sabokbar A, Neale SD, Itonaga I, Torisu T and Athanasou NA (2001) The effect of macrophage-colony stimulating factor and other humoral factors (interleukin-1, -3, -6, and -11, tumor necrosis factor-α, and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor) on human osteoclast formation from circulating cells. Bone 28: 261–267
Quinn JM, Itoh K, Udagawa N, Hausler K, Yasuda H, Shima N, Mizuno A, Higashio K, Takahashi N, Suda T, Martin TJ and Gillespie MT (2001) Transforming growth factor beta affects osteoclast differentiation via direct and indirect actions. J. Bone Miner. Res. 16: 1787–1794
Taranta A, Brama M, Teti A, De luca V, Scandurra R, Spera G, Agnusdei D, Termine JD and Migliaccio S (2002) The selective estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene regulates osteoclast and osteoblast activity in vitro. Bone 30: 368–376
Azuma Y, Kaji K, Katogi R, Takeshita S and Kudo A (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-1α induces differentiation of and bone resorption by osteoclasts. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 4858–4864
Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Maruyama M, Osada H and Tsujimoto M (2000) Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is crucial in osteoclastogenesis induced by tumor necrosis factor. FEBS Lett. 486: 23–28
Zhang YH, Heulsmann A, Tondravi MM, Mukherjee A and Abu-Amer Y (2001) Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF) stimulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via coupling of TNF type 1 receptor and RANK signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 563–568
Abu-Amer Y, Ross FP, Edwards J and Teitelbaum SL (1997) Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated osteoclastogenesis is mediated by tumor necrosis factor via its P55 receptor. J. Clin. Invest. 100: 1557–1565
Abu-Amer Y, Erdmann J, Alexopoulou L, Kollias G and Teitelbaum SL (2000) Tumor necrosis factor receptors types 1 and 2 differentially regulate osteoclastogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 27307–27310
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Lawrence DA, Roy M, Kischkel FC, Dowd P, Huang A, Donahue CJ, Sherwood SW, Baldwin DT, Godowski PJ, Wood WI, Gurney AL, Hillan KJ, Cohen RL, Goddard AD, Botstein D and Ashkenazi A (1998) Genomic amplification of a decoy receptor for Fas ligand in lung and colon cancer. Nature 396: 699–703
Yu KY, Kwon B, Ni J, Zhai Y, Ebner R and Kwon BX (1999) A newly identified member of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TR6) suppresses LIGHT-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 13733–13736
Migone TS, Zhang J, Luo X, Zhuang L, Chen C, Hu B, Hong JS, Perry JW, Chen SF, Zhou JX, Cho YH, Ullrich S, Kanakaraj P, Carrell J, Boyd E, Olsen HS, Hu G, Pukac L, Liu D, Ni J, Kim S, Gentz R, Feng P, Moore PA, Ruben SM and Wei P (2002) TL1A is a TNF-like ligand for DR3 and TR6/DcR3 and functions as a T cell costimulator. Immunity 16: 479–492
Bai C, Connolly B, Metzker ML, Hilliard CA, Liu X, Sandig V, Soderman A, Galloway SM, Liu Q, Austin CP and Caskey CT (2000) Overexpression of M68/DcR3 in human gastrointestinal tract tumors independent of gene amplification and its location in a four-gene cluster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 1230–1235
Tsuji S, Hosotani R, Yonehara S, Masui T, Tulachan SS, Nakajima S, Kobayashi H, Koizumi M, Toyoda E, Ito D, Kami K, Mori T, Fujimoto K, Doi R and Imamura M (2003) Endogenous decoy receptor 3 blocks the growth inhibition signals mediated by Fas ligand in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 106: 17–25
Roth W, Isenmann S, Nakamura M, Platten M, Wick W, Kleihues P, Bahr M, Ohgaki H, Ashkenazi A and Weller M (2001) Soluble decoy receptor 3 is expressed by malignant gliomas and suppresses CD95 ligand-induced apoptosis and chemotaxis. Cancer Res. 61: 2759–2765
Ohshima K, Haraoka S, Sugihara M, Suzumiya J, Kawasaki C, Kanda M and Kikuchi M (2000) Amplification and expression of a decoy receptor for Fas ligand (DcR3) in virus (EBV or HTLV-1) associated lymphomas. Cancer Lett. 160: 89–97
Mild G, Bachmann F, Boulay JL, Glatz K, Laffer U, Lowy A, Metzger U, Reuter J, Terracciano L, Hermann R and Rochitz C (2002) DcR3 locus is a predictive marker for 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 102: 254–257
Wu Y, Han B, Sheng H, Lin M, Moore PA, Zhang J and Wu J (2003) Clinical significance of detecting elevated serum DcR3/TR6/M68 in malignant tumor patients. Int. J. Cancer 105: 724–732
Shi GX, Luo HY, Wan XC, Salcedo TW, Zhang J and Wu JP (2002) Mouse T cells receive costimulatory signals from LIGHT, a TNF family member. Blood 100: 3279–3286
Chen MC, Hwang MJ, Chou YC, Chen WH, Cheng G, Nakano H, Luh TY, Mai SC and Hsieh SL (2003) The role of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in lymphotoxin-β receptor-mediated cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 16073–16081
Yue TL, Ni J, Romanic AM, Gu JL, Keller P, Wang C, Kumar S, Yu GL, Hart TK, Wang X, Xia Z, Dewolf WE and Feuerstein GZ (1999) TL1, a novel tumor necrosis factor-like cytokine, induces apoptosis in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 1479–1486
Yang CR, Hsieh SL, Teng CM, Ho FM, Su WL and Lin WW (2004) Soluble decoy receptor 3 induces angiogenesis by neutralization of TL1A, a cytokine belonging to TNF superfamily and exhibiting angiostatic action. Cancer Res., in press
Hsu TL, Chang YC, Chen SJ, Liu YJ, Chiu AW, Chio CC, Chen L and Hsieh SL (2002) Modulation of dendritic cells differentiation and maturation by decoy receptor 3. J. Immunol. 168: 4846–4853
Chang YC, Hsu TL, Lin HH, Chio CC, Chiu AW, Chen NJ, Lin CH and Hsieh SL (2004) Modulation of macrophage differentiation and activation by decoy receptor 3. J. Leukoc. Biol., in press
Hsu MJ, Lin WW, Tsao WC, Chang YC, Hsu TL, Chiu AW, Chio CC and Hsieh SL (2004) Enhanced adhesion of monocytes via reverse signaling triggered by decoy recaptor 3. Exp. Cell Res. 292: 241–251
Cayabyab M, Phillips JH and Lanier LL (1994) CD40 preferentially costimulates activation of CD4(+) T-lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 152: 1523–1531
Wiley SR, Goodwin RG and Smith CA (1996) Reverse signaling via CD30 ligand. J. Immunol. 157: 3635–3639
Eissner G, Kirchner S, Lindner H, Kolch W, Janosch P, Grell M, Scheurich P, Andreesen R and Holler E (2000) Reverse signaling through transmembrane TNF confers resistance to lipopolysaccharide in human monocytes and macrophages. J. Immunol. 164: 6193–6198
Suzuki I, Martin S, Boursalian TE, Beers C and Fink PJ (2000) Fas ligand costimulates the in vivo proliferation of CD8(+) T cells. J. Immunol. 165: 5537–5543
Julian M, Quinn M, Elliott J, Gillespie MT and Martin TJ (1998) A combination of osteoclast differentiation factor and macrophage-colony stimulating factor is sufficient for both human and mouse osteoclast formation in vitro. Endocrinology 139: 4424–4427
Lam J, Takeshita S, Barker JE, Kanagawa O, Ross FP and Teitelbaum SL (2000) TNF-α induces osteoclastogenesis by direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of RANK ligand. J. Clin. Invest. 106: 1481–1488
Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Saito T, Osada H and Tsujimoto M (2000) Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL). J. Biol. Chem. 275: 31155–31161
Miyazaki T, Katagiri H, Kanegae Y, Takayanagi H, Sawada Y, Yamamoto A, Pando MP, Asano T, Verma IM, Oda H, Nakamura K and Tanaka S (2000) Reciprocal role of ERK and NF-κB pathways in survival and activation of osteoclasts. J. Cell. Biol. 148: 333–342
Mauri DN, Ebner R, Montgomery RI, Kochel KD, Cheung TC, Yu GL, Ruben S, Murphy M, Eisenberg RJ, Cohen GH, Spear PG and Ware CF (1998) LIGHT, a new member of the TNF superfamily, and lymphotoxin alpha are ligands for herpesvirus entry mediator. Immunity 8: 21–30
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E, Gillespie MT and Martin TJ (1999) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr. Rev. 20: 345–357
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ, Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S, Hsu H, Sullivan J, Hawkins N, Davy E, Capparelli C, Eli A, Qian YX, Kaufman S, Sarosi I, Shalhoub V, Senaldi G, Guo J, Delaney J and Boyle WJ (1998) Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93: 165–176
Zou W, Hakim I, Tschoep K, Endres S and Bar-Shavit Z (2001) Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates RANK ligand stimulation of osteoclast differentiation by an autocrine mechanism. J. Cell. Biochem. 83: 70–83
Kong YY, Feige U, Sarosi I, Bolon B, Tafuri A, Morony S, Capparelli C, Li J, Elliott R, McCabe S, Wong T, Campagnuolo G, Moran E, Bogoch ER, Van G, Nguyen LT, Ohashi PS, Lacey DL, Fish E, Boyle WJ and Penninger JM (1999) Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature 402: 304–309
Menaa C, Reddy SV, Kurihara N, Maeda H, Anderson D, Cundy T, Cornish J, Singer FR, Bruder JM and Roodman GD (2000) Enhanced RANK ligand expression and responsivity of bone marrow cells in Paget’s disease of bone. J. Clin. Invest. 105: 1833–1838
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, Tomoyasu A, Yano K, Goto M, Murakami A, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Udagawa N, Takahashi N and Suda T (1998) Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 3597–3602
Chae HJ, Park RK, Chung HT, Kang JS, Kim MS, Choi DY, Bang BG and Kim HR (1997) Nitric oxide is a regulator or bone remodeling. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 49: 897–902
Zhu W, Downey JS, Gu J, Padova FD, Gram H and Han J (2000) Regulation of TNF expression by multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J. Immunol. 164: 6349–6358
Rutault K, Hazzalin CA and Mahadevan LC (2001) Combinations of ERK and p38 MAPK inhibitors ablate tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) mRNA induction. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 6666–6674
Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC and Hogan EL (1998) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-α gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J. Neurosci. 18: 1633–1641
Iotsova V, Caamano J, Lyo J, Yoang Y, Lewin A and Bravo R (1997) Osteopetrosis in mice lacking NF-κB1 and NF-κB2. Nat. Med. 3: 1285–1289
Jimi E, Nakamura I, Ikebe T, Akiyama S, Takahashi N and Suda T (1998) Activation of NF-κB is involved in the survival of osteoclasts promoted by interleukin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 8799–8805
Darnay BG, Ni J, Moore PS and Aggarwal BB (1999) Activation of NF-kappa B by RANK requires tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 and NF-kappa B-inducing kinase – Identification of a novel TRAF6 interaction motif. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 7724–7731
Chou AH, Tsai HF, Lin LL, Hsieh SL, Hsu PI and Hsu PN (2001) Enhanced proliferation and increased IFN-gamma production in T cells by signal transduced through TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J. Immunol. 167: 1347–1352
Zhai Y, Guo R, Hsu TL, Yu GL, Ni J, Kwon BS, Jiang GW, Lu J, Tan J, Ugustus M, Carter K, Rojas L, Zhu F, Lincoln C, Endress G, Xing L, Wang S, Oh KO, Gentz R, Ruben S, Lippman ME, Hsieh SL and Yang D (1998) LIGHT, a novel ligand for lymphotoxin β receptor and TR2/HVEM induces apoptosis and suppresses in vivo tumor formation via gene transfer. J. Clin. Invest. 102: 1142–1151
Chen NJ, Huang MW and Hsieh SL (2001) Enhanced secretion of IFN-gamma by activated Th1 cells occurs via reverse signaling through TNF-related activation-induced cytokine. J. Immunol. 166: 270–276
Huang KC, Chen CW, Chen JC and Lin WW (2003) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors inhibit inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in macrophages. J. Biomed. Sci. 10: 396–405
Acknowledgements
This work was mainly supported by a grant from National Taiwan University Hospital (NTUH91-S055) and from the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC 90-2320-B010-109). Additional support came from the National Health Research Institute, Taiwan (NHRI-CN-BP-8902S) and the Ministry of Education (89-B-FA22-2-4) under the program for Promoting Academic Excellence in Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by M Piacentini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Wang, J., Hsieh, S. et al. Decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) induces osteoclast formation from monocyte/macrophage lineage precursor cells. Cell Death Differ 11 (Suppl 1), S97–S107 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401403
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401403
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TRAIL inhibits RANK signaling and suppresses osteoclast activation via inhibiting lipid raft assembly and TRAF6 recruitment
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Monocytes, Macrophages, and Microglia and the Role of IL-1 in Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease (AIED)
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports (2018)
-
Decoy receptor 3: an endogenous immunomodulator in cancer growth and inflammatory reactions
Journal of Biomedical Science (2017)
-
Mechanisms of Altered Bone Remodeling in Multiple Myeloma
Clinical Reviews in Bone and Mineral Metabolism (2017)
-
Non-Canonical (RANKL-Independent) Pathways of Osteoclast Differentiation and Their Role in Musculoskeletal Diseases
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2016)