Abstract
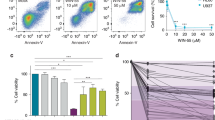
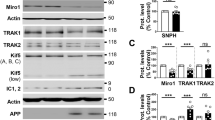
The amyloid precursor protein (APP) has been suggested to regulate gene expression. GeneChip® analysis and in vitro kinase assays revealed potent APP-dependent repression of c-Jun, its target gene SPARC and reduced basal c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity in PC12 cells overexpressing APP. UV-induced activation of the JNK signalling pathway and subsequent apoptosis were likewise reduced by APP and this effect could be mimicked by the indirect JNK inhibitor CEP-11004. Treatment with a B⃗-secretase inhibitor did not affect APP-mediated downmodulation of the JNK signalling pathway, suggesting that the effects might be mediated via α-secretase processing of APP. In support of these data, overexpression of the Swedish mutant of APP did not inhibit SPARC expression, UV-induced JNK activation and cell death. Our data suggest an important physiological role of APP and α-secretase activity in the control of JNK/c-Jun signalling, target gene expression and cell death activation in response to cytotoxic stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer's disease
- AICD:
-
APP intracellular domain
- AP-1:
-
activator protein-1
- APP:
-
amyloid precursor protein
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- JIP-1b:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-interacting protein-1b
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MLK:
-
mixed-lineage kinase
- MnSOD:
-
manganese superoxide dismutase
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-kappa B
- SPARC:
-
secreted protein, acidic and rich in cysteine
References
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81: 741–766
LaFerla FM (2002) Calcium dyshomeostasis and intracellular signalling in Alzheimer's disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3: 862–872
Selkoe DJ and Podlisny MB (2002) Deciphering the genetic basis of Alzheimer's disease. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 3: 67–99
Barger SW and Mattson MP (1996) Induction of neuroprotective kappa B-dependent transcription by secreted forms of the Alzheimer's beta-amyloid precursor. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 40: 116–126
Tanzi RE and Bertram L (2001) New frontiers in Alzheimer's disease genetics. Neuron 32: 181–184
De Strooper B (2003) Aph-1, Pen-2, and Nicastrin with Presenilin generate an active gamma-Secretase complex. Neuron 38: 9–12
Passer B, Pellegrini L, Russo C, Siegel RM, Lenardo MJ, Schettini G, Bachmann M, Tabaton M and D'Adamio L (2000) Generation of an apoptotic intracellular peptide by gamma-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer's amyloid beta protein precursor. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2: 289–301
Cao X and Sudhof TC (2001) A transcriptionally [correction of transcriptively] active complex of APP with Fe65 and histone acetyltransferase Tip60. Science 293: 115–120
Kimberly WT, Zheng JB, Guenette SY and Selkoe DJ (2001) The intracellular domain of the beta-amyloid precursor protein is stabilized by Fe65 and translocates to the nucleus in a notch-like manner. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 40288–40292
Matsuda S, Yasukawa T, Homma Y, Ito Y, Niikura T, Hiraki T, Hirai S, Ohno S, Kita Y, Kawasumi M, Kouyama K, Yamamoto T, Kyriakis JM and Nishimoto I (2001) c-Jun n-terminal kinase (jnk)-interacting protein-1b/islet-brain-1 scaffolds alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein with jnk. J. Neurosci. 21: 6597–6607
Scheinfeld MH, Roncarati R, Vito P, Lopez PA, Abdallah M and D'Adamio L (2002) Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) interacting protein 1 (JIP1) binds the cytoplasmic domain of the Alzheimer's beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP). J. Biol. Chem. 277: 3767–3775
Taru H, Kirino Y and Suzuki T (2002) Differential roles of JIP scaffold proteins in the modulation of amyloid precursor protein metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 27567–27574
Whitmarsh AJ, Kuan CY, Kennedy NJ, Kelkar N, Haydar TF, Mordes JP, Appel M, Rossini AA, Jones SN, Flavell RA, Rakic P and Davis RJ (2001) Requirement of the JIP1 scaffold protein for stress-induced JNK activation. Genes Dev. 15: 2421–2432
Yasuda J, Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Sharma M and Davis RJ (1999) The JIP group of mitogen-activated protein kinase scaffold proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 19: 7245–7254
Herdegen T, Skene P and Bahr M (1997) The c-Jun transcription factor – bipotential mediator of neuronal death, survival and regeneration. Trends Neurosci. 20: 227–231
Kögel D, Schomburg R, Schurmann T, Reimertz C, König HG, Poppe M, Eckert A, Müller WE and Prehn JH (2003) The amyloid precursor protein protects PC12 cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J. Neurochem. 87: 248–256
Eckert A, Steiner B, Marques C, Leutz S, Romig H, Haass C and Muller WE (2001) Elevated vulnerability to oxidative stress-induced cell death and activation of caspase-3 by the Swedish amyloid precursor protein mutation. J. Neurosci. Res. 64: 183–192
Marques CA, Keil U, Bonert A, Steiner B, Haass C, Muller WE and Eckert A (2003) Neurotoxic mechanisms caused by the Alzheimer's disease-linked Swedish amyloid precursor protein mutation: oxidative stress, caspases, and the JNK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 28294–28302
Briggs J, Chamboredon S, Castellazzi M, Kerry JA and Bos TJ (2002) Transcriptional upregulation of SPARC, in response to c-Jun overexpression, contributes to increased motility and invasion of MCF7 breast cancer cells. Oncogene 21: 7077–7091
Minet E, Michel G, Mottet D, Piret JP, Barbieux A, Raes M and Michiels C (2001) c-JUN gene induction and AP-1 activity is regulated by a JNK-dependent pathway in hypoxic HepG2 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 265: 114–124
Rishton GM, Retz DM, Tempest PA, Novotny J, Kahn S, Treanor JJ, Lile JD and Citron M (2000) Fenchylamine sulfonamide inhibitors of amyloid beta peptide production by the gamma-secretase proteolytic pathway: potential small-molecule therapeutic agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J. Med. Chem. 43: 2297–2299
Mielke K, Damm A, Yang DD and Herdegen T (2000) Selective expression of JNK isoforms and stress-specific JNK activity in different neural cell lines. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 75: 128–137
Noguchi K, Kokubu A, Kitanaka C, Ichijo H and Kuchino Y (2001) ASK1-signaling promotes c-Myc protein stability during apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 281: 1313–1320
Tournier C, Hess P, Yang DD, Xu J, Turner TK, Nimnual A, Bar-Sagi D, Jones SN, Flavell RA and Davis RJ (2000) Requirement of JNK for stress-induced activation of the cytochrome c-mediated death pathway. Science 288: 870–874
Selznick LA, Zheng TS, Flavell RA, Rakic P and Roth KA (2000) Amyloid beta-induced neuronal death is bax-dependent but caspase-independent. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 59: 271–279
Murakata C, Kaneko M, Gessner G, Angeles TS, Ator MA, O'Kane TM, McKenna BA, Thomas BA, Mathiasen JR, Saporito MS, Bozyczko-Coyne D and Hudkins RL (2002) Mixed lineage kinase activity of indolocarbazole analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 12: 147–150
Mielke K and Herdegen T (2002) Fatal shift of signal transduction is an integral part of neuronal differentiation: JNKs realize TNFalpha-mediated apoptosis in neuronlike, but not naive, PC12 cells. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 20: 211–224
Xu Y, Kiningham KK, Devalaraja MN, Yeh CC, Majima H, Kasarskis EJ and St Clair DK (1999) An intronic NF-kappaB element is essential for induction of the human manganese superoxide dismutase gene by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta DNA. Cell Biol. 18: 709–722
Krueger WH, Gonye GE, Madison DL, Murray KE, Kumar M, Spoerel N and Pfeiffer SE (1997) TPO1, a member of a novel protein family, is developmentally regulated in cultured oligodendrocytes. J. Neurochem. 69: 1343–1355
Roher AE, Weiss N, Kokjohn TA, Kuo YM, Kalback W, Anthony J, Watson D, Luehrs DC, Sue L, Walker D, Emmerling M, Goux W and Beach T (2002) Increased A beta peptides and reduced cholesterol and myelin proteins characterize white matter degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Biochemistry 41: 11080–11090
Hirai K, Aliev G, Nunomura A, Fujioka H, Russell RL, Atwood CS, Johnson AB, Kress Y, Vinters HV, Tabaton M, Shimohama S, Cash AD, Siedlak SL, Harris PL, Jones PK, Petersen RB, Perry G and Smith MA (2001) Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. 21: 3017–3023
Michalak M, Robert Parker JM and Opas M (2002) Ca(2+) signaling and calcium binding chaperones of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Calcium 32: 269–278
Pu Y and Chang DC (2001) Cytosolic Ca(2+) signal is involved in regulating UV-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 282: 84–89
Mattson MP (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1: 120–129
Holzberg D, Knight CG, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Schneider H, Dorrie A, Hoffmann E, Resch K and Kracht M (2003) Disruption of the c-JUN–JNK complex by a cell-permeable peptide containing the c-JUN delta domain induces apoptosis and affects a distinct set of IL-1-induced inflammatory genes. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 40213–40223
Bornstein P and Sage EH (2002) Matricellular proteins: extracellular modulators of cell function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14: 608–616
Nishimura I, Takazaki R, Kuwako K, Enokido Y and Yoshikawa K (2003) Upregulation and antiapoptotic role of endogenous Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Exp. Cell Res. 286: 241–251
Eilers A, Whitfield J, Shah B, Spadoni C, Desmond H and Ham J (2001) Direct inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in sympathetic neurones prevents c-jun promoter activation and NGF withdrawal-induced death. J. Neurochem. 76: 1439–1454
Xu Z, Maroney AC, Dobrzanski P, Kukekov NV and Greene LA (2001) The MLK family mediates c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in neuronal apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 21: 4713–4724
Tsuruta F, Sunayama J, Mori Y, Hattori S, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y, Yoshioka K, Masuyama N and Gotoh Y (2004) JNK promotes Bax translocation to mitochondria through phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins. EMBO J. 23: 1889–1899
Lei K and Davis RJ (2003) JNK phosphorylation of Bim-related members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 2432–2437
Manning AM and Davis RJ (2003) Targeting JNK for therapeutic benefit: from junk to gold? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2: 554–565
Bozyczko-Coyne D, Saporito MS and Hudkins RL (2002) Targeting the JNK pathway for therapeutic benefit in CNS disease. Curr. Drug Target CNS Neurol. Disord. 1: 31–49
Morishima Y, Gotoh Y, Zieg J, Barrett T, Takano H, Flavell R, Davis RJ, Shirasaki Y and Greenberg ME (2001) Beta-amyloid induces neuronal apoptosis via a mechanism that involves the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and the induction of Fas ligand. J. Neurosci. 21: 7551–7560
Shoji M, Iwakami N, Takeuchi S, Waragai M, Suzuki M, Kanazawa I, Lippa CF, Ono S and Okazawa H (2000) JNK activation is associated with intracellular beta-amyloid accumulation. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 85: 221–233
Zhu X, Raina AK, Rottkamp CA, Aliev G, Perry G, Boux H and Smith MA (2001) Activation and redistribution of c-jun N-terminal kinase/stress activated protein kinase in degenerating neurons in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 76: 435–441
Luo JJ, Wallace MS, Hawver DB, Kusiak JW and Wallace WC (2001) Characterization of the neurotrophic interaction between nerve growth factor and secreted alpha-amyloid precursor protein. J. Neurosci. Res. 63: 410–420
Burton TR, Dibrov A, Kashour T and Amara FM (2002) Anti-apoptotic wild-type Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein signaling involves the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/MEF2 pathway. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 108: 102–120
Barthwal MK, Sathyanarayana P, Kundu CN, Rana B, Pradeep A, Sharma C, Woodgett JR and Rana A (2003) Negative regulation of mixed lineage kinase 3 by protein kinase B/AKT leads to cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 3897–3902
Mudher A, Chapman S, Richardson J, Asuni A, Gibb G, Pollard C, Killick R, Iqbal T, Raymond L, Varndell I, Sheppard P, Makoff A, Gower E, Soden PE, Lewis P, Murphy M, Golde TE, Rupniak HT, Anderton BH and Lovestone S (2001) Dishevelled regulates the metabolism of amyloid precursor protein via protein kinase C/mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun terminal kinase. J. Neurosci. 21: 4987–4995
Garcia-Calvo M, Peterson EP, Rasper DM, Vaillancourt JP, Zamboni R, Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA (1999) Purification and catalytic properties of human caspase family members. Cell Death Differ. 6: 362–369
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW and Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410
Acknowledgements
We thank Hanni Bähler, Petra Mech, Christiane Schettler and Hildegard Schweers for technical assistance, Drs. Christian Haass and Anne Eckert for cell lines, Drs. Stephen P Trusko and Marcel Leist for CEP-11004 and Dr. Kirsten Mielke for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from Alzheimer Forschung Initiative e.V. to DK (AFI Grant 03809) and JHMP (AFI Grant 00808), as well as Science Foundation Ireland (03/RP1/B344) and Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research (IZKF), University of Münster (Bundesministerium für Bildung, Wissenschaft, Forschung und Technologie Grant 01 KS 9604/0) to JHMP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kögel, D., Schomburg, R., Copanaki, E. et al. Regulation of gene expression by the amyloid precursor protein: inhibition of the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Cell Death Differ 12, 1–9 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401495
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401495
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Is brain iron trafficking part of the physiology of the amyloid precursor protein?
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2019)
-
Amyloid Precursor Protein Mediates Neuronal Protection from Rotenone Toxicity
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
URMC-099 facilitates amyloid-β clearance in a murine model of Alzheimer’s disease
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2018)
-
Modulation of BAG3 Expression and Proteasomal Activity by sAPPα Does Not Require Membrane-Tethered Holo-APP
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
Holo-APP and G-protein-mediated signaling are required for sAPPα-induced activation of the Akt survival pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2014)