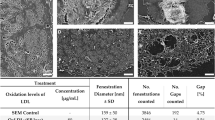
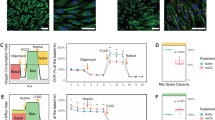
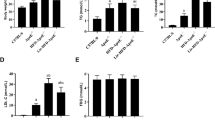
Abstract
Enzymatic modification of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) as it probably occurs in the arterial intima drastically increases its cytotoxicity, which could be relevant for the progression of atherosclerotic lesions. LDL was treated with a protease and cholesterylesterase to generate a derivative similar to lesional LDL, with a high content of free cholesterol and fatty acids. Exposure of endothelial cells to the enzymatically modified lipoprotein (E-LDL), but not to native or oxidized LDL, resulted in programmed cell death. Apoptosis was triggered by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 dependent phosphorylation of p38. Depletion and reconstitution experiments identified free fatty acids (FFA) as the triggers of this pathway. Levels of FFA in native LDL are low and the lipoprotein is therefore not cytotoxic; enzymatic cleavage of cholesterylesters liberates FFA that can rapidly trigger an apoptosis signaling cascade in neighboring cells. Blockade of this pathway can rescue cells from death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ASK1:
-
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- E-LDL:
-
enzymatically modified low-density lipoprotein
- FFA:
-
free fatty acids
- LDL:
-
low-density lipoprotein
- oxLDL:
-
oxidized low-density lipoprotein
- PCD:
-
programmed cell death
- TBARS:
-
thiobarbiturate-reactive substances
References
Martinet W and Kockx MM (2004) Apoptosis in atheroclerosis: implications for plaque destabilization. Verh. K. Acad. Geneeskd. Belg. 66: 61–79
Stoneman VE and Bennett MR (2004) Role of apoptosis in atherosclerosis and its therapeutic implications. Clin. Sci. (London) 107: 343–354
Dimmeler S, Haendeler J and Zeiher AM (2002) Regulation of endothelial cell apoptosis in atherothrombosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 13: 531–536
Artwohl M, Roden M, Waldhausl W, Freudenthaler A and Baumgartner-Parzer SM (2004) Free fatty acids trigger apoptosis and inhibit cell cycle progression in human vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 18: 146–148
Zhu Y, Liao H, Wang N, Ma KS, Verna LK, Shyy JY, Chien S and Stemerman MB (2001) LDL-activated p38 in endothelial cells is mediated by Ras. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 21: 1159–1164
Kruth HS (1985) Cholesterol accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells incorporated into platelet-rich plasma clots. Lab. Invest. 53: 634–638
Seifert PS, Hugo F, Tranum-Jensen J, Zahringer U and Muhly M andBhakdi S (1990) Isolation and characterization of a complement-activating lipid extracted from human atherosclerotic lesions. J. Exp. Med. 172: 547–557
Fowler SD, Mayer EP and Greenspan P (1985) Foam cells and atherogenesis. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 454: 79–90
Steinbrecher UP and Lougheed M (1992) Scavenger receptor-independent stimulation of cholesterol esterification in macrophages by low density lipoprotein extracted from human aortic intima. Arterioscler. Thromb. 12: 608–625
Bhakdi S, Dorweiler B, Kirchmann R, Torzewski J, Weise E, Tranum-Jensen J, Walev I and Wieland E (1995) On the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: enzymatic transformation of human low density lipoprotein to an atherogenic moiety. J. Exp. Med. 182: 1959–1971
Han SR, Momeni A, Strach K, Suriyaphol P, Fenske D, Paprotka K, Hashimoto SI, Torzewski M, Bhakdi S and Husmann M (2003) Enzymatically modified LDL induces cathepsin H in human monocytes: potential relevance in early atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23: 661–667
Hakala JK, Oksjoki R, Laine P, Du H, Grabowski GA, Kovanen PT and Pentikainen MO (2003) Lysosomal enzymes are released from cultured human macrophages, hydrolyze LDL in vitro, and are present extracellularly in human atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23: 1430–1436
Torzewski M, Suriyaphol P, Paprotka K, Spath L, Ochsenhirt V, Schmitt A, Han SR, Husmann M, Gerl VB, Bhakdi S and Lackner KJ (2004) Enzymatic modification of low-density lipoprotein in the arterial wall: a new role for plasmin and matrix metalloproteinases in atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24: 2130–2136
Torzewski M, Klouche M, Hock J, Messner M, Dorweiler B, Torzewski J, Gabbert HE and Bhakdi S (1998) Immunohistochemical demonstration of enzymatically modified human LDL and its colocalization with the terminal complement complex in the early atherosclerotic lesion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 18: 369–378
Bhakdi S, Torzewski M, Klouche M and Hemmes M (1999) Complement and atherogenesis: binding of CRP to degraded, nonoxidized LDL enhances complement activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19: 2348–2354
Bhakdi S, Lackner KJ, Han SR, Torzewski M and Husmann M (2004) Beyond cholesterol: the enigma of atherosclerosis revisited. Thromb. Haemost. 91: 639–645
Moriguchi T, Kuroyanagi N, Yamaguchi K, Gotoh Y, Irie K, Kano T, Shirakabe K, Muro Y, Shibuya H, Matsumoto K, Nishida E and Hagiwara M (1996) A novel kinase cascade mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 and MKK3. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 13675–13679
Tobiume K, Matsuzawa A, Takahashi T, Nishitoh H, Morita K, Takeda K, Minowa O, Miyazono K and Noda T andIchijo H (2001) ASK1 is required for sustained activations of JNK/p38 MAP kinases and apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2: 222–228
Takeda K, Matsuzawa A and Nishitoh H andIchijo H (2003) Roles of MAPKKK ASK1 in stress-induced cell death. Cell. Struct. Funct. 28: 23–29
Murakami M and Kudo I (2003) New phospholipase A(2) isozymes with a potential role in atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 14: 431–436
Baumstark MW, Kreutz W, Berg A and Keul J (1991) Symmetry of the surface, and structure of the central core of human LDL particles, analyzed by X-ray small angle scattering. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 285: 123–130
Kruth HS (1984) Localization of unesterified cholesterol in human atherosclerotic lesions. Demonstration of filipin-positive, oil-red-O-negative particles. Am. J. Pathol. 114: 201–208
Simionescu N, Vasile E, Lupu F, Popescu G and Simionescu M (1986) Prelesional events in atherogenesis. Accumulation of extracellular cholesterol-rich liposomes in the arterial intima and cardiac valves of the hyperlipidemic rabbit. Am. J. Pathol. 123: 109–125
Chao FF, Amende LM, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Skarlatos SI, Gamble W, Resau JH, Mergner WT and Kruth HS (1988) Unesterified cholesterol-rich lipid particles in atherosclerotic lesions of human and rabbit aortas. Am. J. Pathol. 131: 73–83
Kuhn H, Heydeck D, Hugou I and Gniwotta C (1997) In vivo action of 15-lipoxygenase in early stages of human atherogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 99: 888–893
Bhakdi S, Torzewski M, Paprotka K, Schmitt S, Barsoom H, Suriyaphol P, Han SR, Lackner KJ and Husmann M (2004) Possible protective role for C-reactive protein in atherogenesis: complement activation by modified lipoproteins halts before detrimental terminal sequence. Circulation 109: 1870–1876
Suriyaphol P, Fenske D, Zahringer U, Han SR, Bhakdi S and Husmann M (2002) Enzymatically modified nonoxidized low-density lipoprotein induces interleukin-8 in human endothelial cells: role of free fatty acids. Circulation 106: 2581–2587
Klouche M, Gottschling S, Gerl V, Hell W, Husmann M, Dorweiler B, Messner M and Bhakdi S (1998) Atherogenic properties of enzymatically degraded LDL: selective induction of MCP-1 and cytotoxic effects on human macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 18: 1376–1385
Grethe S, Ares MP, Andersson T and Porn-Ares MI (2004) p38 MAPK mediates TNF-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells via phosphorylation and downregulation of Bcl-x(L). Exp. Cell. Res. 298: 632–642
Zhao M, Liu Y, Wang X, New L, Han J and Brunk UT (2002) Activation of the p38 MAP kinase pathway is required for foam cell formation from macrophages exposed to oxidized LDL. Apmis 110: 458–468
Tobiume K, Saitoh M and Ichijo H (2002) Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 by the stress-induced activating phosphorylation of pre-formed oligomer. J. Cell. Physiol. 191: 95–104
Morel DW, Hessler JR and Chisolm GM (1983) Low density lipoprotein cytotoxicity induced by free radical peroxidation of lipid. J. Lipid. Res. 24: 1070–1076
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Bh2/3-3 to S Bhakdi and M Husmann.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by P Nicotera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dersch, K., Ichijo, H., Bhakdi, S. et al. Fatty acids liberated from low-density lipoprotein trigger endothelial apoptosis via mitogen-activated protein kinases. Cell Death Differ 12, 1107–1114 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401633
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401633
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pro-autophagic signal induction by bacterial pore-forming toxins
Medical Microbiology and Immunology (2010)
-
Effects of insulin and free fatty acids on matrix metalloproteinases
Current Diabetes Reports (2008)