Abstract
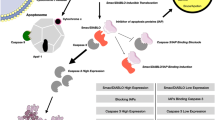
We have characterised the apoptotic defects in cells null for cytochrome c (cyt c−/−). Such cells treated with staurosporine (STS) exhibited translocation to the mitochondria and activation of the proapoptotic signalling molecule Bax but failed to release Smac/DIABLO from these organelles, judged by both confocal microscopy and Western blotting. While reference cells expressing cytochrome c released both it and Smac/DIABLO under a variety of conditions of apoptotic induction, we have never observed release of Smac/DIABLO from cyt c−/− cells. We eliminate the possibility that proteasomal degradation of cytosolically localised Smac/DIABLO is responsible for our failure to visualise the protein outside the mitochondria. Our findings indicate an unanticipated nexus between release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria, previously thought to be a more or less synchronised event early in apoptosis. We suggest that the failure of cyt c−/− cells to release Smac/DIABLO after recruitment of Bax to mitochondria represents an extreme manifestation of some inherent difference in the regulation of release of these two proteins from mitochondria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- cyt c:
-
cytochrome c
- IMS:
-
intermembrane space
- OM:
-
outer membrane
- IAPs:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis proteins
- AIF:
-
apoptosis-inducing factor
- cyt c−/− cells:
-
cytochrome c knockout mouse embryonic fibroblast cells
- STS:
-
staurosporine
- MTR:
-
MitoTracker Red
- Tdt:
-
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
- CHX:
-
cycloheximide
References
Desagher S and Martinou JC (2000) Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 10: 369–377
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ (2001) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292: 727–730
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ and Vaux DL (2000) Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 102: 43–53
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X (2000) Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102: 33–42
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler M, Larochette N, Goodlett DR, Aebersold R, Siderovski DP, Penninger JM and Kroemer G (1999) Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 397: 441–446
Li K, Li Y, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Spencer E, Chen ZJ, Wang X and Williams RS (2000) Cytochrome c deficiency causes embryonic lethality and attenuates stress-induced apoptosis. Cell 101: 389–399
Bertrand R, Solary E, O'Connor P, Kohn KW and Pommier Y (1994) Induction of a common pathway of apoptosis by staurosporine. Exp. Cell Res. 211: 314–321
Froelich-Ammon SJ and Osheroff N (1995) Topoisomerase poisons: harnessing the dark side of enzyme mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 21429–21432
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407: 770–776
Takasawa R and Tanuma S (2003) Sustained release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria commits to undergo UVB-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 8: 291–299
Karpinich NO, Tafani M, Rothman RJ, Russo MA and Farber JL (2002) The course of etoposide-induced apoptosis from damage to DNA and p53 activation to mitochondrial release of cytochrome c. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 16547–16552
Jiang S, Cai J, Wallace DC and Jones DP (1999) Cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis in cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Signaling pathway involving release and caspase 3 activation is conserved. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 29905–29911
MacFarlane M, Merrison W, Bratton SB and Cohen GM (2002) Proteasome-mediated degradation of Smac during apoptosis: XIAP promotes Smac ubiquitination in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 36611–36616
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Eskes R and Martinou JC (2000) Bax oligomerization is required for channel-forming activity in liposomes and to trigger cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Biochem. J. 345: 271–278
Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G, Ellisman MH, Latterich M, Schneiter R, Green DR and Newmeyer DD (2002) Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell 111: 331–342
Rehm M, Dussmann H and Prehn JH (2003) Real-time single cell analysis of Smac/DIABLO release during apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 162: 1031–1043
Springs SL, Diavolitsis VM, Goodhouse J and McLendon GL (2002) The kinetics of translocation of Smac/DIABLO from the mitochondria to the cytosol in HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 45715–45718
Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X and Shi Y (2000) Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 406: 855–862
Wang JL, Liu D, Zhang ZJ, Shan S, Han X, Srinivasula SM, Croce CM, Alnemri ES and Huang Z (2000) Structure-based discovery of an organic compound that binds Bcl-2 protein and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97: 7124–7129
An J, Chen Y and Huang Z (2004) Critical upstream signals of cytochrome c release induced by a novel bcl-2 inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 19133–19140
Scorrano L, Ashiya M, Buttle K, Weiler S, Oakes SA, Mannella CA and Korsmeyer SJ (2002) A distinct pathway remodels mitochondrial cristae and mobilizes cytochrome c during apoptosis. Dev. Cell 2: 55–67
Boehning D, Patterson RL, Sedaghat L, Glebova NO, Kurosaki T and Snyder SH (2003) Cytochrome c binds to inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate receptors, amplifying calcium-dependent apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 5: 1051–1061
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B and Nicotera P (2003) Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4: 552–565
Arnoult D, Gaume B, Karbowski M, Sharpe JC, Cecconi F and Youle RJ (2003) Mitochondrial release of AIF and EndoG requires caspase activation downstream of Bax/Bak-mediated permeabilization. EMBO J. 22: 4385–4399
Schmitt E, Parcellier A, Ghiringhelli F, Casares N, Gurbuxani S, Droin N, Hamai A, Pequignot M, Hammann A, Moutet M, Fromentin A, Kroemer G, Solary E and Garrido C (2004) Increased immunogenicity of colon cancer cells by selective depletion of cytochrome c. Cancer Res. 64: 2705–2711
Waterhouse NJ, Goldstein JC, von Ahsen O, Schuler M, Newmeyer DD and Green DR (2001) Cytochrome c maintains mitochondrial transmembrane potential and ATP generation after outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during the apoptotic process. J. Cell Biol. 153: 319–328
Jiang S, Cai J, Wallace DC and Jones DP (1999) Cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis in cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Signaling pathway involving release and caspase 3 activation is conserved. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 29905–29911
King MP and Attardi G (1989) Human cells lacking mtDNA: repopulation with exogenous mitochondria by complementation. Science 246: 500–503
Adrain C, Creagh EM and Martin SJ (2001) Apoptosis-associated release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria requires active caspases and is blocked by Bcl-2. EMBO J. 20: 6627–6636
Acknowledgements
The excellent technical assistance of Susan Ekkel is gratefully acknowledged. We thank Professor N Hoogenraad (La Trobe University) for his gift of antibodies specific for Hsp60, and Dr. R Baker (Australian National University) for helpful advice on proteasome inhibitors and ubiquitinylation. This work was supported by the Australian Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by P Mehlen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansen, T., Smith, D. & Nagley, P. Smac/DIABLO is not released from mitochondria during apoptotic signalling in cells deficient in cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ 13, 1181–1190 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401795
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401795
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Study on norcantharidin-induced apoptosis in SMMC-7721 cells through mitochondrial pathways
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2010)
-
Smac-mediated sensitization of human B-lymphoma cells to staurosporine- and lactacystin-triggered apoptosis is apoptosome-dependent
Leukemia (2007)
-
SMAC/Diablo mediates the proapoptotic function of PUMA by regulating PUMA-induced mitochondrial events
Oncogene (2007)
-
Differential Regulation of Smac/DIABLO and Hsp-70 during Brain Maturation
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2007)