Abstract
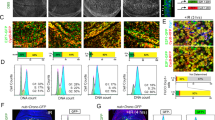
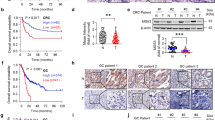
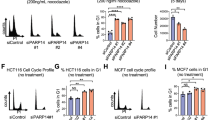
Although cyclin G1 has been implicated in certain p53-related biological phenomena, other aspects of its function remain unclear. Here we report hitherto unknown mechanism by which cyclin G1 increases radiation sensitivity by regulating the level of cyclin B1. Overexpression of cyclin G1 was observable in lung carcinoma tissues. Irradiation of human lung cells with cyclin G1 overexpression resulted in increased cell death and γ-H2AX foci suggesting that cyclin G1 rendered the cells more susceptible to DNA damage. Enhanced radiosensitivity by cyclin G1 was correlated with increased cyclin B1, CDC2/cyclin B1 complex, and MPM2. Cell cycle synchronization clearly showed coexpression of cyclin G1 and cyclin B1 in G2/M phase. Depletion of cyclin G1 by interference RNA revealed that cyclin G1 regulated transcription of cyclin B1 in a p53-independent manner, and confirmed that the increased mitotic cells and cell death by cyclin G1 were dependent upon cyclin B1. Therefore, our data suggest that cyclin G1 enhanced radiation sensitivity by overriding radiation-induced G2 arrest through transcriptional upregulation of cyclin B1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CDK5:
-
cyclin-dependent kinase 5
- GAK:
-
cyclin G associated kinase
- siRNA:
-
interference RNAs
References
Okamoto K and Beach D (1995) Cyclin G is a transcriptional target of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. EMBO J. 13: 4816–4822
Zauberman A, Lupo A and Oren M (1995) Identification of p53 target genes through immune selection of genomic DNA: the cyclin G gene contains two distinct p53 binding sites. Oncogene 10: 2361–2366
Kanaoka Y, Kimura SH, Okazaki I, Ikeda M and Nojima H (1997) GAK: a cyclin G associated kinase contains a tensin/auxilin-like domain. FEBS Lett. 402: 73–80
Kimura SH, Tsuruga H, Yabuta N, Endo Y and Nojima H (1997) Structure, expression, and chromosomal localization of human GAK. Genomics 44: 179–187
Reimer CL, Borras AM, Kurdistani SK, Garreau JR, Chung M, Aaronson SA and Lee SW (1999) Altered regulation of cyclin G in human breast cancer and its specific localization at replication foci in response to DNA damage in p53+/+ cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 11022–11029
Baek WK, Kim D, Jung N, Yi YW, Kim JM, Cha SK, Bae I and Cho CH (2003) Increased expression of cyclin G1 in leiomyoma compared with normal myometrium. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 188: 634–649
Kimura SH and Nojima H (2002) Cyclin G1 associates with MDM2 and regulates accumulation and degradation of p53 protein. Genes Cell 7: 869–880
Okamoto K and Prives C (1999) A role of cyclin G in the process of apoptosis. Oncogene 18: 4606–4615
Teyssier F, Bay JO, Dionet C and Verrelle P (1999) Cell cycle regulation after exposure to ionizing radiation. Bull. Cancer 86: 345–357
Hartwell LH and Kastan MB (1994) Cell cycle control and cancer. Science 266: 1821–1828
Morgan DO (1997) Cyclin dependent kinases, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13: 261–291
Gould KL and Murse P (1989) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature 342: 39–45
Krek W and Nigg EA (1991) Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 10: 3331–3341
Gautier J, Solomon MJ, Booher RN, Bazan JF and Kirschner MW (1991) Cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell 67: 197–211
Dunphy WG and Kumagai A (1991) The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell 67: 189–196
Borgne A and Meijer L (1996) Sequential dephosphorylation of p34cdc2 on Thr-14 and Try-15 at the prophase/metaphase transition. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 27847–27854
Kang CM, Park KP, Song JE, Jeoung DI, Cho CK, Kim TH, Bae S, Lee SJ and Lee YS (2003) Possible biomarkers for ionizing radiation exposure in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Radiat. Res. 159: 312–319
Rimokh R, Berger F, Bastard C, Klein B, French M, Archimbaud E, Rouault JP, Santa Lucia B, Duret L, Vuillaume M, Coiffer B, Bryon P and Magoud JP (1994) Rearrangement of CCND1 (BCL1/PRAD1) 3′ untranslated region in mantle-cell lymphomas and t(11q13)-associated leukemias. Blood 83: 3689–3696
Banath JP, Macphail SH and Olive PL (2004) Radiation sensitivity, H2AX phosphorylation, and kinetics of repair of DNA strand breaks in irradiated cervical cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 64: 7144–7149
Cho HN, Lee SJ, Park SH, Lee YJ, Cho CK and Lee YS (2001) Overexpression of heat-shock protein 25 augments radiation-induced cell-cycle arrest in murine L929 cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 77: 225–233
Zhao L, Samuels T, Winckler S, Korgaonkar C, Tompkins V, Horne MC and Quelle DE (2004) Cyclin G1 has growth inhibitory activity linked to the ARF-Mdm2-p53 and pRb tumor suppressor pathways. Mol. Cancer Res. 1: 195–206
Xu B, Kim ST, Lim DS and Kastan MB (2002) Two molecularly distinct G(2)/M checkpoints are induced by ionizing irradiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22: 1049–1059
Smith ML, Bortnick RA, Sheikh MS and Fornace Jr AJ (1998) Chromatin relaxation by overexpression of 1. mutant p53, HPV16-E6, or cyclin G1 transgens. Exp. Cell Res. 242: 235–243
Shimizu A, Nishida J, Ueoka Y, Kato K, Hachiya T, Kuriaki Y and Wake N (1998) Cyclin G contributes to G2/M arrest of cells in response to DNA damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 242: 529–533
King RW, Jackson P and Kirschner MW (1994) Mitosis in transition. Cell 79: 563–571
Dong Y, Sui L, Watanabe Y, Sugimoto K and Tokuda M (2002) Clinical relevance of cyclin B1 overexpression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 177: 13–19
Jin P, Hardy S and David OM (2002) Nuclear localization of cyclin B1 controls mitotic entry after DNA damage. J. Cell Biol. 141: 875–885
Takeno S, Noguchi T, Kikuchi R, Uchida Y, Yokoyama S and Müller W (2002) Prognostic value of cyclin B1 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 94: 2874–2881
Li JQ, Kubo A, Wu F, Usuki H, Fujita J, Bandoh S, Masaki T, Saoo K, Takeuchi H, Kobayashi S, Imaida K, Maeta H, Ishida T and Kuriyama S (2003) Cyclin B1, unlike cyclin G1, increases significantly during colorectal carcinogenesis and during later metastasis to lymph nodes. Int. J. Oncol. 22: 1101–1110
Jackman MR and Pines J (1997) Cyclins and the G2/M transition. Cancer Surv. 29: 47–73
Cogswell JP, Godlevski MM, Bonham M, Bisi J and Babiss L (1995) Upstream stimulatory factor regulates expression of the cell cycle dependent cyclin B1 gene promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 2782–2790
Hwang A, Maity A, McKenna WG and Muschel RJ (1995) Cell cycle dependent regulation of the cyclin B1 promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 28419–28424
Piaggio G, Farina A, Perrotti D, Manni I, Fuschi P, Sacchi A and Gaetano C (1995) Structure and growth-dependent regulation of the human cyclin B1 promoter. Exp. Cell Res. 216: 396–402
Katula KS, Wright KL, Paul H, Surman DR, Nuckolls FJ, Smith JW, Ting JP, Yates J and Cogswell JP (1997) Cyclin dependent kinase activation and S-phase induction of the cyclin B1 gene are linked through the CCAAT elements. Cell Growth Differ. 8: 811–820
Park M, Chae HD, Yun J, Jung M, Kim YJ, Kim SH, Han MH and Shin DY (2000) Constitutive activation of cyclin B1-associated cdc2 kinase overrides p53-mediated G2-M arrest. Cancer Res. 60: 542–545
Ruth AC and Roninson IB (2000) Effects of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein on cellular responses to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 60: 2576–2578
Yoshikawa R, Kusunoki M, Yanagi H, Noda M, Furuyama JI, Yamamura T and Hashimoto-Tamaoki T (2002) Dual antitumor effects of 5-fluorouracil on the cell cycle in colorectal carcinoma cells: a novel target mechanism concept for pharmacokinetic modulating chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 61: 1029–1037
Ling YH, Leibes L, Jiang JD, Holland JF, Elliott PJ, Adams J, Muggia FM and Perez-Soler R (2003) Mechanisms of proteasome inhibitor PS-341-induced G2–M Phase arrest and apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 9: 1145–1154
Wasner M, Tschop K, Spiesbach K, Haugwitz U, Johne C, Mossner J, Mantovani R and Engeland K (2004) Cyclin B1 transcription is enhanced by the p300 coactivator and regulated during the cell cycle by a CHR-dependent repression mechanism. FEBS Lett. 536: 66–70
Cho HN, Lee YJ, Cho CK, Lee SJ and Lee YS (2002) Downregulation of ERK2 is essential for the inhibition of radiation-induced cell death in HSP25 overexpressed L929 cells. Cell Death Differ. 9: 448–456
Lee YJ, Soh JW, Dean NM, Cho CK, Kim TH, Lee SJ and Lee YS (2003) Protein kinase C delta overexpression enhances radiation sensitivity via extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2 activation, abolishing the radiation-induced G(2)–M arrest. Cell Growth Differ. 13: 237–246
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) and by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) through the National Nuclear Technology Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by M Blagosklonny
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, H., Lee, D., Lee, H. et al. Cyclin G1 overcomes radiation-induced G2 arrest and increases cell death through transcriptional activation of cyclin B1. Cell Death Differ 13, 1475–1484 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401822
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401822
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Atypical cyclins: the extended family portrait
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2020)
-
Raltitrexed increases radiation sensitivity of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells
Cancer Cell International (2019)
-
Comprehensive phenotypic analysis of knockout mice deficient in cyclin G1 and cyclin G2
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
ELAS1-mediated inhibition of the cyclin G1–B'γ interaction promotes cancer cell apoptosis via stabilization and activation of p53
Oncogene (2015)
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of cyclins D1, D3 and G1 and proliferation of human cancer cells depend on IMP-3 nuclear localization
Oncogene (2014)