Abstract
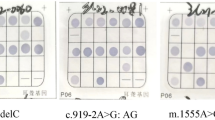
Mutations in the Cx26 (GJB2) gene have been shown to be responsible for a major part of autosomal recessive non-syndromic inherited prelingual deafness. We have sequenced the coding region of GJB2 gene from 169 Taiwanese patients with prelingual deafness and 100 unrelated normal individuals. In the deaf patients, three mutations were found: two novel mutations, 551G→A, and 299-300delAT, and one previously described mutation, 235delC. Four previously reported polymorphisms, 79G→A, 109G→A, 341A→G, and 608T→C, were also found in both deaf patients and normal individuals and one new possible polymorphism, 558G→A, which was only found in a patient. Interestingly, we did not find the 35delG allele, which is commonly found in the Caucasian population, either in the patients or in normal individuals we examined. Our data also showed 235delC to be the most common type of mutation found in Cx26 mutants (approximately 57%). Therefore, based on our findings, we have developed a simple molecular test for the 235delC mutation and it should be of considerable help to those families to understand the cause of their children having the prelingual deafness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Morton NE . Genetic epidemiology of hearing impairment Ann NY Acad Sci 1991 630: 16–31
Zelante L, Gasparini P, Estivill X et al. Connexin26 mutations associated with the most common form of non-syndromic neurosensory autosomal recessive deafness (DFNB1) in Mediterraneans Hum Mol Genet 1997 6: 1605–1609
Cohn ES, Kelley PM . Clinical phenotype and mutations in connexin 26 (DFNB1/GJB2), the most common cause of childhood hearing loss Am J Med Genet 1999 89: 130–136
Kudo T, Ikeda K, Kure S et al. Novel Mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) responsible for childhood deafness in the Japanese population Am J Med Genet 2000 90: 141–145
Salt AN, Melichar I, Thalmann R . Mechanisms of endocochlear potential generation by stria vascularis Laryngoscope 1987 97: 984–991
Salt AN, DeMott JE . Ionic and potential changes of the endolymphatic sac induced by endolymph volume changes Hear Res 2000 149: 46–54
Kelsell DP, Dunlop J, Stevens HP et al. Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness Nature 1997 387: 80–83
White TW . Functional analysis of human Cx26 mutations associated with deafness Brain Res Rev 2000 32: 181–183
Denoyelle F, Weil D, Maw MA et al. Prelingual deafness: high prevalence of a 30delG 30delG mutation in the connexin 26 gene Hum Mol Genet 1997 6: 2173–2177
Gasparini P, Estivill X, Volpini V et al. Linkage of DFNB1 to non-syndromic neurosensory autosomal-recessive deafness in Mediterranean families Eur J Hum Genet 1997 5: 83–88
Guilford P, Ben Arab S, Blanchard S et al. A non-syndromic form of neurosensory, recessive deafness maps to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 13q Nature Genet 1994 6: 24–28
Maw MA, Allen-Powell DR, Goodey RJ et al. The contribution of the DFNB1 locus to neurosensory deafness in a Caucasian population Am J Hum Genet 1995 57: 629–635
Kelley PM, Harris DJ, Comer BC et al. Novel mutations in the connexin 26 gene (IGJB2) that cause autosomal recessive (DFNB1) hearing loss Am J Hum Genet 1998 62: 792–799
Krutovskikh V, Yamasaki H . Connexin gene mutations in human genetic diseases Mut Res 2000 462: 197–207
Cartegni L, Chew SL, Krainer AR . Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: exonic mutations that affect splicing Nat Rev Genet 2002 3: 285–298
Tekin M, Akar N, Cin S et al. Connexin 26 (GJB2) mutations in the Turkish population: implications for the origin and high frequency of the 35delG mutation in Caucasians Hum Genet 2001 108: 385–389
Acknowledgements
We thank Kuei-Hsiang Hung, Chung-Hsiang Yang, Yu-Che Cheng, Shi-Hsin Huang, and Chien-Hsun Wu for their technical assistance and to National Health Research Institute for support to CCL (NHRI-Ex90-8933SL). This work is supported by National Science Council, Republic of China (NSC 89-2745-P-040-002, NSC 89-2320-B-040-061, and NSC 90-2320-B-040-032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YC., Kung, CY., Su, MC. et al. Mutations of Cx26 gene (GJB2) for prelingual deafness in Taiwan. Eur J Hum Genet 10, 495–498 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200838
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200838
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel method for detecting nine hotspot mutations of deafness genes in one tube
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Rare compound heterozygosity involving dominant and recessive mutations of GJB2 gene in an assortative mating hearing impaired Indian family
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology (2017)
-
Dew inspired breathing-based detection of genetic point mutation visualized by naked eye
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Lower carrier rate of GJB2 W24X ancestral Indian mutation in Roma samples from Hungary: implication for public health intervention
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Genetic mutations in nonsyndromic deafness patients of Chinese minority and han ethnicities in Yunnan, China
Journal of Translational Medicine (2013)