Abstract
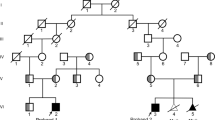
Manic depressive illness (MDI) segregates within a founder population originating from S, a mountain village in Southern Italy. Identity by descent of affected persons cannot be established by direct genealogical methods. A 56 000 persons family reconstruction data base encompasses the whole population of S in the 17th and 18th centuries, and part of the population of S and neighbouring villages in the 19th and 20th centuries. We selected 10 MDI probands who were members of the S population and not evident close relatives of each other. A total of 10 other MDI probands not evidently related to the S population formed a first control group. A second control group was formed with 10 not closely related persons originating within the S population. We determined the founders common ancestors to all the probands of one group but not ancestors to the probands of other groups, and computed the genetic contribution of each founder to each proband. The distance between probands in the S MDI group was calculated with respect to all the founders. In all, 17 founders present in the ascendancy of all individuals of the S MDI group are not present in the ascendancy of the control groups: MDI patients are derived from a subpopulation within S. Two S MDI probands are far from one another in respect of the ‘nonspecific’ founders, but are very close in respect of the specific founders: a putative MDI trait originated from specific founders of the MDI subpopulation, and hence is identical by descent in the S population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Mendlewicz J, Rainer JD : Adoption study supporting genetic transmission in manic-depressive illness. Nature 1977; 268: 327–329.
Kelsoe JR, Ginns EI, Egeland JA et al: Re-evaluation of the linkage relationship between chromosome 11p loci and the gene for bipolar affective disorder in the Old Order Amish. Nature 1989; 342: 238–242.
American Psychiatric Association: Descriptive and statistical manual-IV. Washington DC: American Psychiatric association, 1994.
Foncin JF, Salmon D, Supino-Viterbo V et al: Démence présenile d' Alzheimer transmise dans une famille étendue. Rev Neurol 1985; 141: 194–202.
Sherrington R, Rogaev EI, Liang Y et al: Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature 1995; 375: 754–760.
Bruni AC, Montesi MP, Manfredi R, Gei G, Ermio C, Caruso G : Un esteso ceppo con probabile psicosi maniaco-depressiva. Riv Psichiatria 1989; 24: 175–181.
Bruni AC, Montesi MP, Manfredi R et al: Linkage studies of major affective disorders: The impact of the extension of the pedigrees. Eur Psychiatry 1992; 7: 145–146.
Perri C, Ouellette G, Foncin J-F et al: From pedigree to population studies in bipolar disorders. 6th World Congress on Psychiatric Genetics, Bonn, 6–10 October, 1998. Abstract in: Am J Med. Genet (Neuropsychiatric Genetics) 1998; 81: 492.
Bruni F . Storia di Serrastretta dalle origini al 1938. Rubettino, Soveria Manelli, 1980.
Heyer E, Tremblay M : Variability of the genetic contribution of Québec population founders associated with some deleterious genes. Am J Hum Genet 1995; 56: 970–978.
Bruni AC, Montesi MP, Gei G, Ermio C, Rainero I, Foncin J-F : The common origin of FAD in Calabria. In Iqbal K, McLachlan DRC, Winblad B, Wisniewski H (eds): Alzheimer's disease: basic mechanisms, diagnosis and therapeutic strategies. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 1991, pp. 451–455.
Kraepelin E . Psychiatrie, ein Lehrbuch für Studierenden und Ärtzte, 4th ed., Leipzig: Abel Meiner, 1893.
Bellivier F, Laplanche JL, Leboyer M, Feingold J : Serotonine transporter gene and manic depressive illness: an association study: Biol Psychiatry 1997; 41: 750–752.
Perri C, De Vito O, Foncin JF, Bruni AC : Correlation between mood disorders and fitness. Am J Med Genet – Neuropsychiatric Genet 2002; 114: 714.
Gundmundsson H, Gudbjartson DF, Kong A et al: Inheritance of human longevity in Iceland. Eur J Hum Genet 2000; 8: 743–749.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by Assessorato alla Sanità, Regione Calabria, and by Associazione per la Ricerca Neurogenetica–Onlus (ARN). BT was supported by a research grant from Association Française contre les Myopathies. We thank Nicoletta Smirne and Cinzia Calignano for transcription of public records into the database, and Antonio Rotella for upgrading and maintaining that database. Municipal officials in N… and S…, and the parish rector of S… generously helped us in our exploration of the archives under their jurisdiction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heyer, E., Toupance, B., Perri, C. et al. Manic depressive illness in a founder population. Eur J Hum Genet 11, 597–602 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201001
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201001