Abstract
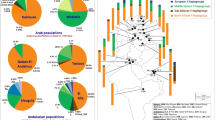
Within Europe, classical genetic markers, nuclear autosomal and Y-chromosome DNA polymorphisms display an east–west frequency gradient. This has been taken as evidence for the westward migration of Neolithic farmers from the Middle East. In contrast, most studies of mtDNA variation in Europe and the Middle East have not revealed clinal distributions. Here we report an analysis of dys44 haplotypes, consisting of 35 polymorphisms on an 8 kb segment of the dystrophin gene on Xp21, in a sample of 1203 Eurasian chromosomes. Our results do not show a significant genetic structure in Europe, though when Middle Eastern samples are included a very low but significant genetic structure, rooted in Middle Eastern heterogeneity, is observed. This structure was not correlated to either geography or language, indicating that neither of these factors are a barrier to gene flow within Europe and/or the Middle East. Spatial autocorrelation analysis did not show clinal variation from the Middle East to Europe, though an underlying and ancient east–west cline across the Eurasian continent was detected. Clines provide a strong signal of ancient major population migration(s), and we suggest that the observed cline likely resulted from an ancient, bifurcating migration out of Africa that influenced the colonizing of Europe, Asia and the Americas. Our study reveals that, in addition to settlements from the Near East, Europe has been influenced by other major population movements, such as expansion(s) from Asia, as well as by recent gene flow from within Europe and the Middle East.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Barbujani G, Bertorelle G : Genetics and the population history of Europe. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 22–25.
Richards M, Corte-Real H, Forster P et al: Paleolithic and neolithic lineages in the European mitochondrial gene pool. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 59: 185–203.
Cavalli-Sforza LL, Minch E : Paleolithic and Neolithic lineages in the European mitochondrial gene pool. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 61: 247–254.
Barbujani G, Bertorelle G, Chikhi L : Evidence for Paleolithic and Neolithic gene flow in Europe. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 62: 488–492.
Ammerman AJ, Cavalli-Sforza LL : The Neolithic Transition and the Genetics of Populations in Europe. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1984.
Dennell R : European Economic Prehistory: A New Approach. London: Academic, 1983.
Menozzi P, Piazza A, Cavalli-Sforza L : Synthetic maps of human gene frequencies in Europeans. Science 1978; 201: 786–792.
Cavalli-Sforza LL, Menozzi P, Piazza A : The History and Geography of Human Genes. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1994.
Piazza A, Rendine S, Minch E, Menozzi P, Mountain J, Cavalli-Sforza LL : Genetics and the origin of European languages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 5836–5840.
Chikhi L, Destro-Bisol G, Bertorelle G, Pascali V, Barbujani G : Clines of nuclear DNA markers suggest a largely neolithic ancestry of the European gene pool. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 9053–9058.
Chikhi L, Destro-Bisol G, Pascali V, Baravelli V, Dobosz M, Barbujani G : Clinal variation in the nuclear DNA of Europeans. Hum Biol 1998; 70: 643–657.
Rosser ZH, Zerjal T, Hurles ME et al: Y-chromosomal diversity in Europe is clinal and influenced primarily by geography, rather than by language. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 67: 1526–1543.
Semino O, Passarino G, Oefner PJ et al: The genetic legacy of paleolithic homo sapiens sapiens in extant europeans: A Y chromosome perspective (in process citation). Science 2000; 290: 1155–1159.
Torroni A, Lott MT, Cabell MF, Chen YS, Lavergne L, Wallace DC : mtDNA and the origin of Caucasians: identification of ancient Caucasian-specific haplogroups, one of which is prone to a recurrent somatic duplication in the D-loop region. Am J Hum Genet 1994; 55: 760–776.
Sajantila A, Lahermo P, Anttinen T et al: Genes and languages in Europe: an analysis of mitochondrial lineages. Genome Res 1995; 5: 42–52.
Comas D, Calafell F, Mateu E, Perez-Lezaun A, Bosch E, Bertranpetit J : Mitochondrial DNA variation and the origin of the Europeans. Hum Genet 1997; 99: 443–449.
Richards MB, Macaulay VA, Bandelt HJ, Sykes BC : Phylogeography of mitochondrial DNA in western Europe. Ann Hum Genet 1998; 62: 241–260.
Simoni L, Calafell F, Pettener D, Bertranpetit J, Barbujani G : Geographic patterns of mtDNA diversity in Europe. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 66: 262–278.
Richards M, Macaulay V, Hickey E et al: Tracing European founder lineages in the near eastern mtDNA pool. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 67: 1251–1276.
Richards M, Macaulay V, Torroni A, Bandelt HJ : In search of geographical patterns in European mitochondrial DNA. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1168–1174.
Zietkiewicz E, Yotova V, Jarnik M et al: Genetic structure of the ancestral population of modern humans. J Mol Evol 1998; 47: 146–155.
Labuda D, Zietkiewicz E, Yotova V : Archaic lineages in the history of modern humans. Genetics 2000; 156: 799–808.
Zietkiewicz E, Yotova V, Jarnik M et al: Nuclear DNA diversity in worldwide distributed human populations. Gene 1997; 205: 161–171.
Hammer MF, Redd AJ, Wood ET et al: Jewish and Middle Eastern non-Jewish populations share a common pool of Y-chromosome biallelic haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 6769–6774.
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P : A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 978–989.
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM : Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992; 131: 479–491.
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L : Arlequin: A Software for Population Genetics Data Analysis. Switzerland: Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, Department of Anthropology, University of Geneva, 2000.
Bertorelle G, Barbujani G : Analysis of DNA diversity by spatial autocorrelation. Genetics 1995; 140: 811–819.
Sokal RR, Oden NL : Spatial autocorrelation in biology. Biol J Linn Soc 1978; 10: 199–249.
Mantel N : The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 1967; 27: 209–220.
Rousset F : Genetic differentiation and estimation of gene flow from F-statistics under isolation by distance. Genetics 1997; 145: 1219–1228.
Excoffier L, Harding RM, Sokal RR, Pellegrini B, Sanchez-Mazas A : Spatial differentiation of RH and GM haplotype frequencies in Sub-Saharan Africa and its relation to linguistic affinities. Hum Biol 1991; 63: 273–307.
Poloni ES, Semino O, Passarino G et al: Human genetic affinities for Y-chromosome P49a,f/TaqI haplotypes show strong correspondence with linguistics. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 61: 1015–1035.
Ruhlen M : A Guide to the World's Languages. London: Edward Arnold, 1987.
Ewens WJ : The sampling theory of selectively neutral alleles. Theor Popul Biol 1972; 3: 87–112.
Sokal RR : Genetic, geographic, and linguistic distances in Europe. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988; 85: 1722–1726.
Cavalli-Sforza LL : Population structure and human evolution. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1966; 164: 362–379.
Tajima F : Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989; 123: 585–595.
Oudet C, Hanauer A, Clemens P, Caskey T, Mandel JL : Two hot spots of recombination in the DMD gene correlate with the deletion prone regions. Hum Mol Genet 1992; 1: 599–603.
Seielstad MT, Minch E, Cavalli-Sforza LL : Genetic evidence for a higher female migration rate in humans. Nat Genet 1998; 20: 278–280.
Sokal RR, Harding RM, Oden NL : Spatial patterns of human gene frequencies in Europe. Am J Phys Anthropol 1989; 80: 267–294.
Zerjal T, Wells RS, Yuldasheva N, Ruzibakiev R, Tyler-Smith C : A genetic landscape reshaped by recent events: Y-chromosomal insights into central Asia. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 466–482.
Cavalli-Sforza LL, Menozzi P, Piazza A : Demic expansions and human evolution. Science 1993; 259: 639–646.
Barbujani G, Pilastro A, De Domenico S, Renfrew C : Genetic variation in North Africa and Eurasia: neolithic demic diffusion vs Paleolithic colonisation. Am J Phys Anthropol 1994; 95: 137–154.
Lahr MM, Foley RA : Multiple dispersals and modern human origins. Evol Anthropol 1994; 3: 48–60.
Lahr MM, Foley RA : Towards a theory of modern human origins: geography, demography, and diversity in recent human evolution. Am J Phys Anthropol 1998; 27 (Suppl): 137–176.
Karafet TM, Zegura SL, Posukh O et al: Ancestral Asian source(s) of new world Y-chromosome founder haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 64: 817–831.
Santos FR, Pandya A, Tyler-Smith C et al: The central Siberian origin for native American Y chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 64: 619–628.
Wells RS, Yuldasheva N, Ruzibakiev R et al: The Eurasian heartland: a continental perspective on Y-chromosome diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 10244–10249.
Brace CL, Nelson AR, Seguchi N et al: Old World sources of the first New World human inhabitants: a comparative craniofacial view. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 10017–10022.
Malhi RS, Smith DG : Brief communication: Haplogroup X confirmed in prehistoric North America. Am J Phys Anthropol 2002; 119: 84–86.
Brown MD, Hosseini SH, Torroni A et al: mtDNA haplogroup X: an ancient link between Europe/Western Asia and North America? Am J Hum Genet 1998; 63: 1852–1861.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all DNA donors who made this study possible. Tina Wambach provided many valuable comments on a draft manuscript. The manuscript was significantly improved, thanks to comments from three anonymous reviewers. This work was supported by a grant (# MOP-12782) from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to DL. FXX was a recipient of a fellowship from the Research Center of Sainte-Justine Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, FX., Yotova, V., Zietkiewicz, E. et al. Human X-chromosomal lineages in Europe reveal Middle Eastern and Asiatic contacts. Eur J Hum Genet 12, 301–311 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201097
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201097
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic polymorphisms of 10 X-STR among four ethnic populations in northwest of China
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)
-
Tracing genetic history of modern humans using X-chromosome lineages
Human Genetics (2007)
-
Genetic variability in a genomic region with long-range linkage disequilibrium reveals traces of a bottleneck in the history of the European population
Human Genetics (2005)