Abstract
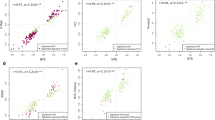
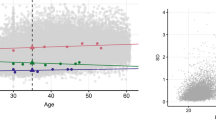
To investigate the genetic influence on X chromosome inactivation and on age-related skewing of X inactivation, in particular, we analysed the X inactivation pattern (XIP) in peripheral blood cells from 118 young monozygotic (MZ) twin pairs (18–53 years), 82 elderly MZ twin pairs (55–94 years), 146 young dizygotic (DZ) twin pairs (20–54 years) and 112 elderly DZ twin pairs (64–95 years). Elderly twins had a higher frequency of skewed X inactivation (34%) than young twins (15%) (P<0.001). Our data suggest that the increase in skewing occurs after age 50–60 years. The intraclass correlation was 0.61 and 0.58 in young and elderly MZ twin pairs, and 0.08 and 0.09 in young and elderly DZ twin pairs. Biometric analysis showed that dominant genetic effects accounted for 63 and 58% of the variance of XIP in the young and elderly twin pairs, respectively. The dominant genetic effect and the shared environment for monochorionic MZ twins may explain the high intraclass correlation for the MZ twin pairs compared to the DZ twin pairs. We did not observe a significant decrease in the intraclass correlation in elderly MZ twins compared to young MZ twins, which would be expected if age-related skewing were due to stochastic factors. We conclude that the increased skewing with age implies that a genetically dependent selection of blood cells take place.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lyon MF : Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L). Nature 1961; 190: 372–373.
Belmont JW : Genetic control of X inactivation and processes leading to X-inactivation skewing. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 1101–1108.
Van den Veyver IB : Skewed X inactivation in X-linked disorders. Semin Reprod Med 2001; 19: 183–191.
Migeon BR, Haisley-Royster C : Familial skewed X inactivation and X-linked mutations: unbalanced X inactivation is a powerful means to ascertain X-linked genes that affect cell proliferation. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 62: 1555–1557; discussion 1557–1558.
Cattanach BM, Perez JN, Pollard CE : Controlling elements in the mouse X-chromosome. II. Location in the linkage map. Genet Res 1970; 15: 183–195.
Naumova AK, Plenge RM, Bird LM et al: Heritability of X chromosome – inactivation phenotype in a large family. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 1111–1119.
Plenge RM, Hendrich BD, Schwartz C et al: A promoter mutation in the XIST gene in two unrelated families with skewed X-chromosome inactivation. Nat Genet 1997; 17: 353–356.
Naumova AK, Olien L, Bird LM et al: Genetic mapping of X-linked loci involved in skewing of X chromosome inactivation in the human. Eur J Hum Genet 1998; 6: 552–562.
Christensen K, Kristiansen M, Hagen-Larsen H et al: X-linked genetic factors regulate hematopoietic stem-cell kinetics in females. Blood 2000; 95: 2449–2451.
Percec I, Plenge RM, Nadeau JH, Bartolomei MS, Willard HF : Autosomal dominant mutations affecting X inactivation choice in the mouse. Science 2002; 296: 1136–1139.
Busque L, Mio R, Mattioli J et al: Nonrandom X-inactivation patterns in normal females: lyonization ratios vary with age. Blood 1996; 88: 59–65.
Abkowitz JL, Catlin SN, Guttorp P : Evidence that hematopoiesis may be a stochastic process in vivo. Nat Med 1996; 2: 190–197.
Champion KM, Gilbert JG, Asimakopoulos FA, Hinshelwood S, Green AR : Clonal haemopoiesis in normal elderly women: implications for the myeloproliferative disorders and myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1997; 97: 920–926.
Gale RE, Fielding AK, Harrison CN, Linch DC : Acquired skewing of X-chromosome inactivation patterns in myeloid cells of the elderly suggests stochastic clonal loss with age. Br J Haematol 1997; 98: 512–519.
Tonon L, Bergamaschi G, Dellavecchia C et al: Unbalanced X-chromosome inactivation in haemopoietic cells from normal women. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 996–1003.
Abkowitz JL, Taboada M, Shelton GH, Catlin SN, Guttorp P, Kiklevich JV : An X chromosome gene regulates hematopoietic stem cell kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 3862–3866.
McGue M, Christensen K : Genetic and environmental contributions to depression symptomatology: evidence from Danish twins 75 years of age and older. J Abnorm Psychol 1997; 106: 439–448.
Christensen K, Gaist D, Jeune B, Vaupel JW : A tooth per child? Lancet 1998; 352: 204.
Skytthe A, Kyvik K, Holm NV, Vaupel JW, Christensen K : The Danish Twin Registry: 127 birth cohorts of twins. Twin Res 2002; 5: 352–357.
Schousboe K, Visscher PM, Henriksen JE, Hopper JL, Sørensen TI, Kyvik KO : Twin study of genetic and environmental influences on glucose tolerance and indices of insulin sensitivity and secretion. Diabetologia 2003; 46: 1276–1283.
Nybo H, Gaist D, Jeune B et al: The Danish 1905 cohort: a genetic-epidemiological nationwide survey. J Aging Health 2001; 13: 32–46.
Kristiansen M, Helland A, Kristensen GB et al: X chromosome inactivation in cervical cancer patients. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2003; 146: 73–76.
Ørstavik KH, Berg K : Skewed X chromosome inactivation pattern in healthy females 83 years or older. Eur J Hum Genet 1998; 6: Suppl 1 A116.
Allen RC, Zoghbi HY, Moseley AB, Rosenblatt HM, Belmont JW : Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet 1992; 51: 1229–1239.
Diggle PJ, Liang KY, Zeger SL : Fitting smooth curves to longitudinal data; in: Atkinson AC, Copas JB, Pierce DA, Schervish MJ, Titterington DM (eds): Analysis of Longitudinal Data. Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1994, pp 41–47.
Nance WE : Do twin Lyons have larger spots? Am J Hum Genet 1990; 46: 646–648.
Hall JG : Twins and twinning. Am J Med Genet 1996; 61: 202–204.
Monteiro J, Derom C, Vlietinck R, Kohn N, Lesser M, Gregersen PK : Commitment to X inactivation precedes the twinning event in monochorionic MZ twins. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 63: 339–346.
Neale MC, Cardon LR : Methodology for Genetic Studies of Twins and Families. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1992.
Akaike H : Factor analysis and AIC. Psychometrika 1987; 52: 317–332.
Neale MC, Boker SM, Xie G, Maes HH : Mx: Statistical Modeling, 6th ed. Richmond, VA: Department of Psychiatry, MCV, 2002.
Looijenga LH, Gillis AJ, Verkerk AJ, van Putten WL, Oosterhuis JW : Heterogeneous X inactivation in trophoblastic cells of human full-term female placentas. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 64: 1445–1452.
Uehara S, Tamura M, Nata M et al: X-chromosome inactivation in the human trophoblast of early pregnancy. J Hum Genet 2000; 45: 119–126.
Fialkow PJ : Primordial cell pool size and lineage relationships of five human cell types. Ann Hum Genet 1973; 37: 39–48.
Puck JM, Stewart CC, Nussbaum RL : Maximum-likelihood analysis of human T-cell X chromosome inactivation patterns: normal women versus carriers of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Am J Hum Genet 1992; 50: 742–748.
Machin G, Keith L : Biology of Twins and Other Multiple Pregnancies. New York, Parthenon, 1999.
Goodship J, Carter J, Burn J : X-inactivation patterns in monozygotic and dizygotic female twins. Am J Med Genet 1996; 61: 205–208.
Cattanach BM : Control of chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet 1975; 9: 1–18.
Johnston PG, Cattanach BM : Controlling elements in the mouse. IV. Evidence of non-random X-inactivation. Genet Res 1981; 37: 151–160.
Plenge RM, Percec I, Nadeau JH, Willard HF : Expression-based assay of an X-linked gene to examine effects of the X-controlling element (Xce) locus. Mamm Genome 2000; 11: 405–408.
Albertini RJ, DeMars R : Mosaicism of peripheral blood lymphocyte populations in females heterozygous for the Lesch-Nyhan mutation. Biochem Genet 1974; 11: 397–411.
Tomkins DJ, McDonald HL, Farrell SA, Brown CJ : Lack of expression of XIST from a small ring X chromosome containing the XIST locus in a girl with short stature, facial dysmorphism and developmental delay. Eur J Hum Genet 2002; 10: 44–51.
Hoffman EP, Pegoraro E : Skewed X inactivation can be inherited as a Mendelian trait in humans. Am J Hum Genet 1995; Suppl 57: A49.
Ørstavik KH, Ørstavik RE, Schwartz M : Skewed X chromosome inactivation in a female with haemophilia B and in her non-carrier daughter: a genetic influence on X chromosome inactivation? J Med Genet 1999; 36: 865–866.
Derom R, Derom C, Vlietinck R : Placentation; in: Keith LG, Papiernik E, Keith DM, Luke B (eds): Multiple Pregnancy: Epitemiology, Gestation and Perinatal Outcome. Parthenon Publishing: New York, 1995, pp 113–128.
Chitnis S, Derom C, Vlietinck R, Derom R, Monteiro J, Gregersen PK : X chromosome-inactivation patterns confirm the late timing of monoamniotic–MZ twinning. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 65: 570–571.
Trejo V, Derom C, Vlietinck R et al: X chromosome inactivation patterns correlate with fetal-placental anatomy in monozygotic twin pairs: implications for immune relatedness and concordance for autoimmunity. Mol Med 1994; 1: 62–70.
Sharp A, Robinson D, Jacobs P : Age- and tissue-specific variation of X chromosome inactivation ratios in normal women. Hum Genet 2000; 107: 343–349.
Hatakeyama C, Anderson C, Beever C, Penaherrera M, Brown C, Robinson W : The dynamics of X-inactivation skewing as women age. Clin Genet 2004; 66: 327–332.
Vickers MA, McLeod E, Spector TD, Wilson IJ : Assessment of mechanism of acquired skewed X inactivation by analysis of twins. Blood 2001; 97: 1274–1281.
Cazzola M, May A, Bergamaschi G, Cerani P, Rosti V, Bishop DF : Familial-skewed X-chromosome inactivation as a predisposing factor for late-onset X-linked sideroblastic anemia in carrier females. Blood 2000; 96: 4363–4365.
Au WY, Ma ES, Lam VM, Chan JL, Pang A, Kwong YL : Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in elderly Chinese women heterozygous for G6PD variants. Am J Med Genet 2004; 129A: 208–211.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Council of Norway, The Norwegian Cancer Association, US National Institute on Aging (AG-08761), the Danish Interdisciplinary Research Council, and the Danish National Research Foundation to KC, and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) operating grant to AKN. MK and GPSK are Research Council of Norway scholarship recipients. AKN is a CIHR New Investigator. We acknowledge Thore Egeland for statistical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kristiansen, M., Knudsen, G., Bathum, L. et al. Twin study of genetic and aging effects on X chromosome inactivation. Eur J Hum Genet 13, 599–606 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201398
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201398
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
X chromosome inactivation skewing is common in advanced carotid atherosclerotic lesions in females and predicts secondary peripheral artery events
Biology of Sex Differences (2023)
-
A novel quantitative targeted analysis of X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) using nanopore sequencing
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
X-linked dystonia parkinsonism: epidemiology, genetics, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment
Acta Neurologica Belgica (2023)
-
X-chromosome inactivation patterns depend on age and tissue but not conception method in humans
Chromosome Research (2023)
-
Equivalent DNA methylation variation between monozygotic co-twins and unrelated individuals reveals universal epigenetic inter-individual dissimilarity
Genome Biology (2021)