Abstract
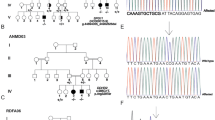
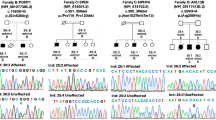
Autosomal recessive ulcero-mutilating neuropathy with spastic paraplegia is a very rare disease since only few cases were described up to date. We report in this study a consanguineous Moroccan family with four affected males with this syndrome. The disease onset was in early infancy, with spastic paraplegia and sensory loss leading to mutilating acropathy. Electrophysiological studies revealed a severe axonal sensory neuropathy, magnetic resonance imaging ruled out compression of spinal cord and biological investigations showed decreased levels of Apo B, total cholesterol and triglycerides. A genomewide search was conducted in this family and linkage was found to chromosome 5p. Analysis of recombination events and LOD score calculation map the responsible gene in a 25 cM genetic interval between markers D5S2054 and D5S648. A maximum LOD score value of 3.92 was obtained for all markers located in this candidate interval. This study establishes the presence of a locus for autosomal recessive mutilating sensory neuropathy with spastic paraplegia on chromosome 5p15.31–14.1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Reilly MM, Hanna MG : Genetic neuromuscular disease. Neurol Pract 2002; 73: ii12–ii21.
Van Epps C, Kerr HD : Familial lumbosarcal syringomyelia. Radiology 1940; 35: 160–173.
Khalifeh RR, Zellweger H : Hereditary sensory neuropathy with spinal cord disease. Neurology 1963; 13: 405–411.
Koenig RH, Spiro AJ : Hereditary spastic paraplegia with sensory neuropathy. Dev Med Child Neurol 1970; 12: 576–581.
Cavanagh NP, Eames RA, Calvin RJ, Brett EM, Kelly RE : Hereditary sensory neuropathy with spastic paraplegia. Brain 1979; 102: 79–94.
Thomas PK, Misra VP, King HM et al: Autosomal recessive hereditary sensory neuropathy with spastic paraplegia. Brain 1994; 117: 651–659.
Tenembaum SN, Reisin RC, Taratuto AL, Fejerman N : Spastic paraplegia and sensory neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 1996; 19: 649–653.
Kherbaoui-Redouani L, Ploton D, Abely M et al: Hereditary sensory neuropathy with spastic paraplegia. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2004; 8: 95–99.
Adams RH, Betz H, Puschel AW : A novel class of murine semaphorins with homology to thrombospondin is differentially expressed during early embryogenesis. Mech Dev 1996; 57: 33–45.
Yokota S, Yanagi H, Yura T, Kubota H : Cytosolic chaperonin-containing t-complex polypeptide 1 changes the content of a particular subunit species concomitant with substrate binding and folding activities during the cell cycle. Eur J Biochem 2001; 268: 4664–4673.
Lee MJ, Stephenson DA, Groves MJ et al: Hereditary sensory neuropathy is caused by a mutation in the delta subunit of the cytosolic chaperonin-contaning t-complex peptide-1 (Cct4) gene. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 1917–1925.
Hansen JJ, Dürr A, Cournu I et al: Hereditary spastic paraplegia SPG13 is associated with a mutation in the gene encoding the Mitochondrial chaperonin Hsp60. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 70: 1328–1332.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the family members for their cooperation throughout this study. This research was supported by the Presidency of the University Mohamed V – Souissi (Rabat, Morocco), and the Association Marocaine de Neurogénétique (Morocco). We are grateful for Genome Biotechnology SARL for their collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouhouche, A., Benomar, A., Bouslam, N. et al. Autosomal recessive mutilating sensory neuropathy with spastic paraplegia maps to chromosome 5p15.31–14.1. Eur J Hum Genet 14, 249–252 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201537
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201537
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A review of the genetic spectrum of hereditary spastic paraplegias, inherited neuropathies and spinal muscular atrophies in Africans
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2022)
-
Lipid chaperones and associated diseases: a group of chaperonopathies defining a new nosological entity with implications for medical research and practice
Cell Stress and Chaperones (2020)
-
Bridging human chaperonopathies and microbial chaperonins
Communications Biology (2019)
-
Hereditary spastic paraplegia: clinico-pathologic features and emerging molecular mechanisms
Acta Neuropathologica (2013)
-
Mechanisms of disease in hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies
Nature Reviews Neurology (2012)