Abstract
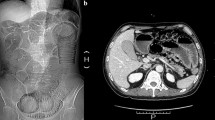
Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIIP) is a rare and severe clinical syndrome characterized by symptoms and signs of intestinal occlusion, in the absence of any mechanical obstruction of the gut lumen. In the attempt to identify the genetic basis of CIIP, we analyzed a Turkish pedigree with a high degree of consanguinity in which three siblings presented with a syndromic form of CIIP. All affected family members were characterized by recurrent, self-limiting subocclusive episodes, long-segment Barrett esophagus, and a variety of minor cardiac valve or septal defects. In some patients full-thickness intestinal biopsy samples were obtained and tissues were processed for immunohistochemistry using antibodies to different markers of the intestinal neuromuscular tract. Full-thickness biopsies of the gut wall showed abnormalities of both the neural and muscular components suggesting an underlying intestinal neuro-myopathy. Blood samples were collected for DNA extraction from each available family member and DNAs were genotyped using 382 microsatellites spanning the entire genome with the aim to take advantage of the homozygosity mapping approach. Linkage analysis identified a new syndromic locus on chromosome 8q23–q24 (multipoint LOD score=5.01). Our data strongly support the presence of a new genetic locus associated with CIIP, long-segment Barrett esophagus, and cardiac involvement on chromosome 8.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Malagelada JR, Camilleri M, Stanghellini V : Manometric Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders. New York: Thieme, 1986.
Stanghellini V, Corinaldesi R, Barbara L : Pseudo-obstruction syndromes. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol 1988; 2: 225–254.
De Giorgio R, Stanghellini V, Barbara G et al: Primary enteric neuropathies underlying gastrointestinal motor dysfunction. Scand J Gastroenterol 2000; 35: 114–121.
Stanghellini V, Cogliandro R, De Giorgio R et al: Natural history of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adults: a single center study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 3: 449–458.
Camilleri M, Phillips SF : Acute and chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Adv Intern Med 1991; 36: 287–306.
Di Lorenzo C : Pseudo-obstruction: current approaches. Gastroenterology 1999; 116: 980–987.
Coulie B, Camilleri M : Intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Annu Rev Med 1999; 50: 37–55.
Krishnamurthy S, Schuffler MD : Pathology of neuromuscular disorders of the small intestine and colon. Gastroenterology 1987; 93: 610–639.
De Giorgio R, Sarnelli G, Corinaldesi R, Stanghellini V : Advances in our understanding of the pathology of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Gut 2004; 53: 1549–1552.
Schuffler MD, Pope CE : Studies of idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. II. Hereditary hollow visceral myopathy: family studies. Gastroenterology 1977; 73: 339–344.
Roper EC, Gibson A, McAlindon ME et al: Familial visceral neuropathy: a defined entity? Am J Med Genet 2005; 137: 249–254.
Tanner MS, Smith B, Lloyd JK : Functional intestinal obstruction due to deficiency of argyrophil neurones in the myenteric plexus. Familial syndrome presenting with short small bowel, malrotation, and pyloric hypertrophy. Arch Dis Chil 1976; 51: 837–841.
Auricchio A, Brancolini V, Casari G et al: The locus for a novel syndromic form of neuronal intestinal pseudoobstruction maps to Xq28. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 743–748.
FitzPatrick DR, Strain L, Thomas AE et al: Neurogenic chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, patent ductus arteriosus, and thrombocytopenia segregating as an X-linked recessive disorder. J Med Genet 1997; 34: 666–669.
De Giorgio R, Seri M, Cogliandro R et al: Analysis of candidate genes for intrinsic neuropathy in a family with chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Clin Genet 2001; 59: 131–133.
Nishino I, Spinazzola A, Hirano M : Thymidine phosphorylase gene mutations in MNGIE, a human mitochondrial disorder. Science 1999; 283: 689–692.
Van Goethem G, Schwartz M, Lofgren A, Dermaut B, Van Broeckhoven C, Vissing J : Novel POLG mutations in progressive external ophthalmoplegia mimicking mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy. Eur J Hum Genet 2003; 11: 547–549.
Pingault V, Girard M, Bondurand N et al: SOX10 mutations in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction suggest a complex physiopathological mechanism. Hum Genet 2002; 111: 198–206.
Mungan Z, Akyuz F, Bugra Z et al: Familial visceral myopathy with pseudo-obstruction, megaduodenum, Barrett's esophagus, and cardiac abnormalities. Am J Gastroenterol 2003; 98: 2556–2560.
De Giorgio R, Barbara G, Stanghellini V et al: Clinical and morphofunctional features of idiopathic myenteric ganglionitis underlying severe intestinal motor dysfunction: a study of three cases. Am J Gastroenterol 2002; 97: 2454–2459.
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ : Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature 1990; 348: 334–336.
Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve-Daly MP, Lander ES : Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 1347–1363.
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE : PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 63: 259–266.
Thiele H, Nurnberg P : HaploPainter: a tool for drawing pedigrees with complex haplotypes. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 1730–1732.
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM, Julier C, Ott J : Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1984; 81: 3443–3446.
Sobel E, Lange K : Descent graphs in pedigree analysis: applications to haplotyping, location scores, and marker-sharing statistics. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 1323–1337.
Seve M, Chimienti F, Devergnas S, Favier A : In silico identification and expression of SLC30 family genes: an expressed sequence tag data mining strategy for the characterization of zinc transporters’ tissue expression. BMC Genomics 2004; 5: 32.
Ohtani K, Suzuki Y, Eda S et al: Molecular cloning of a novel human collectin from liver (CL-L1). J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 13681–13689.
Yoshizawa K, Inaba K, Mannen H, Kikuchi T, Mizutani M, Tsuji S : Analyses of beta-1 syntrophin, syndecan 2 and gem GTPase as candidates for chicken muscular dystrophy. Exp Anim 2003; 52: 391–396.
Bott L, Boute O, Mention K, Vinchon M, Boman F, Gottrand F : Congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction and hydrocephalus with stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius. Am J Med Genet 2004; 130: 84–87.
Peters JH, Hagen JA, DeMeester SR : Barrett's esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg 2004; 8: 1–17.
Flejou JF : Barrett's oesophagus: from metaplasia to dysplasia and cancer. Gut 2005; 54 (Suppl 1): i6–i12.
Hu FZ, Preston RA, Post JC et al: Mapping of a gene for severe pediatric gastroesophageal reflux to chromosome 13q14. JAMA 2000; 284: 325–334.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (COFIN Project No. 2004062155 to RDeG, 2004055120 to GB and 2003064378 to RDeG, GB and VS), by grants from FIRB Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research and from the European Commission (Project QLRT-2000-01646) to GR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deglincerti, A., De Giorgio, R., Cefle, K. et al. A novel locus for syndromic chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction maps to chromosome 8q23–q24. Eur J Hum Genet 15, 889–897 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201844
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201844
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The enteric nervous system in gastrointestinal disease etiology
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Mutations in SGOL1 cause a novel cohesinopathy affecting heart and gut rhythm
Nature Genetics (2014)