Summary
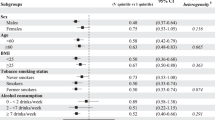
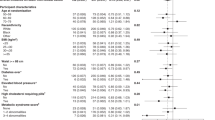
Although several dietary compounds are hypothesized to have anticarcinogenic properties, the role of specific micronutrients in the development of breast cancer remains unclear. To address this issue, we assessed intake of retinol, β-carotene, vitamin C and vitamin E in relation to breast cancer risk in a case–control study in Greece. Eight hundred and twenty women with histologically confirmed breast cancer were compared with 1548 control women. Dietary data were collected through a 115-item semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. Data were modelled by logistic regression, with adjustment for total energy intake and established breast cancer risk factors, as well as mutual adjustment among the micronutrients. Among post-menopausal women, there was no association between any of the micronutrients evaluated and risk of breast cancer. Among premenopausal women, β-carotene, vitamin C and vitamin E were each inversely associated with breast cancer risk, but after mutual adjustment among the three nutrients only β-carotene remained significant; the odds ratio (OR) for a one-quintile increase in β-carotene intake was 0.84 (95% confidence interval 0.73–0.97). The inverse association observed with β-carotene intake, however, is slightly weaker than the association previously observed with vegetable intake in these data, raising the possibility that the observed β-carotene effect is accounted for by another component of vegetables.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Albanes, D. (1987). Total calories, body weight, and tumor incidence in mice. Cancer Res 47: 1987–1992.
Ames, B. N. (1983). Dietary carcinogens and anticarcinogens. Oxygen radicals and degenerative diseases. Science 221: 1256–1264.
Block, G. (1991). Vitamin C and cancer prevention: the epidemiologic evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 53: 270S–282S.
Breslow, N. E. & Day, N. E. (1980). The analysis of case–control studies. Statistical Methods in Cancer Research. Vol. 1. IARC scientific publication no. 32. International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon
Buell, P. (1973). Changing incidence of breast cancer in Japanese–American women. J Natl Cancer Inst 51: 1479–1483.
Ewertz, M. & Gill, C. (1990). Dietary factors and breast cancer risk in Denmark. Int J Cancer 46: 779–784.
Freudenheim, J. L., Marshall, J. R., Vena, J. E., Laughlin, R., Brasure, J. R., Swanson, M. K., Nemoto, T. & Graham, S. (1996). Premenopausal breast cancer risk and intake of vegetables, fruits, and related nutrients. J Natl Cancer Inst 88: 340–348.
Gerber, M., Richardson, S., Cavallo, F., Marubini, E., Crastes de Paulet, P., Crastes de Paulet, A. & Pujol, H. (1990). The role of diet history and biologic assays in the study of ‘diet and breast cancer’. Tumori 76: 321–330.
Gnardellis, C., Trichopoulou, A., Katsouyanni, K., Polychronopoulos, E., Rimm, E. B. & Trichopoulos, D. (1995). Reproducibility and validity of an extensive semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among Greek school teachers. Epidemiology 6: 74–77.
Graham, S., Dayal, H., Swanson, M., Mittelman, A. & Wilkinson, G. (1978). Diet in the epidemiology of cancer of the colon and rectum. J Natl Cancer Inst 61: 709–714.
Graham, S., Marshall, J., Mettlin, C., Rzepka, T., Nemoto, T. & Byers, T. (1982). Diet in the epidemiology of breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol 116: 68–75.
Graham, S., Hellmann, R., Marshall, J., Freudenheim, J., Vena, J., Swanson, M., Zielezny, M., Nemoto, T., Stubbe, N. & Raimondo, T. (1991). Nutritional epidemiology of postmenopausal breast cancer in western New York. Am J Epidemiol 134: 552–566.
Graham, S., Zielezny, M., Marshall, J., Priore, R., Freudenheim, J., Brasure, J., Haughey, B., Nasca, P. & Zdeb, M. (1992). Diet in the epidemiology of postmenopausal breast cancer in the New York State Cohort. Am J Epidemiol 136: 1327–1337.
Greenberg, E. R., Baron, J. A., Stukel, T. A., Stevens, M. M., Mandel, J. S., Spencer, S. K., Elias, P. M., Lowe, N., Nierenberg, D. W., Bayrd, G., Vance, J. C., Freeman, D. H., Clendenning, W. E. & Kwan, T., the Skin Cancer Prevention Study Group (1990). A clinical trial of beta carotene to prevent basal-cell and squamous-cell cancers of the skin. N Engl J Med 323: 789–795, [Erratum, N Engl J Med (1991) 325: 1324]
Greenberg, E. R., Baron, J. A., Tosteson, T. D., Freeman, D. H., Beck, G. J., Bond, J. H., Colacchio, T. A., Coller, J. A., Frankl, H. D., Haile, R. W., Mandel, J. S., Nierenberg, D. W., Rothstein, R., Snover, D. C., Stevens, M. M., Summers, R. W. & Van Stolk, R. U. (1994). for the Polyp Prevention Study Group A clinical trial of antioxidant vitamins to prevent colorectal adenoma. N Engl J Med 331: 141–147.
Hennekens, C. H., Buring, J. E., Manson, J. E., Stampfer, M., Rosner, B., Cook, N. R., Belanger, C., LaMotte, F., Gaziano, J. M., Ridker, P. M., Willett, W. & Peto, R. (1996). Lack of effect of long-term supplementation with beta carotene on the incidence of malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 334: 1145–1149.
Holmberg, L., Ohlander, E. M., Byers, T., Zack, M., Wolk, A., Bergstrom, R., Bergkvist, L., Thurfjell, E., Bruce, A. & Adami, H-O (1994). Diet and breast cancer risk: results from a population-based case–control study in Sweden. Arch Intern Med 154: 1805–1811.
Howe, G. R., Hirohata, T., Hislop, T. G., Iscovich, J. M., Yuan, J-M, Katsouyanni, K., Lubin, F., Marubini, E., Modan, B., Rohan, T., Toniolo, P. & Shunzhang, Y. (1990). Dietary factors and risk of breast cancer: combined analysis of 12 case–control studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 561–569.
Hunter, D. J. & Willett, W. C. (1996). Nutrition and breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control 7: 56–68.
Hunter, D. J., Manson, J. E., Colditz, G. A., Stampfer, M. J., Rosner, B., Hennekens, C. H., Speizer, F. E. & Willett, W. C. (1993). A prospective study of the intake of vitamins C, E, and A and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 329: 234–240.
Ingram, D. M., Nottage, E. & Roberts, T. (1991). The role of diet in the development of breast cancer: a case–control study of patients with breast cancer, benign epithelial hyperplasia and fibrocystic disease of the breast. Br J Cancer 64: 187–191.
Iscovich, J. M., Iscovich, R. B., Howe, G., Shiboski, S. & Kaldor, J. M. (1989). A case–control study of diet and breast cancer in Argentina. Int J Cancer 44: 770–776.
Katsouyanni, K., Willett, W., Trichopoulos, D., Boyle, P., Trichopoulou, A., Vasilaros, S., Papadiamantis, J. & MacMahon, B. (1988). Risk of breast cancer among Greek women in relation to nutrient intake. Cancer 61: 181–185.
Katsouyanni, K., Skalkidis, Y., Petridou, E., Polychronopoulou-Trichopoulou, A., Willett, W. & Trichopoulos, D. (1991 a). Diet and peripheral arterial occlusive disease: the role of poly-, mono-, and saturated fatty acids. Am J Epidemiol 133: 24–31.
Katsouyanni, K., Trichopoulou, A., Trichopoulos, D. & Willett, W. (1991 b). Dietary Variability in Greece. A Report to the Secretaria of Research and Technology. 1–64, Ministery of Industry, Research and Technology: Athens
Katsouyanni, K., Trichopoulou, A., Stuver, S., Garas, Y., Kritselis, A., Kyriakou, G., Stoikidou, M., Boyle, P. & Trichopoulos, D. (1994 a). The association of fat and other macronutrients with breast cancer: a case–control study from Greece. Br J Cancer 70: 537–541.
Katsouyanni, K., Trichopoulou, A., Stuver, S., Vassilaros, S., Papadiamantis, Y., Bournas, N., Skarpou, N., Mueller, N. & Trichopoulos, D. (1994 b). Ethanol and breast cancer: an association that may be both confounded and causal. Int J Cancer 58: 356–361.
Katsouyanni, K., Rimm, E. B., Gnardellis, C., Trichopoulos, D., Polychronopoulos, E. & Trichopoulou, A. (1997). Reproducibility and relative validity of an extensive semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire using dietary records and biochemical markers among Greek schoolteachers. Int J Epidemiol 26: S118–S127.
Kushi, L. H., Fee, R. M., Sellers, T. A., Zheng, W. & Folsom, A. R. (1996). Intake of vitamins A, C, and E and postmenopausal breast cancer: the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Am J Epidemiol 144: 165–174.
Landa, M-C, Frago, N. & Tres, A. (1994). Diet and the risk of breast cancer in Spain. Eur J Cancer Prev 3: 313–320.
La Vecchia, C., Decarli, A., Franceschi, S., Gentile, A., Negri, E. & Parazzini, F. (1987). Dietary factors and the risk of breast cancer. Nutr Cancer 10: 205–214.
Lee, H. P., Gourley, L., Duffy, S. W., Esteve, J., Lee, J. & Day, N. E. (1991). Dietary effects on breast-cancer risk in Singapore. Lancet 337: 1197–1200.
Lee, H. P., Gourley, L., Duffy, S. W., Esteve, J., Lee, J. & Day, N. E. (1992). Risk factors for breast cancer by age and menopausal status: a case–control study in Singapore. Cancer Causes Control 3: 313–322.
Levi, F., La Vecchia, C., Gulie, C. & Negri, E. (1993). Dietary factors and breast cancer risk in Vaud, Switzerland. Nutr Cancer 19: 327–335.
London, S. J., Stein, E. A., Henderson, I. C., Stampfer, M. J., Wood, W. C., Remine, S., Dmochowski, J. R., Robert, N. J. & Willett, W. C. (1992). Carotenoids, retinol, and vitamin E and risk of proliferative benign breast disease and breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control 3: 503–512.
Marubini, E., Decarli, A., Costa, A., Mazzoleni, C., Andreoli, C., Barbieri, A., Capitelli, E., Carlucci, M., Cavallo, F., Monferroni, N., Pastorino, U. & Salvini, S. (1988). The relationship of dietary intake and serum levels of retinol and beta-carotene with breast cancer: results of a case–control study. Cancer 61: 173–180.
Negri, E., La Vecchia, C., Franceschi, S., D’Avanzo, B., Talamini, R., Parpinel, M., Ferraroni, M., Filiberti, R., Montella, M., Falcini, F., Conti, E. & Decarli, A. (1996). Intake of selected micronutrients and the risk of breast cancer. Int J Cancer 65: 140–144.
Omenn, G. S., Goodman, G. E., Thornquist, M. D., Balmes, J., Cullen, M. R., Glass, A., Keogh, J. P., Meyskens, F. L., Valanis, B., Williams, J. H., Barnhart, S. & Hammar, S. (1996). Effects of a combination of beta carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 334: 1150–1155.
Paganini-Hill, A., Chao, A., Ross, R. K. & Henderson, B. E. (1987). Vitamin A, β-carotene, and the risk of cancer: a prospective study. J Natl Cancer Inst 79: 443–448.
Peto, R., Doll, R., Buckley, J. D. & Sporn, M. B. (1981). Can dietary beta-carotene materially reduce human cancer rates?. Nature 290: 201–208.
Potter, J. D. & Steinmetz, K. (1996). Vegetables, fruit and phytoestrogens as preventive agents. Principles of Chemoprevention, Stewart BW, McGregor D, Kleihues P (eds), pp. 61–90, International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon
Richardson, S., Gerber, M. & Cenee, S. (1991). The role of fat, animal protein and some vitamin consumption in breast cancer: a case–control study in southern France. Int J Cancer 48: 1–9.
Rohan, T. E., McMichael, A. J. & Baghurst, P. A. (1988). A population-based case–control study of diet and breast cancer in Australia. Am J Epidemiol 128: 478–489.
Rohan, T. E., Howe, G. R., Friedenreich, C. M., Jain, M. & Miller, A. B. (1993). Dietary fiber, vitamins A, C, and E, and risk of breast cancer: a cohort study. Cancer Causes Control 4: 29–37.
Sankaranarayanan, R., Mathew, B., Varghese, C., Sudhakaran, P. R., Menon, V., Jayadeep, A., Nair, M. K., Mathews, C., Mahalingam, T. R., Balaram, P. & Nair, P. P. (1997). Chemoprevention of oral leukoplakia with vitamin A and beta carotene: an assessment. Oral Oncol 33: 231–236.
Shimizu, H., Ross, R. K., Bernstein, L., Yatani, R., Henderson, B. E. & Mack, T. M. (1991). Cancers of the prostate and breast among Japanese and white immigrants in Los Angeles County. Br J Cancer 63: 963–966.
Sporn, M. B. & Roberts, A. B. (1983). Role of retinoids in differentiation and carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 43: 3034–3040.
Steinmetz, K. A. & Potter, J. D. (1991). Vegetables, fruit, and cancer. II. Mechanisms. Cancer Causes Control 2: 427–442.
Tannenbaum, A. (1942). The genesis and growth of tumors. III. Effects of a high-fat diet. Cancer Res 2: 468–475.
The Alpha-Tocopherol Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study Group (1994). The effect of vitamin E and beta carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers. N Engl J Med 330: 1029–1035.
Thomas, D. B. & Karagas, M. R. (1987). Cancer in first and second generation Americans. Cancer Res 47: 5771–5776.
Toniolo, P., Riboli, E., Protta, F., Charrel, M. & Cappa, A. P. M. (1989). Calorie-providing nutrients and risk of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 81: 278–286.
Trichopoulou, A. (1992). Composition of Greek Foods and Dishes. Athens School of Public Health: Athens
Trichopoulou, A., Katsouyanni, K., Stuver, S., Tzala, L., Gnardellis, C., Rimm, E. & Trichopoulos, D. (1995). Consumption of olive oil and specific food groups in relation to breast cancer risk in Greece. J Natl Cancer Inst 87: 110–116.
Van’t Veer, P., Kolb, C. M., Verhoef, P., Kok, F. J., Schouten, E. G., Hermus, R. J. J. & Sturmans, F. (1990). Dietary fiber, beta-carotene and breast cancer: results from a case–control study. Int J Cancer 45: 825–828.
Verhoeven, D. T. H., Assen, N., Goldbohm, R. A., Dorant, E., Van’t Veer, P., Sturmans, F., Hermus, R. J. J. & Van den Brandt, P. A. (1997). Vitamins C and E, retinol, beta-carotene and dietary fibre in relation to breast cancer risk: a prospective cohort study. Br J Cancer 75: 149–155.
Yuan, J-M, Wang, Q-S, Ross, R. K., Henderson, B. E. & Yu, M. C. (1995). Diet and breast cancer in Shanghai and Tianjin, China. Br J Cancer 71: 1353–1358.
Zaridze, D., Lifanova, Y., Maximovitch, D., Day, N. E. & Duffy, S. W. (1991). Diet, alcohol consumption and reproductive factors in a case–control study of breast cancer in Moscow. Int J Cancer 48: 493–501.
Ziegler, R. G., Hoover, R. N., Pike, M. C., Hildesheim, A., Nomura, A. M. Y., West, D. W., Wu-Williams, A. H., Kolonel, L. N., Horn-Ross, P. L., Rosenthal, J. F. & Hyer, M. B. (1993). Migration patterns and breast cancer risk in Asian–American women. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 1819–1827.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Bohlke, K., Spiegelman, D., Trichopoulou, A. et al. Vitamins A, C and E and the risk of breast cancer: results from a case-control study in Greece. Br J Cancer 79, 23–29 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690006
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690006
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic applications of bacterial pigments: a review of current status and future opportunities
3 Biotech (2018)
-
Carotenoids and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis and meta-regression
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2012)
-
Retinol, vitamins A, C, and E and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis and meta-regression
Cancer Causes & Control (2011)
-
Vitamin supplement use and risk for breast cancer: the Shanghai Breast Cancer Study
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2008)