Summary
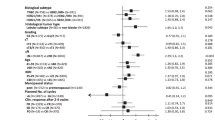
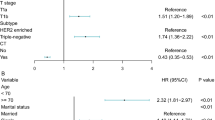
There is controversy regarding the prognostic value of cathepsin-D in primary breast cancer. An increased level of cathepsin-D in tumour extracts has been found to be associated with a poor relapse-free and overall survival. Studies performed with immunohistochemistry or Western blotting have produced diverse results. We have analysed 2810 cytosolic extracts obtained from human primary breast tumours for cathepsin-D expression, and have correlated their levels with prognosis. The median follow-up of the patients still alive was 88 months. Patients with high cathepsin-D levels had a significantly worse relapse-free and overall survival, also in multivariate analysis (P < 0.0001). Adjuvant therapy which was associated with an improved prognosis in node-positive patients in univariate analysis, also significantly added to the multivariate models for relapse-free and overall survival. There were no statistically significant interactions between the levels of cathepsin-D and any of the classical prognostic factors in analysis for relapse-free survival, suggesting that the prognostic value of cathepsin-D is not different in the various subgroups of patients. Indeed, multivariate analyses in subgroups of node-negative and -positive patients, pre- and post-menopausal patients, and their combinations, showed that tumours with high cathepsin-D values had a significantly poor relapse-free survival, with relative hazard rates ranging from 1.3 to 1.5, compared with tumours with low cathepsin-D levels. The results presented here on 2810 patients confirm that high cytosolic cathepsin-D values are associated with poor prognosis in human primary breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Barlow, R. E., Bartholomew, D. J., Bremner, J. M. & Brunk, H. D. (1972). Statistical Interference Under Order Restrictions, John Wiley & Sons: London
Benraad, T. h., Geurts-Moespot, A., Sala, M., Piffanelli, A. & Ross, A., Foekens, J. A. on behalf of the EORTC Receptor Study Group (1992). Quality control of cathepsin D measurement by the EORTC Receptor Study Group. Eur J Cancer 28: 72–75.
Briozzo, P., Morisset, M., Capony, F., Rougeot, C. & Rochefort, H. (1988). In vitro degradation of extracellular matrix with Mr 52 000 cathepsin D secreted by breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 48: 3688–3692.
Briozzo, P., Badet, J., Capony, F., Pieri, I., Montcourrier, P., Barritault, D. & Rochefort, H. (1991). MCF-7 mammary cancer cells respond to bFGF and internalize it following its release from extracellular matrix: a permissive role of cathepsin D. Exp Cell Res 194: 252–259.
Cardiff, R. D. (1994). Cathepsin D and breast cancer: useful?. Hum Pathol 25: 847–848.
Conover, C. A. & De Leon, D. D. (1994). Acid-activated insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 proteolysis in normal and transformed cells: role of cathepsin D. J Biol Chem 269: 7076–7080.
Cox, D. R. (1972). Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc 34: 187–220.
Duffy, M. J., O’Grady, P., Devaney, D., O’Sorian, L., Fennelly, J. J. & Lijnen, H. J. (1988). Urokinase-plasminogen activator, a marker for aggressive breast cancers. Cancer 62: 531–533.
Domagala, W., Striker, G., Szadowska, A., Dukowicz, A., Weber, K. & Osborn, M. (1992). Cathepsin D in invasive ductal NOS breast carcinoma as defined by immunohistochemistry: no correlations with survival at 5 years. Am J Pathol 141: 1003–1012.
Emmert-Buck, M. R. (1996). Cathepsin D and prognosis in breast cancer: one piece of a larger puzzle?. Hum Pathol 27: 869–871.
EORTC Breast Cancer Cooperative Group (1980). Revision of the standards for the assessment of hormone receptors in human breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 16: 1513–1515.
Ferrandina, G., Scambia, G., Bardelli, F., Panici, P. B. & Massori, A. (1997). Relationship between cathepsin-D content and disease-free survival in node-negative breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 76: 661–666.
Foekens, J. A., Portengen, H., van Putten, W. L. J., Peters, H. A., Krijnen, HLJM, Alexieva-Figusch, J. & Klijn, J. G. M. (1989). Prognostic value of estrogen and progesterone receptors measured by enzyme immunoassays in human breast tumor cytosols. Cancer Res 49: 5823–5828.
Foekens, J. A., van Putten, W. L. J., Portengen, H., de Koning, HYWCM, Thirion, B., Alexieva-Figusch, J. & Klijn, J. G. M. (1993). Prognostic value of PS2 and cathepsin D in 710 human primary breast tumors: multivariate analysis. J Clin Oncol 11: 899–908.
Foekens, J. A., Schmitt, M., van Putten, W. L. J., Peters, H. A., Portengen, H., Kramer, M. D., Jänicke, F. & Klijn, J. G. M. (1994). Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and prognosis in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 12: 1648–1658.
Foekens, J. A., Berns, EMJJ, Look, M. P. & Klijn, J. G. M. (1996). Prognostic factors in node-negative breast cancer (1996). In Hormone-Dependent Cancer, Pasqualini JR, Katzenellebogen BS (eds), pp. 217–252, Marcel Dekker: New York
Garcia, M., Derocq, D., Pujol, P. & Rochefort, H. (1990). Overexpression of transfected cathepsin D in transformed cells increases their malignant phenotype and metastatic potency. Oncogene 5: 1809–1814.
Gray, R. J. (1992). Flexible methods for analyzing survival data using splines, with applications to breast cancer prognosis. J Am Stat Assoc 87: 942–952.
Henry, J. A., McCarthy, A. L., Angus, B., Westley, B. R., May, F. E. B., Nicholson, S., Cairns, J., Harris, A. L. & Horne, C. H. W. (1990). Prognostic significance of the estrogen-regulated protein, cathepsin D, in breast cancer. Cancer 65: 265–271.
Isola, J., Weitz, S., Visakorpi, T., Holli, K., Shea, R., Khabbaz, N. & Kallioniemi, O. P. (1993). Cathepsin D expression detected by immunohistochemistry has independent prognostic value in axillary node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 11: 36–43.
Jänicke, F., Schmitt, M., Hafter, R., Hollreider, A., Babic, R., Ulm, K., Grössner, W. & Graeff, H. (1990). Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PA) antigen is a predictor of early relapse in breast cancer. Fibrinolysis 4: 69–78.
Joensuu, H., Toikkanen, S. & Isola, J. (1995). Stromal cell cathepsin D expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 71: 155–159.
Kaplan, E. L. & Meier, P. (1958). Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53: 457–481.
Kute, T. E., Shao, Z. M., Sugg, N. K., Long, R. T., Russell, G. B. & Case, L. D. (1992). Cathepsin D as a prognostic indicator for node-negative breast cancer patients using both immunoassays and enzymatic assays. Cancer Res 52: 5198–5203.
Liaudet, E., Derocq, D., Rochefort, H. & Garcia, M. (1995). Transfected cathepsin D stimulates high density cancer cell growth by inactivating secreted growth inhibitors. Cell Growth Differ 6: 1045–1052.
Nadji, M., Fresno, M., Nassiri, M., Conner, G., Herrero, A. & Morales, A. R. (1996). Cathepsin D in host stromal cells, but not in tumor cells, is associated with aggressive behavior in node-negative breast cancer. Hum Pathol 27: 890–895.
O’Donoghue, AEMA, Poller, D. N., Bell, J. A., Galea, M. H., Elston, C. W., Blamey, R. W. & Ellis, I. O. (1995). Cathepsin D in primary breast carcinoma: adverse prognosis is associated with expression in cathepsin D in stromal cells. Breast Cancer Res Treatment 33: 137–145.
Ravdin, P. (1993). Evaluation of cathepsin D as a prognostic factor in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treatment 24: 219–226.
Ravdin, P. M., Tandon, A. K., Allred, C. D. C., Clark, G. M., Fuqua, S. A. W., Hilsenbeck, S. H., Chamness, G. C. & Osborne, C. K. (1994). Cathepsin D by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry: failure to confirm correlations with prognosis in node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 12: 467–474.
Razumovic, J. J., Stojkovic, R. R., Petrovecki, M. & Gamulin, S. (1997). Correlation of two methods for determination of cathepsin D in breast carcinoma (immunohistochemistry and ELISA in cytosol). Breast Cancer Res Treatment 43: 117–122.
Remmele, W. & Sauer-Manthey, J. (1993). Comparative biochemical and immunohistochemical studies on the cathepsin D content of human breast cancer. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat 422: 467–473.
Rochefort, H. (1994). Oestrogens, proteases and breast cancer. From cell lines to clinical applications. Eur J Cancer 10: 1583–1586.
Rochefort, H. (1996). The prognostic value of cathepsin D in breast cancer. A long road to the clinic. Eur J Cancer 32A: 7–8.
Roger, P., Montcourrier, P., Maudelonde, T., Brouillet, J-P, Pages, A., Laffarque, F. & Rochefort, H. (1994). Cathepsin D immunostaining in paraffin-embedded breast cancer cells and macrophages: correlation with cytosolic assay. Hum Pathol 25: 863–871.
Saftig, P., Hetman, M., Schmahi, L., Weber, K., Heine, L., Mossman, H., Koster, A., Hess, B., Evers, M., von Figura, K. & Peters, C. (1995). Mice deficient for the lysosomal proteinase cathepsin D exhibit progressive atrophy of the intestinal mucosa and profound destruction of lymphoid cells. EMBO J 14: 3599–3608.
Spyratos, F., Brouillet, J. P., Defrenne, A., Hacène, K., Rouesse, J., Moudelonde, T., Brunet, M., Andrieu, C., Desplaces, A. & Rochefort, H. (1989). Cathepsin-D: an independent prognostic factor for metastasis of breast cancer. Lancet i: 1115–1118.
Tandon, A. K., Clark, G. M., Chamness, G. C., Chirgwin, J. M. & McGuire, W. L. (1990). Cathepsin D and prognosis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 332: 297–302.
Têtu, B., Brisson, J., Côté, C., Brisson, S., Potvin, D. & Roberge, N. (1993). Prognostic significance of cathepsin D expression in node-positive breast carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study. Int J Cancer 55: 429–435.
Thorpe, S. M., Rochefort, H., Garcia, M., Freiss, G., Christensen, I. J., Khalaf, S., Paolucci, F., Pau, B., Rasmussen, B. B. & Rose, C. (1989). Association between high concentrations of Mr 52 000 cathepsin D and poor prognosis in primary human breast cancer. Cancer Res 49: 6008–6014.
Vignon, F., Capony, F., Chambon, M., Freiss, G., Garcia, M. & Rochefort, H. (1986). Autocrine growth stimulation of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells by the estrogen-regulated 52 k protein. Endocrinology 118: 1537–1540.
Westley, B. R. & Rochefort, H. (1979). Estradiol induced proteins in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 90: 410–416.
Westley, B. R. & Rochefort, H. (1980). A secreted glycoprotein induced by estrogen in human breast cancer cell lines. Cell 20: 353–362.
Westley, B. R. & May, F. E. B. (1996). Cathepsin D and breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 32A: 15–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Foekens, J., Look, M., Vries, Jd. et al. Cathepsin-D in primary breast cancer: prognostic evaluation involving 2810 patients. Br J Cancer 79, 300–307 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690048
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690048
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Endosomes, lysosomes, and the role of endosomal and lysosomal biogenesis in cancer development
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
-
Immunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer with cathepsin D-targeting antibodies
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2019)
-
Hispolon suppresses metastasis via autophagic degradation of cathepsin S in cervical cancer cells
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
Post-operative nomogram for predicting freedom from recurrence after surgery in localised breast cancer receiving adjuvant hormone therapy
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2015)
-
Role of cathepsin D activation in major adverse cardiovascular events and new-onset heart failure after STEMI
Herz (2015)