Summary
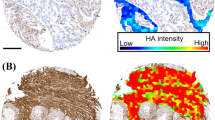
Hyaluronan (HA), an extracellular high-molecular-mass polysaccharide, is supposed to be involved in the growth and progression of malignant tumours. We studied the cellular expression of HA in 215 operated stage I–IV gastric cancer patients using a specific biotinylated probe. Most (93%) of the tumours showed HA staining in their parenchyma, whereas the stroma inside and around the tumour was stained in every case. When HA expression was compared with the clinical and histological features of the tumours, a strong staining intensity in the tumour parenchyma was found to be associated with deep tumour invasion (pT3 or 4) and with mixed type of Laurén. A high proportion of HA-positive cells of all neoplastic cells was significantly associated with deep tumour invasion, nodal metastasis, positive lymphatic invasion, poor differentiation grade, as well as with inferior prognosis in univariate survival analysis. However, in multivariate analysis, only pT, pN, and vascular and lymphatic invasion emerged as independent predictors of survival in gastric cancer. The results indicate that ectopic HA expression is a frequent feature of gastric adenocarcinoma, and is associated with tumour progression and poor survival rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Catterall, J. B., Gardner, M. J. & Turner, G. A. (1995). Hyaluronic acid, cell adhesion and metastasis (review). Cancer J 8: 320–323.
Cox, D. R. (1972). Regression models and life tables with discussion. J Stat Soc B 34: 187–192.
Hall, C. L., Yang, B., Yang, X., Zhang, S., Turley, M., Samuel, S., Lange, L. A., Wang, C., Curpen, G. D. & Savani, R. C. (1995). Overexpression of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM is transforming and is also required for H-ras transformation. Cell 82: 19–26.
Hong, R-L, Lee, W-J, Shun, C-T, Chu, J-S & Chen, Y-C (1995). Expression of CD44 and its clinical implication in diffuse-type and intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinomas. Oncology 52: 334–339.
Kaplan, E. L. & Meier, P. (1958). Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53: 457–481.
Knudson, W. (1996). Tumor-associated hyaluronan. Providing an extracellular matrix that facilitates invasion (commentary). Am J Pathol 148: 1721–1726.
Knudson, W., Biswas, C. & Toole, B. P. (1984). Interactions between human tumor cells and fibroblasts stimulate hyaluronate synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 6767–6771.
Laurén, P. (1965). The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 64: 31–49.
Liu, D., Pearlman, E., Diaconu, E., Guo, K., Mori, H., Haqqi, T., Markowitz, S., Willson, J. & Sy, M-S (1996). Expression of hyaluronidase by tumor cells induces angiogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 7832–7837.
Maeda, K., Ching, Y., Takatsuka, S., Ogawa, Y., Sawada, T., Yamashita, Y., Onoda, N., Kato, Y., Nitta, A., Arimoto, Y., Kondo, Y. & Sowa, M. (1995). Tumor angiogenesis as a predictor of recurrence in gastric carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 13: 477–481.
Mayer, B., Jauch, K. W., Günthert, U., Figdor, C. G., Schildberg, F. W., Funke, I. & Johnson, J. P. (1993). De-novo expression of CD44 and survival in gastric cancer. Lancet 342: 1019–1022.
Müller, W., Schneiders, A., Heider, K. H., Meier, S., Hommel, G. & Gabbert, H. E. (1997). Expression and prognostic value of the CD44 splicing variants v5 and v6 in gastric cancer. J Pathol 183: 222–227.
Noguchi, T., Uchida, Y., Oya, M., Kubo, N. & Murakami, S. (1993). Histochemical study of the extra-cellular stroma in gastric cancer. In Recent Advances in Management of Digestive Cancers, Takahashi T (ed.), pp. 263–265, Springer-Verlag: Tokyo
Pauli, B. U. & Knudson, W. (1988). Tumor invasion: a consequence of destructive and compositional matrix alterations. Hum Pathol 19: 628–639.
Ripellino, J. A., Klinger, M. M., Margolis, R. U. & Margolis, R. K. (1985). The hyaluronic acid binding region as a specific probe for the localization of hyaluronic acid in tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 33: 1060–1066.
Rooney, P., Kumar, S., Ponting, J. & Wang, M. (1995). The role of hyaluronan in tumor neovascularization (review). Int J Cancer 60: 632–636.
Ropponen, K., Tammi, M., Parkkinen, J., Eskelinen, M., Tammi, R., Lipponen, P., Ågren, U., Alhava, E. & Kosma, V-M (1998). Tumor cell associated hyaluronan as an unfavorable prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 58: 342–347.
Rudzki, Z. & Jothy, S. (1997). CD44 and the adhesion of neoplastic cells (review). J Clin Pathol Mol Pathol 50: 57–71.
Setälä, L. P., Kosma, V-M, Marin, S., Lipponen, P. K., Eskelinen, M. J., Syrjänen, K. J. & Alhava, E. M. (1996). Prognostic factors in gastric cancer: the value of vascular invasion, mitotic rate and lymphoplasmocytic infiltration. Br J Cancer 74: 766–772.
Sobue, M., Takeuchi, J., Tsukidate, K., Toida, M., Goto, K. & Nakashima, N. (1983). Influence of fixed fibroblasts on glycosaminoglycan synthesis of human gastric carcinoma cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res 149: 527–534.
Sowa, M., Kato, Y., Nishimura, M., Yoshino, H., Kubo, T. & Umeyama, K. (1989). Clinico-histochemical study on type 4 carcinoma of the stomach – with special reference to mucopolysaccharides and sialic acid in tumor tissue. Jpn J Surg 19: 153–162.
Streit, M., Schmidt, R., Hilgenfeld, R. U., Thiel, E. & Kreuser, E-D (1996). Adhesion receptors in malignant transformation and dissemination of gastrointestinal tumors. J Mol Med 74: 253–268.
Tahara, E. (1995). Molecular biology of gastric cancer. World J Surg 19: 484–490.
Tammi, R., Ågren, U., Tuhkanen, A-L & Tammi, M. (1994a). Hyaluronan metabolism in skin. Prog Histochem Cytochem 29: 1–81.
Tammi, R., Rönkkö, S., Ågren, U. & Tammi, M. (1994b). Distribution of hyaluronan in bull reproductive organs. J Histochem Cytochem 42: 1479–1486.
Tanigawa, N., Amaya, H., Matsumura, M., Shimomatsuya, T., Horiuchi, T., Muraoka, R. & Iki, M. (1996). Extent of tumor vascularization correlates with prognosis and hematogenous metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res 56: 2671–2676.
Toole, B. (1991). Proteoglycans and hyaluronan in morphogenesis and differentiation. In Cell Biology of the Extracellular Matrix, ED Hay (ed.), pp. 305–341, Plenum Press: New York
Turley, E. (1992). Hyaluronan and cell locomotion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11: 21–30.
UICC (1987). TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, Hermanek P, Sobin LH (ed.), pp. 43–45, Springer Verlag: Berlin
Underhill, C. (1992). CD44: the hyaluronan receptor (commentary). J Cell Sci 103: 293–298.
Wang, C., Tammi, M. & Tammi, R. (1992). Distribution of hyaluronan and its CD44 receptor in the epithelia of human skin appendages. Histochemistry 98: 326–332.
Wang, C., Tammi, M., Guo, H. & Tammi, R. (1996). Hyaluronan distribution in the normal epithelium of esophagus, stomach, and colon and their cancers. Am J Pathol 148: 1861–1869.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Setälä, L., Tammi, M., Tammi, R. et al. Hyaluronan expression in gastric cancer cells is associated with local and nodal spread and reduced survival rate. Br J Cancer 79, 1133–1138 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690180
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690180
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lymphatic trafficking of immune cells and insights for cancer metastasis
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2023)
-
Overexpression of KIAA1199, a novel strong hyaluronidase, is a poor prognostic factor in patients with osteosarcoma
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2021)
-
Extracellular matrix and its therapeutic potential for cancer treatment
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
Stromal hyaluronan accumulation is associated with low immune response and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Phase 1 trials of PEGylated recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20 in patients with advanced solid tumours
British Journal of Cancer (2018)