Summary
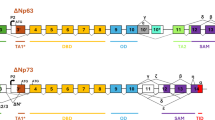
p73, the first homologue of the tumour suppressor protein p53, was recently discovered on chromosome 1p36 and has been shown to induce apoptosis in a p53-like manner. The present study was performed with the aim of investigating the expression of p53, its new homologue p73 and the occurrence of apoptosis in cholangiocellular carcinoma. Protein levels of p73 were examined in 41 patients with curatively (R0-) resected cholangiocellular carcinomas with an antiserum, raised against a peptide in the N-terminal domain of p73. The incidence of mutations in the p53 gene was analysed by direct sequencing and also immunohistochemically. Apoptotic cell death was assessed using in-situ end-labelling (ISEL) technique in combination with morphological criteria. The results obtained were correlated with patient survival. Immunostaining of p73 protein was detected in 17/41 carcinomas examined (41%). The immunoreactivity was confined to the cell nucleus. In 15/41 patients (37%), mutations of the p53 gene were observed. Eleven out of these 15 patients stained also positive for p73. In contrast, out of 26 patients without any detectable p53 mutation, only six exhibited p73 immunostaining. We failed to observe a correlation between p73 expression or p53 and apoptosis within a given tumour. Survival analysis including the parameters stage and grade of disease, p73 and p53, and also apoptosis, showed that tumour stage and grade as well as p53 and p73 were significantly related to prognosis. In Cox regression survival analysis, however, only extent of primary tumour and lymph node status had an independent prognostic impact. Our results with a high prevalence of p73 within tumours harbouring mutated p53 gene suggest that p73 could compensate for p53 function. We failed to establish p73 or p53 as independent prognostic factors in cholangiocellular carcinoma of the liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Clurman, B. & Groudine, M. (1997). Killer in search of a motive? Nature 389: 122–123.
Harris, C. C. (1996). Molecular epidemiology of human cancer: insights from the mutational analysis of the p53 tumour-suppressor gene. Br J Cancer 73: 261–269.
Hui, A-M, Kanai, Y., Sakamoto, M., Tsuda, H. & Hirohashi, S. (1997). Reduced p21WAF1/CIP1 expression and p53 mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 25: 575–579.
Jost, C. A., Marin, M. C. & Kaelin, W. G. (1997). p73 is a human p53-related protein that can induce apoptosis. Nature 389: 191–194.
Kaghad, M., Bonnet, H., Yang, A., Creancier, L., Biscan, J. C., Valent, A., Minty, A., Chalon, P., Lelias, J. M., Dumont, X., Ferrara, P., McKeon, F. & Caput, D. (1997). Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell 90: 809–819.
Mai, M., Yokomizo, A., Quian, C., Yang, P., Tindall, D. J., Smith, D. I. & Liu, W. (1998). Activation of p73 silent allele in lung cancer. Cancer Res 58: 2347–2349.
Nomoto, S., Haruki, N., Kondo, N., Konishi, H., Takahashi, T., Takahashi, T. & Takahashi, T. (1998). Search for mutations and examination of allelic expression of the p73 gene at 1p36.33 in human lung cancers. Cancer Res 58: 1380–1383.
Ohashi, K., Nakajima, Y., Kanehiro, H., Tsutsumi, M., Taki, J., Aomatsu, Y., Yoshimura, A., Ko, S., Kin, T., Yagura, K., Konishi, Y. & Nakano, H. (1995). Ki-ras mutations and p53 protein expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas: relation to gross tumor morphology. Gastroenterology 109: 1612–1617.
Orita, M., Suzuki, Y. & Hayashi, K. (1989). Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutation and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5: 874–879.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, pp E3–E4. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Sun, X. F., Carstensen, J. M., Zhang, H., Stal, O., Wingren, S., Hatschek, T. & Nordenskjöld, B. (1992). Prognostic significance of cytoplasmic p53 oncoprotein in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Lancet 340: 1369–1373.
Takahashi, H., Ichimiya, S., Nimura, Y., Watanabe, M., Furusato, M., Wakui, S., Yatani, R., Aizawa, S. & Nakagawara, A. (1998). Mutation, allelotyping, and transcription analysis of the p73 gene in prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 58: 2076–2077.
Tannapfel, A., Hahn, H., Katalinic, A., Fietkau, R., Kühn, R. & Wittekind, C. H. (1996). Prognostic value of ploidy and proliferation markers in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 77: 164–171.
Tannapfel, A., Nüsslein, S., Fietkau, R., Katalinic, A., Köckerling, F. & Wittekind, C. (1998). Apoptosis, proliferation, bax, bcl-2 and p53 status prior to and after preoperative radiochemotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Radiation Oncol Biol Phys 41: 585–591.
Uhlman, D. L., Nguyen, P. L., Manivel, C., Aeppli, D., Resnick, J. M., Fraley, E. E., Zhang, G. & Niehans, G. A. (1994). Association of immunostaining for p53 with metastatic progression and poor survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 86: 1470–1475.
Sobin, L. H. & Wittekind, C. H. (eds) (1997). UICC: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 5th edn. New York: Wiley-Liss
Ishak, T. et al (1994). WHO: Histological Typing of Tumours of the Liver, 2nd edn. Berlin: Springer Verlag
Wittekind, C. (1995). Hepatocellular carcinoma. In Prognostic Factors in Cancer. Hermanek P, Gospodarowicz MK, Henson DE, Hutter RVP and Sobin LH (eds) Berlin: Springer Verlag
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Tannapfel, A., Engeland, K., Weinans, L. et al. Expression of p73, a novel protein related to the p53 tumour suppressor p53, and apoptosis in cholangiocellular carcinoma of the liver. Br J Cancer 80, 1069–1074 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690465
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690465
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Label-free, automated classification of microsatellite status in colorectal cancer by infrared imaging
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Serum p53 antibody as a potential tumor marker in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Surgery Today (2017)
-
Dynamic changes of tumor gene expression during repeated pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) in women with peritoneal cancer
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
Quercetin abrogates chemoresistance in melanoma cells by modulating ΔNp73
BMC Cancer (2010)
-
Disruption of p73-MDM2 binding synergizes with gemcitabine to induce apoptosis in HuCCT1 cholangiocarcinoma cell line with p53 mutation
Tumor Biology (2010)