Abstract
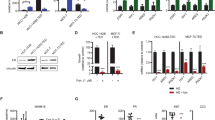
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is secreted by breast tumours and shows synergistic activity with 17β-oestradiol (E2), leading to increases in reductive 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in breast cancer epithelial cells. However, the mechanisms involved are poorly understood. Using short-term epithelial cultures established from primary breast tumours, we have examined whether IL-6 could directly affect transcriptional activity of oestrogen reception α (ERα). Tumour epithelial cultures were established from 15 breast tumours, grown to 70% confluence and transiently transfected with a plasmid reporter containing the vitellogenin oestrogen response element and the luciferase coding sequence (ERE-TK-LUC). Following transfection, cells were incubated with E2, IL-6, the pure anti-oestrogen ZM 182780 or combinations of these substances for 48 h. Luciferase activity was then measured in cell lysates. E2 caused a dose-dependent increase in luciferase expression, causing a maximum threefold stimulation at 100 p M. In the presence of IL-6, transcriptional activity was increased by up to 2.5-fold in ERα+cultures (11/15). In combination with E2, synergistic effects were observed with increases in luciferase activity of up to sixfold over controls. This effect could be blocked by treatment with ZM 182780. Pre-incubation of cells with an antibody directed against the signalling component of IL-6, gp130, was ineffective in blocking the E2 response. This antibody reduced, but did not completely block the effect of IL-6 either alone or in combination with E2, suggesting cross-talk between the two signalling pathways. In conclusion, these results provide evidence for direct transcriptional activation of ERα by IL-6. © 2000 Cancer Research Campaign
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Asgeirsson KS, Olafsdottir K, Jonasson JG and Ogmunsdottir HM (1998) The effects of IL-6 on cell adhesion and E-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Cytokine 10: 720–728
Basolo F, Fiore L, Fontanini G, Conaldi G, Calvo S, Falcone V and Toniolo A (1996) Expression and response to interleukin 6 (IL6) in human mammary tumours. Cancer Res 56: 3118–3122
Berthois Y, Katzenellenbogen JA and Katzenellenbogen BS (1986) Phenol red in tissue culture medium is a weak estrogen: implications concerning the study of estrogen-responsive cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2496–2500
Chiu JJ, Sgagias MK and Cowan KH (1996) Interleukin 6 acts as a paracrine growth factor in human mammary carcinoma cells lines. Clin Cancer Res 2: 215–221
Crichton MB, Nichols JE, Zhao Y, Bulun SE and Simpson ER (1996) Expression of transcripts of interleukin-6 and related cytokines by human breast tumors, breast cancer cells and adipose stromal cells. Mol Cell Endocr 118: 215–220
Cowley SM, Hoare S, Mosselman S and Parker MG (1997) Estrogen receptors α and β form heterodimers on DNA. J Biol Chem 272: 19858–19862
Dickson RB, McManaway ME and Lippman ME (1986) Estrogen-induced factors of breast cancer cells partially replace estrogen to promote tumour growth. Science 232: 1540–1543
Douglas AM, Goss GA, Sutherland RL, Hilton DJ, Berndt MC, Nicola NA and Begley CG (1997) Expression and function of members of the cytokine receptor superfamily on breast cancer cells. Oncogene 14: 661–669
Duncan LJ, Coldham NG and Reed MJ (1994) The interaction of cytokines in regulation of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in MCF-7 cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 49: 63–68
Fontanini G, Campani D, Roncella M, Cecchetti D, Calvo S, Toniolo A and Basolo F (1999) Expression of interleukin 6 (IL-6) correlates with oestrogen receptor in human breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer 80: 579–584
Green S, Walter P, Kumar V, Krust A, Bornert JM, Argos P and Chambon P (1986) Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature 320: 134–139
Green AR, Green VL, White MC and Speirs V (1997) Expression of cytokine messenger RNA in normal and neoplastic human breast tissue: identification of interleukin-8 as a potential regulatory factor in breast tumours. Int J Cancer 72: 937–941
Greene GL, Gilna P, Waterfield M, Baker A, Hort Y and Shine J (1986) Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science 231: 1150–1154
Hobisch A, Eder IE, Putz T, Horninger W, Bartsch G, Klocker H and Culig Z (1998) Interleukin-6 regulates prostate-specific protein expression in prostate carcinoma cells by activation of the androgen receptor. Cancer Res 58: 4640–4645
Ignar-Trowbridge DM, Pimentel M, Parker MG, McLachlan JA and Korach KS (1996) Peptide growth factor cross-talk with the estrogen receptor requires the A/B domain and occurs independently of protein kinase C or estradiol. Endocrinology 137: 1735–1744
Kishimoto T, Akira S and Taga T (1992) Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science 258: 593–597
Lee AV, C-N Weng, Jackson JG and Yee D (1997) Activation of estrogen-receptor mediated gene transcription by IGF-I in human breast cancer cells. J Endocrinol 152: 39–47
Mackiewicz A, Wiznerowicz M, Roeb E, Karczewska A, Nowak J, Heinrich PC and Rose-John S (1995) Soluble interleukin 6 receptor is biologically active in vivo. Cytokine 7: 142–149
Meyer T, Koop R, von Angerer E, Schonenberger H and Holler E (1994) A rapid luciferase transfection assay for transcription activation effects and stability control of estrogenic drugs in cell cultures. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 120: 359–364
Mosselman S, Polman J and Dijkema R (1996) ER-β: identification and characterisation of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett 392: 49–53
Newton CJ, Trapp T, Pagotto U, Renner U, Buric R and Stalla GK (1994a) The oestrogen receptor modulates growth of pituitary tumour cells in the absence of exogenous oestrogen. J Molec Endocrinol 12: 303–312
Newton CJ, Buric R, Trapp T, Brockmeier S, Pagotto U and Stalla G (1994b) The unliganded estrogen receptor (ER) transduces growth factor signals. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 48: 481–486
Novick D, Schulman LM, Chen L and Revel M (1992) Enhancement of IL-6 cytostatic effect on human breast carcinoma cells by IL-6 soluble receptor. Cytokine 4: 6–11
Pace P, Taylor J, Suntharalingam S, Coombes RC and Ali S (1997) Human estrogen receptor β binds DNA in a manner similar to and dimerises with estrogen receptor α. J Biol Chem 272: 25832–25838
Reed MJ and Purohit A (1997) Breast cancer and the role of cytokines in regulating estrogen synthesis: an emerging hypothesis. Endo Rev 18: 701–715
Singh A, Purohit A, Wang DY, Duncan LJ, Ghilchik MW and Reed MJ (1995) IL-6sR: release from MCF-7 breast cancer cells and role in regulating peripheral oestrogen synthesis. J Endocrinol 147: R9–R12
Speirs V, Adams EF, Rafferty B and White MC (1993) Interactive effects of interleukin-6, 17β-estradiol and progesterone on growth and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in human breast carcinoma cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 46: 11–15
Speirs V, Green AR and White MC (1996a) Collagenase III: a superior enzyme for complete disaggregation and improved viability of normal and malignant human breast tissue. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 32: 72–74
Speirs V, Green AR and White MC (1996b) A comparative study of cytokine gene transcripts in normal and malignant human breast tissue and primary cell cultures derived from the same tissue samples. Int J Cancer 66: 551–556
Speirs V, Green AR, Walton DS, Kerin MJ, Fox JN, Carleton PJ, Desai SB and Atkin SL (1998) Short-term primary culture of epithelial cells derived from human breast tumours. Br J Cancer 78: 1421–1429
Speirs V, Walton DS, Hall M-C and Atkin SL (1999) In vivo and in vitro expression of steroid-converting enzymes in human breast tumours: associations with interleukin-6. Br J Cancer 81: 690–695
Takada T, Kurachi H, Yamamoto T, Nishio Y, Nakatsuji Y, Morishge K, Miyake A and Murata Y (1998) Crosstalk between the interleukin-6 (IL-6)-JAK-STAT and the glucocorticoid-nuclear receptor pathway: synergistic activation of IL-6 response element by IL-6 and glucocorticoid. J Endocrinol 159: 323–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Speirs, V., Kerin, M., Walton, D. et al. Direct activation of oestrogen receptor- α by interleukin-6 in primary cultures of breast cancer epithelial cells. Br J Cancer 82, 1312–1316 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.1999.1097
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.1999.1097
This article is cited by
-
Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 are variable in breast cancer and benign stem/progenitor cell populations
BMC Cancer (2014)
-
Prognostic value of serum levels of interleukin 6 and of serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in hormone-refractory metastatic breast cancer patients
British Journal of Cancer (2003)