Abstract
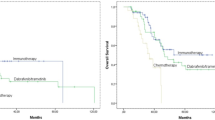
The adjuvant treatment of high-risk malignant melanoma remains problematic. Previously we reported moderate success in the treatment of metastatic disease using tamoxifen, cisplatin, dacarbazine and carmustine. Based upon data that suggested tamoxifen and cisplatin were the active agents in this regimen, we initiated a phase II trial of this combination in the adjuvant setting. We treated 153 patients with 4 cycles of tamoxifen (160 mg day–1, days 1–7) and cisplatin (100 mg m–2, day 2) for 28-day intervals. Patients received an anti-nausea regimen of dexamethasone with ondansetron or granisetron. During the first 2 years of follow-up, patients were evaluated every 2 months with a history, physical exam, laboratory work and computed tomography scans of the chest, abdomen and pelvis every 4 months. Thereafter, patients were evaluated every 3 months and radiographic studies were performed if necessary. Currently, with a median follow-up of 36 months, the disease-free survival (DFS) is 68.4% and overall survival (OS) is 84.5%. Kaplan–Meier analysis predicts a 5-year DFS of 62% with an OS of 79%. Relapses after 20 months have been rare. No effect of gender or number of positive lymph nodes was noted, however, stage of disease prior treatment was a factor. The major toxicity proved to be gastrointestinal in nature with nausea the most prevalent symptom. Minimal renal, haematologic and neurologic toxicity occurred. These preliminary results suggest that there is a positive impact of tamoxifen and cisplatin on both the DFS and OS of high-risk malignant melanoma patients. The 5-year projected DFS and OS compare favourably with those reported for the ECOG 1684 trial and warrant confirmation in a prospective randomized trial. © 2000 Cancer Research Campaign
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Anderson C, Buzaid A and Legha S (1995) Systemic treatments for advanced cutaneous melanoma. Oncology 9: 1149–1157
Cascinelli N, Bufalino R, Morabito A and Makie R (1994) Results of adjuvant interferon study in WHO melanoma programme. Lancet 343: 913–914
Clark WH, Elder DE, Guerry DP, Braitman LE, Trock BJ, Schultz D, Synnestvedt M and Halpern AC (1989) Model predicting survival in stage I melanoma based on tumor proression. J Natl Cancer Inst 81: 1893–1904
Cocconi G, Bella M, Calabresi F, Tonato M, Canaletti R, Boni C, Buzzi F, Ceci G, Corgna E and Costa P (1992) Treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma with dacarbazine plus tamoxifen. N Engl J Med 327: 516–523
Cole BF, Gelber RD, Kirkwood JM, Goldhirsch A, Barylak E and Borden E (1996) Quality-of-Life-Adjusted Survival Analysis of Interferon Alfa-2a Adjuvant Treatment of High-Risk Resected Cutaneous Melanoma: An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 14: 2666–2673
Creagan ET, Dalton RJ, Ahmann DL, Jung SH, Morton RF, Langdon RM, Kugker J and Rodrigue LJ (1995) Randomized, surgical adjuvant clinical trial of recombinant Interferon alfa-2a in selected patients with malignant melanoma. J Clin Oncol 13: 2776–2783
Creagan ET, Suman VJ, Dalton RJ, Pitot HC, Long HJ, Veeder MH, Vukov A, Rowland KM, Krook JE and Michalak JC (1999) Phase III clinical trial of the combination of cisplatin, dacarbazine, and carmustine with or without tamoxifen in patients with advanced malignant melanoma. J Clin Oncol 17: 1884–1890
Czarnetzki BM, Macher E, Suciu S, Thomas D, Steerenberg PA and Rumke P (1993) Long-term adjuvant immunotherapy in stage I high risk malignant melanoma, comparing two BCG preparations versus non-treatment in a randomised multicentre study (EORTC Protocol 18781). Eur J Cancer 9: 1237–1242
DelPrete SA, Maurer LH, O’Donnell J, Forcier FJ and LeMarbre P (1993) Combination chemotherapy with cisplatin, carmustine, dacarbazine and tamoxifen in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Treat Rep 68: 1403–1405
Kaplan BL and Meier P (1958) Non-parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53: 457–461
Kirkwood J, Strawderman MH, Ernstoff MS, Smith TJ, Borden EC and Blum RH (1996) Interferon α-2a adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol 14: 7–17
Kirkwood JM and Agarwala SS (1998) Adjuvant systemic therapy. InCutaneous melanoma, Balch CM, Houghton AN, Sorber AJ, Soong S (eds), p451. Quality Medical Publishing: St Louis, MO
Lattanzi SC, Tosteson T, Maurer LH, O’Donnell J, LeMarbre PJ, Del Prete SA, Forcier RJ and Ernstoff MS (1993) Dacarbazine (D), cisplatin (C), carmustine (B) +/– tamoxifen (T) in the treatment of patients (pts.) with metastatic melanoma: results of 5-year follow-up. Proc ASCO 390,
Lejeune FJ, Macher E and Kleeberg U (1988) An assessement of DTIC versus levamisole or placebo in the treatment of high risk stage I patients under surgical removal of a primary melanoma of the skin. A phase II adjuvant study (EORTC protocol 18761). Eur J Cancer 24: S81
McClay EF, Mastrangelo MJ, Bellet RE and Berd D (1987) Combination chemo/hormonal therapy in the treatment of malignant melanoma. Cancer Treat Rep 71: 465–469
McClay EF, Sprandio JD, Mastrangelo MJ, Bellet RE and Berd D (1988) Importance of tamoxifen to a combination chemotherapy regimen for melanoma. Proc ASCO 7: 250
McClay EF, Mastrangelo MJ, Sprandio JD, Bellet RE and Berd D (1989) The importance of tamoxifen to a cisplatin containing regimen in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Cancer 63: 1292–1295
McClay EF, Christen R, Albright KA, Jones JA, Eastman A and Howell SB 1992 a) Modulation of cisplatin resistance in human malignant melanoma cells. Cancer Res 52: 6790–6796
McClay EF, Mastrangelo MJ, Berd D and Bellet RE 1992 b) Effective combination chemo/hormonal therapy for malignant melanoma: experience with three consecutive trials. Int J Cancer 50: 553–556
McClay EF, Albright KA, Jones JA, Christen R and Howell SB 1993 a) Tamoxifen modulation of cisplatin sensitivity in human malignant melanoma cells. Cancer Res 53: 1571–1576
McClay EF, Albright KD, Jones JA, Christen RD and Howell SB 1993 b) Tamoxifen modulation of cisplatin cytotoxicity in human malignancies. Int J Cancer 55: 1018–1022
McClay EF, McClay ME, Albright KA, Jones JA, Christen R, Alcaraz J and Howell SB 1993 c) Tamoxifen modulation of cisplatin resistance in patients with metastatic melanoma: a biologically important observation. Cancer 72: 1914–1918
McClay EF, Albright KA, Jones JA, Christen RD and Howell SB (1994) Tamoxifen delays the in vitro development of resistance of cisplatin in human malignancies. Br J Cancer 70: 449–452
Pectasides D, Alevizakos N, Bafaloukos D, Tzonou A, Asimakopoulos G, Varthalitis I, Dimitriadis M and Athanassiou A (1994) Adjuvant chemotherapy with dacarbazine, vindesine, and cisplatin in pathological stage II malignant melanoma. Am J Clin Oncol 17: 55–59
Pehamberger H, Soyer P, Steiner A, Kofler R, Binder M, Mischer P, Pachinger W, Aubock P, Kerl H and Wolff K (1998) Adjuvant interferon α-2a treatment in resected primary stage II cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol 16: 1425–1429
Quirt IC, Shelley WE, Pater JL, Bodurtha AJ, McCulloch PB, McPherson TA, Paterson AHG, Prentice R, Silver HKB, Willan AR, Wilson K and Zee B (1991) Improved survival in patients with poor-prognosis malignant melanoma treated with adjuvant levamisole: a phase III study by the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 9: 729–735
Retsas S, Quigley M, Pectasides D, Macrae K and Henry K (1995) Clinical and histologic involvement of regional lymph nodes in malignant melanoma. Cancer 73: 2119–2130
Richards JM, Gilewski TA, Ramming K, Mitchell B, Doane LL and Vogelzang NJ (1992) Effective chemotherapy for melanoma after treatment with interleukin-2. Cancer 69: 427–429
Rusthoven JJ, Quirt IC, Iscoe NA, McCulloch PB, James KW, Lohmann RC, Jensen J, Burdette-Radoux S, Bodurtha AJ, Silver HKB, Verma S, Armitage GR, Zee B and Bennett K (1996) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial comparing the response rates of carmustine, dacarbazine and cisplatin with and without tamoxifen in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol 14: 2083–2090
Saba HI, Cruse CW, Wells KE, Klein CJ and Reintgen DS (1992) Treatment of stage IV malignant melanoma with dacarbazine, carmustine, cisplatin, and tamoxifen regimens: A University of South Florida and H. Lee Moffitt Melanoma Center study. Ann Plast Surg 28: 65–69
Saxman SB, Meyers ML, Chapman PB, Destro AN, Panageas KS, Begg CB, Monaco F, Agarwala SS, Schuchter LM, Ernstoff MS, Einhorm LH, Kirkwood JM and Houghton AN (1999) A phase III multicenter randomized trial of DTIC, cisplatin, BCNU and tamoxifen versus DTIC alone in patients with metastatic melanoma. Proc ASCO 18: 536a
Spitler LE (1991) A randomized trial of levamisole versus placebo as adjuvant therapy in malignant melanoma. J Clin Oncol 9: 736–740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
McClay, E., McClay, M., Monroe, L. et al. The effect of tamoxifen and cisplatin on the disease-free and overall survival of patients with high risk malignant melanoma. Br J Cancer 83, 16–21 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.1999.1220
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.1999.1220
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Serum estrogen and its soluble receptor levels in Egyptian patients with acute leukemia: case-control study
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2021)
-
Tamoxifen and TRAIL synergistically induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells
Oncogene (2008)