Abstract
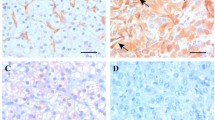
Chronic hypoxia up-regulated the mRNA and protein expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in EMT-6 tumour cells exposed to interferon (IFN)-gamma and interleukin (IL)-I beta. Low concentrations of cytokines (1 unit ml–1) in 1% but not in 21% oxygen induced a remarkable increase in NO production and a 1.8-fold hypoxic cell radiosensitization. Therefore, chronic hypoxia may potentially be exploited to increase tumour cell radioresponse through the cytokine-inducible iNOS pathway. © 2001 Cancer Research Campaign
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Ambs S, Merriam WG, Bennett WP, Felley-Bosco E, Ogunfusika MO, Oser SM, Klein S, Shields PG, Billiar TR and Harris CC (1998) Frequent nitric oxide synthase-2 expression in human colon adenomas: implication for tumor angiogenesis and colon cancer progression. Cancer Res 58: 334–341
Dachs GU and Stratford IJ (1996) The molecular response of mammalian cells to hypoxia and the potential for exploitation in cancer therapy. Br J Cancer 74: (Suppl XXVII) S126–S132
Dachs GU and Tozer GM (2000) Hypoxia modulated gene expression: angiogenesis, metastasis and therapeutic exploitation. Eur J Cancer 36: 1649–1660
Griffin RJ, Makepeace CM, Hur WJ and Song CW (1996) Radiosensitization of hypoxic tumor cells in vitro by nitric oxide. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys 36: 377–383
Janssens MY, Van den Berge DL, Verovski VN, Monsaert C and Storme GA (1998) Activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase results in nitric oxide-mediated radiosensitization of hypoxic EMT-6 tumor cells. Cancer Res 58: 5646–5648
Janssens MY, Verovski VN, Van den Berge DL, Monsaert C and Storme GA (1999) Radiosensitization of hypoxic tumour cells by S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine implicates a bioreductive mechanism of nitric oxide generation. Br J Cancer 79: 1085–1089
Melillo G, Musso T, Sica A, Taylor LS, Cox GW and Varesio L (1995) A hypoxia-responsive element mediates a novel pathway of activation of the inducible nitric oxide synthase promoter. J Exp Med 182: 1683–1693
Mitchell JB, Cook JA, Krishna MC, DeGraff W, Gamson J, Fisher J, Christodoulou D and Wink DA (1996) Radiation sensitisation by nitric oxide releasing agents. Br J Cancer 74: (Suppl XXVII) S181–S184
Salzman A, Denenberg AG, Ueta I, O’Connor M, Linn SC and Szabom C (1996) Induction and activity of nitric oxide synthase in cultured human intestinal epithelial monolayers. Am J Physiol 270: G565–G573
Thomsen LL and Miles DW (1998) Role of nitric oxide in tumour progression: lessons from human tumours. Cancer Metastasis Rev 17: 107–118
Thomsen LL, Lawton FG, Knowles RG, Beesley JE, Riveros-Moreno V and Moncada S (1994) Nitric oxide synthase activity in human gynecological cancer. Cancer Res 54: 1352–1354
Thomsen LL, Miles DW, Happerfield L, Bobrow LG, Knowles RG and Moncada S (1995) Nitric oxide synthase activity in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer 72: 41–44
Titheradge MA (1998) Enzymatic measurement of nitrate and nitrite. Titheradge MA (ed) Nitric oxide protocols, pp. 83–92, Humana P: New Jersey
Verovski VN, Van den Berge DL, Soete GA, Bols BL and Storme GA (1996) Intrinsic radiosensitivity of human pancreatic tumour cells and the radiosensitising potency of the nitric oxide donor sodium nitroprusside. Br J Cancer 74: 1734–1742
Wink DA, Vodovotz Y, Laval J, Laval F, Dewhirst MW and Mitchell JB (1998) The multifaceted roles of nitric oxide in cancer. Carcinogenesis 19: 711–721
Yoshioka K, Thompson J, Miller MJ and Fisher JW (1997) Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and erythropoietin production in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 232: 702–706
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Berge, D., Ridder, M., Verovski, V. et al. Chronic hypoxia modulates tumour cell radioresponse through cytokine-inducible nitric oxide synthase. Br J Cancer 84, 1122–1125 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1719
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1719
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
NF-κB inhibition impairs the radioresponse of hypoxic EMT-6 tumour cells through downregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
British Journal of Cancer (2003)