Abstract
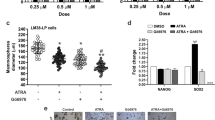
Retinoids inhibit the proliferation of several types of tumour cells, and are used for patients with several malignant tumours. In this study, we examined the effect of retinoic acids (RAs) on the invasive potentials of the oral squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells, BHY and HNt. BHY cells expressed all of retinoid nuclear receptors (RARα, β, γ, and RXRα) and cytoplasmic retinoic acid binding proteins (CRABP1 and CRABP2). HNt cells lacked the expression of RARβ, but expressed other nuclear receptors and CRABPs. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and 13-cis retinoic acid (13-cisRA) (10–6 and 10–7 M) inhibited the growth of the cells, but low-dose ATRA and 13-cisRA (10–8 M) marginally affected the growth of the cells. Surprisingly, low-dose RAs enhanced the activity of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA), and activated pro-matrix metalloproteinases (proMMP2 and proMMP9). Activation of proMMP2 and proMMP9 was inhibited by aprotinin, a serine-proteinase, tPA inhibitor. Furthermore, low-dose RAs enhanced the in vitro invasiveness of BHY cells. These results indicate that low-dose RAs enhances the in vitro invasiveness of oral SCC cells via an activation of proMMP2 and proMMP9 probably mediated by the induction of tPA. © 2001 Cancer Research Campaign http://www.bjcancer.com
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Baramova EN, Bajou K, Remacle A, L’Hoir C, Krell HW, Weidle UH, Noel A and Foidart JM (1997) Involvement of PA/plasmin system in the processing of pro-MMP-9 and in the second step of pro-MMP-2 activation. FEBS Lett 405: 157–162
Bracke ME, Van Larebeke NA, Vyncke BM and Mareel MM (1991) Retinoic acid modulates both invasion and plasma membrane ruffling of MCF-7 human mammary carcinoma cells in vitro. Br J Cancer 63: 867–872
Bulens F, Merchiers P, Ibanez-Tallon I, De Vriese A, Nelles L, Claessens F, Belayew A and Collen D (1997) Identification of a multihormone responsive enhancer far upstream from the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene. J Biol Chem 272: 663–671
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna JD and Mitchell JB (1987) Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated calorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res 47: 936–942
He LZ, Merghoub T and Pandolfi PP (1999) In vivo analysis of the molecular pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia in the mouse and its therapeutic implications. Oncogene 18: 5278–5292
Hendrix MJ, Wood WR, Seftor EA, Lotan D, Nakajima M, Misiorowski RL, Seftor RE, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Bevacqua SJ, Liotta LA, Sobel ME, Raz A and Lotan R (1990) Retinoic acid inhibition of human melanoma cell invasion through a reconstituted basement membrane and its relation to decreases in the expression of proteolytic enzymes and motility factor receptor. Cancer Res 50: 4121–4130
Hong WK, Lippman SM, Itri LM, Karp DD, Lee JS, Byers RM, Schantz SP, Kramer AM, Lotan R, Peters LJ, Dimery IW, Bown BW and Goepfert H (1990) Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 323: 795–801
Imai S, Okuno M, Moriwaki H, Muto Y, Murakami K, Shudo K, Suzuki Y and Kojima S (1997) 9,13-di-cis-Retinoic acid induces the production of tPA and activation of latent TGF-beta via RAR alpha in a human liver stellate cell line, LI90. FEBS Lett 411: 102–106
Jetten AM, Kim JS, Sacks PG, Rearick JI, Lotan D, Hong WK and Lotan R (1990) Inhibition of growth and squamous-cell differentiation markers in cultured human head and neck squamous carcinoma cells by beta-all-trans retinoic acid. Int J Cancer 45: 195–202
Kawamata H, Nakashiro K, Uchida D, Harada K, Yoshida H and Sato M (1997) Possible contribution of active MMP2 to lymph-node metastasis and secreted cathepsin L to bone invasion of newly established human oral-squamous-cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 70: 120–127
Kawamata H, Uchida D, Hamano H, Kimura-Yanagawa T, Nakashiro K, Hino S, Omotehara F, Yoshida H and Sato M (1998) Active-MMP2 in cancer cell nests of oral cancer patients: correlation with lymph node metastasis. Int J Oncol 13: 699–704
Komiyama S, Hiroto I, Ryu S, Nakashima T, Kuwano M and Endo H (1978) Synergistic combination therapy of 5-fluorouracil, vitamin A and cobalt-60 radiation upon head and neck tumors. Oncology 35: 253–257
Lansink M, Koolwijk P, van Hinsbergh V and Kooistra T (1998) Effect of steroid hormones and retinoids on the formation of capillary-like tubular structures of human microvascular endothelial cells in fibrin matrices is related to urokinase expression. Blood 92: 927–938
Lippman SM, Glisson BS, Kavanagh JJ, Lotan R, Hong WK, Paredes-Espinoza M, Hittelman WN, Holdener EE and Krakoff IH (1993) Retinoic acid and interferon combination studies in human cancer. Eur J Cancer 29A: S9–13
Lo-Coco F, Nervi C, Avvisati G and Mandelli F (1998) Acute promyelocytic leukemia: a curable disease. Leukemia 12: 1866–1880
Lotan R (1994) Suppression of squamous cell carcinoma growth and differentiation by retinoids. Cancer Res 54: 1987s–1990s
Lotan R (1997) Retinoids and chemoprevention of aerodigestive tract cancers. Cancer Metastasis Rev 16: 349–356
Lotan R, Dawson MI, Zou CC, Jong L, Lotan D and Zou CP (1995) Enhanced efficacy of combinations of retinoic acid-and retinoid X receptor-selective retinoids and alpha-interferon in inhibition of cervical carcinoma cell proliferation. Cancer Res 55: 232–236
Mars WM, Zarnegar R and Michalopoulos GK (1993) Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the plasminogen activators uPA and tPA. Am J Pathol 143: 949–958
Mitchell MF, Hittelman WK, Lotan R, Nishioka K, Tortolero-Luna G, Richards-Kortum R, Wharton JT and Hong WK (1995) Chemoprevention trials and surrogate end point biomarkers in the cervix. Cancer 76: 1956–1977
Oridate N, Lotan D, Xu XC, Hong WK and Lotan R (1996) Differential induction of apoptosis by all-trans-retinoic acid and N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 2: 855–863
Oridate N, Suzuki S, Higuchi M, Mitchell MF, Hong WK and Lotan R (1997) Involvement of reactive oxygen species in N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide-induced apoptosis in cervical carcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 89: 1191–1198
Pemrick SM, Lucas DA and Grippo JF (1994) The retinoid receptors. Leukemia 8: 1797–1806
Sun SY, Li W, Yue P, Lippman SM, Hong WK and Lotan R (1999a) Mediation of N-(4-hydoxyphenyl) retinamide-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells by different mechanisms. Cancer Res 59: 2493–2498
Sun SY, Yue P, Wu GS, El-Deiry WS, Shroot B, Hong WK and Lotan R (1999b) Mechanisms of apoptosis induced by the synthetic retinoid CD437 in human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Oncogene 18: 2357–2365
Sun SY, Yue P and Lotan R (1999c) Induction of apoptosis by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide and its association with reactive oxygen species, nuclear retinoic acid receptors, and apoptosis-related genes in human prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 55: 403–410
Tiberio A, Farina AR, Tacconelli A, Cappabianca L, Gulino A and Mackay AR (1997) Retinoic acid-enhanced invasion through reconstituted basement membrane by human SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells involves membrane-associated tissue-type plasminogen activator. Int J Cancer 73: 740–748
Vermeulen SJ, Bruyneel EA, van Roy FM, Mareel MM and Bracke ME (1995) Activation of the E-cadherin/catenin complex in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells by all-trans-retinoic acid. Br J Cancer 72: 1447–1453
Wan H, Oridate N, Lotan D, Hong WK and Lotan R (1999) Overexpression of retinoic acid receptor beta in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells increases their sensitivity to retinoid-induced suppression of squamous differentiation by retinoids. Cancer Res 59: 3518–3526
Webber MM and Waghray A (1995) Urokinase-mediated extracellular matrix degradation by human prostatic carcinoma cells and its inhibition by retinoic acid. Clin Cancer Res 1: 755–761
Wood WR, Seftor EA, Lotan D, Nakajima M, Misiorowski RL, Seftor RE, Lotan R and Hendrix MJ (1990) Retinoic acid inhibits human melanoma tumor cell invasion. Anticancer Res 10: 423–432
Xu XC, Liu X, Tahara E, Lippman SM and Lotan R (1999) Expression and up-regulation of retinoic acid receptor-beta is associated with retinoid sensitivity and colony formation in esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 59: 2477–2483
Yamamoto H, Itoh F, Hinoda Y and Imai K (1995) Suppression of matrilysin inhibits colon cancer cell invasion in vitro. Int J Cancer 61: 218–222
Zou CP, Kurie JM, Lotan D, Zou CC, Hong WK and Lotan R (1998) Higher potency of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide than all-trans-retinoic acid in induction of apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 4: 1345–1355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Uchida, D., Kawamata, H., Nakashiro, K. et al. Low-dose retinoic acid enhances in vitro invasiveness of human oral squamous-cell-carcinoma cell lines. Br J Cancer 85, 122–128 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.1862
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.1862
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effectiveness of cetuximab as preemptive postsurgical therapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients with major risk: a single‐center retrospective cohort study
Investigational New Drugs (2021)
-
Enhancement of ATRA-induced differentiation of neuroblastoma cells with LOX/COX inhibitors: an expression profiling study
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2010)