Abstract
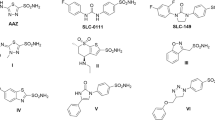
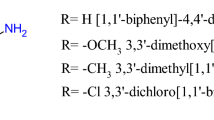
A series of benzo(b)thiophenesulfonamide 1,1-dioxide derivatives (BTS) have been designed and synthesized as candidate antineoplastic drugs. Several of these compounds have shown in vitro cytotoxic activity on leukaemic CCRF-CEM cells. The cytotoxic BTS, but not the inactive ones, were able to inhibit a tumour cell-specific NADH oxidase activity present in the membrane of CCRF-CEM cells. © 2001 Cancer Research Campaign http://www.bjcancer.com
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Bacakova L, Mares V, Lisa V and Kocourek F (1997) Sex-dependent differences in growth and morphology of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells from newborn rats. Physiol Res 46: 403–406
Gil MJ, Manu MA, Arteaga C, Migliaccio M, Encio I, Gonzalez A and Martinez-Merino V (1999) Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of N-(2-pyridylsulfenyl)urea derivatives. A new class of potential antineoplastic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 2321–2324
Howbert JJ, Grossman CS, Crowell TA, Rieder BJ, Harper RW, Kramer KE, Tao EV, Aikins J, Poore GA and Rinzel SM et al (1990) Novel agents effective against solid tumors: the diarylsulfonylureas. Synthesis, activities, and analysis of quantitative structure-activity relationships. J Med Chem 33: 2393–2407
Houghton PJ and Houghton JA (1996) Antitumor diarylsulfonylureas: novel agents with unfulfilled promise. Invest New Drugs 14, (3):271–280
Huschtscha LI, Bartier WA, Ross CE and Tattersall MH (1996) Characteristics of cancer cell death after exposure to cytotoxic drugs in vitro. Br J Cancer 73: 54–60
Kim C, MacKellar WC, Cho NM, Byrn SR and Morre DJ (1997) Impermeant antitumor sulfonylurea conjugates that inhibit plasma membrane NADH oxidase and growth of HeLa cells in culture. Identification of binding proteins from sera of cancer patients. Biochim Biophys Acta 1324: 171–181
Martinez-Merino V, Gil MJ, Encío I, Migliaccio M and Arteaaga C (2000) Benzo[b]thiophene sulfonamide-1, 1-dioxido derivatives and their use as antineoplastic agents. Patent N˚ WO 00/63202
Morre DJ, Chueh PJ and Morre DM (1995a) Capsaicin inhibits preferentially the NADH oxidase and growth of transformed cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 1831–1835
Morre DJ, Morre DM, Stevenson J, MacKellar W and McClure D (1995b) HeLa plasma membranes bind the antitumor sulfonylurea LY181984 with high affinity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1244: 133–140
Morre DJ, Wilkinson FE, Lawrence J, Cho N and Paulik M (1995c) Identification of antitumor sulfonylurea binding proteins of HeLa plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1236: 237–243
Morre DJ, Wu LY and Morre DM (1995d) The antitumor sulfonylurea N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-N′-(4-chlorophenyl) urea (LY181984) inhibits NADH oxidase activity of HeLa plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1240: 11–17
Morre DJ, Kim C, Paulik M, Morre DM and Faulk WP (1997) Is the drug-responsive NADH oxidase of the cancer cell plasma membrane a molecular target for adriamycin?. J Bioenerg Biomembr 29: 269–280
Morre DJ, Grieco PA and Morre DM (1998) Mode of action of the anticancer quassinoids–inhibition of the plasma membrane NADH oxidase. Life Sci 63: 595–604
Sosinski J, Thakar JH, Germain GS, Harwood FC and Houghton PJ (1993) Proliferation-dependent and -independent cytotoxicity by antitumor diarylsulfonylureas. Indication of multiple mechanisms of drug action. Biochem Pharmacol 45: 2135–2142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Alonso, M., Encío, I., Martínez-Merino, V. et al. New cytotoxic benzo(b)thiophenilsulfonamide 1,1-dioxide derivatives inhibit a NADH oxidase located in plasma membranes of tumour cells. Br J Cancer 85, 1400–1402 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.2083
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.2083
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Down-Regulation of Tumor-Associated NADH Oxidase, tNOX (ENOX2), Enhances Capsaicin-Induced Inhibition of Gastric Cancer Cell Growth
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2011)
-
Benzo[b]thiophenesulphonamide 1,1-dioxide derivatives inhibit tNOX activity in a redox state-dependent manner
British Journal of Cancer (2005)
-
New benzo(b)thiophenesulphonamide 1,1-dioxide derivatives induce a reactive oxygen species-mediated process of apoptosis in tumour cells
Oncogene (2003)