Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To compare the outcome of two groups of 16 patients with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets (HELLP) syndrome treated with heparin therapy or treated conservatively in the postpartum period.
STUDY DESIGN:
This is a retrospective cohort study comparing 16 consecutive patients with HELLP syndrome admitted to the ICU at the University of Florence (Italy) after delivery and treated with heparin, to 16 patients with the same disease admitted to the University of Virginia (UVA, USA) and treated with supportive therapy.
RESULTS:
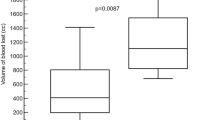
Nine patients in the Florence group developed disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Six of them developed postpartum hemorrhage that was medically and surgically controlled. Five hysterectomies were performed and seven other laparotomies were necessary in four patients to control further bleeding complications. In the UVA group, one patient developed DIC and another one a retroperitoneal hematoma that resolved with no need for surgical intervention.
CONCLUSIONS:
Heparin therapy for postpartum patients with HELLP syndrome was associated with bleeding complications. We speculate that the heparin therapy was the cause for the bleeding complications occurred in the Florence group of patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinstein L . Syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet count: a severe consequence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982;142:159–167.
Van Dam PA, Reiner M, Baekelandt M, Buytaert P, Uyttenbroeck F . Disseminated intravascular coagulation and the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets in severe preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 1989;73:97–102.
Visser W, Wallenburg HCS . Temporising management of severe pre-eclampsia with and without the HELLP syndrome. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1995;102:111–117.
Magann EF, Bass D, Chauhan SP, Sullivan L, Martin RW, Martin Jr JN . Antepartum corticosteroids: disease stabilization in patients with the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP). Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1148–1153.
Brain MC, Baker LRI, McBride JA, Rubenberg ML, Dacie JV . Treatment of patients with microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia with heparin. Br J Haematol 1968;15:603–621.
Butler BC, Taylor Sr HC, Graff S . The relationship of disorders of the blood clotting mechanism to toxemia of pregnancy and the value of heparin therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1950;60:564–574.
Howie PW, Prentice CRM, Forbes CD . Failure of heparin therapy to affect the clinical course of severe pre-eclampsia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1975;82:711–717.
Goldsmith HJ, Menzies DN, De Boer CH, Caplan W, McCandless A . Delivery of healthy infant after five weeks’ dialysis treatment for fulminating toxaemia of pregnancy. Lancet 1971;2:738–741.
Thiagarajah S, Wheby MS, Jain R, May HV, Bourgeois J, Kitchin III JD . Disseminated intravascular coagulation in pregnancy. The role of heparin therapy. J Reprod Med 1981;26:17–20.
Heene DL . Disseminated intravascular coagulation: evaluation of therapeutic approaches. Semin Thromb Hemost 1977;3:291–310.
Feinstein DI . Diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation: the role of heparin therapy. Blood 1982;60:284–287.
Sher G, Statland BE . Abruptio placentae with coagulopathy: a rational basis for management. Clin Obstet Gynecol 1985;28:15–23.
Sibai BM, Anderson GD, McCubbin JH . Eclampsia. II. Clinical significance of laboratory findings. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59:153–157.
Sibai BM . The HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets): much ado about nothing? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990; 162:311–316.
Hellgren M, Egberg N, Eklund J . Blood coagulation and fibrinolytic factors and their inhibitors in critically ill patients. Intens Care Med 1984;10:23–28.
Bick RL . Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Objective clinical and laboratory diagnosis, treatment, and assessment of therapeutic response. Semin Thromb Hemost 1996;22:69–88.
Sibai BM, Ramadan MK, Usta I, Salama M, Mercer BM, Friedman SA . Maternal morbidity and mortality in 442 pregnancies with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets (HELLP syndrome). Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:1000–1006.
Martin JN, Reiehart BK, May WL, Magann EF, Terrone DA, Blake PG . The spectrum of severe preeclampsia: comparative analysis by HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome classification. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:1373–1384.
Sibai BM, Taslimi MM, El-Naser A, Amor E, Mabie BL, Ryan GM . Maternal–perinatal outcome associated with the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets in severe preeclampsia–eclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1986;155:501–509.
Martin Jr JN, Blake PG, Lowry SL, Perry KG, Files JC, Morrison JC . Pregnancy complicated by preeclampsia–eclampsia with the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count: how rapid is postpartum recovery? Obstet Gynecol 1990;76:737–741.
Magann EF, Perry KJ, Meydrech EF, Harris RL, Chauhan SP, Martin Jr JN . Postpartum corticosteroids: accelerated recovery from the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP). Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:1154–1158.
Martin Jr JN, Perry Jr KG, Blake PG, May WA, Moore A, Robinette L . Better maternal outcomes are achieved with dexamethasone therapy for post-partum HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and thrombocytopenia) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1011–1017.
Skelly H, Morivate M, Norman R, Kenoyer G, Martin R . Consumptive coagulopathy following fetal death in a triplet pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982;142:595–596.
Romero R, Duffy TP, Berkowitz RL, Chang E, Hobbins JC . Prolongation of a preterm pregnancy complicated by death of a single twin in utero and disseminated intravascular coagulation. N Engl J Med 1984;310:772–773.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Detti, L., Mecacci, F., Piccioli, A. et al. Postpartum Heparin Therapy for Patients with the Syndrome of Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, and Low Platelets (HELLP) is Associated with Significant Hemorrhagic Complications. J Perinatol 25, 236–240 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211265
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211265
This article is cited by
-
The HELLP syndrome: Clinical issues and management. A Review
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2009)