ABSTRACT
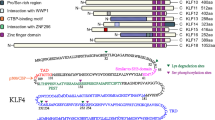
Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) are evolutionarily conserved zinc finger-containing transcription factors with diverse regulatory functions in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and embryogenesis. KLF4 and KLF5 are two closely related members of the KLF family that have a similar tissue distribution in embryos and adults. However, the two KLFs often exhibit opposite effects on regulation of gene transcription, despite binding to similar, if not identical, cis-acting DNA sequences. In addition, KLF4 and 5 exert contrasting effects on cell proliferation in many instances; while KLF4 is an inhibitor of cell growth, KLF5 stimulates proliferation. Here we review the biological properties and biochemical mechanisms of action of the two KLFs in the context of growth regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BTE:
-
basic transcription element
- BTEB2:
-
basic transcription element binding protein 2
- CYP1A1:
-
cytochrome P-450IA1
- KLF:
-
Krüppel-like factor
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
References
Yang VW . Eukaryotic transcription factors: identification, characterization and functions. J Nutr 1998; 128:2045–51.
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001; 409:860–921.
Schuh R, Aicher W, Gaul U, et al. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell 1986; 47:1025–32.
Dang DT, Pevsner J, Yang VW . The biology of the mammalian Krüppel-like family of transcription factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2000; 32:1103–21.
Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW . Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest. J Biol Chem 1996; 271:20009–17.
Shields JM, Yang VW . Two potent nuclear localization signals in the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor define a subfamily of closely related Krüppel proteins. J Biol Chem 1997; 272:18504–7.
Conkright MD, Wani MA, Anderson KP, Lingrel JB . A gene encoding an intestinal-enriched member of the Krüppel-like factor family expressed in intestinal epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1999; 27:1263–70.
Sogawa K, Imataka H, Yamasaki Y, et al. cDNA cloning and transcriptional properties of a novel GC box-binding protein, BTEB2. Nucleic Acids Res 1993; 21:1527–32.
Ton-That H, Kaestner KH, Shields JM, Mahatanankoon CS, Yang VW . Expression of the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor gene during development and intestinal tumorigenesis. FEBS Lett 1997; 419:239–43.
Ohnishi S, Laub F, Matsumoto N, et al. Developmental expression of the mouse gene coding for the Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF5. Dev Dyn 2000; 217:421–9.
Shields JM, Yang VW . Identification of the DNA sequence that interacts with the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor. Nucleic Acids Res 1998; 26:796–802.
Zhang W, Shields JM, Sogawa K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Yang VW . The gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor suppresses the activity of the CYP1A1 promoter in an Sp1-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem 1998; 273:17917–25.
Dang DT, Zhao W, Mahatan CS, Geiman DE, Yang VW . Opposing effects of Krüppel-like factor 4 (gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor) and Krüppel-like factor 5 (intestinal-enriched Krüppel-like factor) on the promoter of the Krüppel-like factor 4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30:2736–41.
Liu Y, Sinha S, Owens G . A transforming growth factor-beta control element required for SM alpha-actin expression in vivo also partially mediates GKLF-dependent transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:48004–11.
Piccinni SA, Bolcato-Bellemin AL, Klein A, et al. Krüppel-like factors regulate the Lama1 gene encoding the laminin alpha1 chain. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:9103–14.
Zhang W, Geiman DE, Shields JM, et al. The gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor (Krüppel-like factor 4) mediates the transactivating effect of p53 on the p21WAF1/Cip1 promoter. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:18391–8.
Yoon HS, Chen X, Yang VW . Krüppel-like factor 4 mediates p53-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:2101–5.
Yoon HS, Yang VW . Requirement of Krüppel-like factor 4 in preventing entry into mitosis following DNA damage. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:5035–41.
Shie JL, Chen ZY, Fu M, Pestell RG, Tseng CC . Gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor represses cyclin D1 promoter activity through Sp1 motif. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28:2969–76.
Chen X, Whitney EM, Gao SY, Yang VW . Transcriptional profiling of Krüppel-like factor 4 reveals a function in cell cycle regulation and epithelial differentiation. J Mol Biol 2003; 326:665–77.
Yoon HS, Ghaleb AM, Nandan NO, et al. Krüppel-like factor 4 prevents centrosome amplification following γ irradiation-induced DNA damage. Oncogene, in press.
Dang DT, Bachman KE, Mahatan CS, et al. Decreased expression of the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor gene in intestinal adenomas of multiple intestinal neoplasia mice and in colonic adenomas of familial adenomatous polyposis patients. FEBS Lett 2000; 476:203–7.
Zhao W, Hisamuddin IM, Nandan MO, et al. Identification of Krüppel-like factor 4 as a potential tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2004; 23:395–402.
Dang DT, Chen X, Feng J, et al. Overexpression of Krüppel-like factor 4 in the human colon cancer cell line RKO leads to reduced tumorigenecity. Oncogene 2003; 22:3424–30.
Ohnishi S, Ohnami S, Laub F, et al. Downregulation and growth inhibitory effect of epithelial-type Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF4, but not KLF5, in bladder cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 308:251–6.
Sun R, Chen X, Yang VW . Intestinal-enriched Krüppel-like factor (Krüppel-like factor 5) is a positive regulator of cellular proliferation. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:6897–900.
Chanchevalap S, Nandan MO, Merlin D, Yang VW . All-trans retinoic acid inhibits proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells by inhibiting expression of the gene encoding Krüppel-like factor 5. FEBS Lett 2004; 578:99–105.
Nandan MO, Yoon HS, Zhao W, et al. Krüppel-like factor 5 mediates the transforming activity of oncogenic H-Ras. Oncogene 2004; 23:3404–13.
Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E . Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat Genet 1999; 22:356–60.
Jaubert J, Cheng J, Segre JA . Ectopic expression of Krüppel like factor 4 (Klf4) accelerates formation of the epidermal permeability barrier. Development 2003; 130:2767–77.
Patel S, Kartasova T, Segre JA . Mouse Sprr locus: a tandem array of coordinately regulated genes. Mamm Genome 2003; 14:140–8.
Katz JP, Perreault N, Goldstein BG, et al. The zinc-finger transcription factor Klf4 is required for terminal differentiation of goblet cells in the colon. Development 2002; 129:2619–28.
Shindo T, Manabe I, Fukushima Y, et al. Krüppel-like zinc-finger transcription factor KLF5/BTEB2 is a target for angiotensin II signaling and an essential regulator of cardiovascular remodeling. Nat Med 2002; 8:856–63.
Foster KW, Ren S, Louro ID, et al. Oncogene expression cloning by retroviral transduction of adenovirus E1A-immortalized rat kidney RK3E cells: transformation of a host with epithelial features by c-MYC and the zinc finger protein GKLF. Cell Growth Differ 1999; 10:423–34.
Foster KW, Frost AR, McKie-Bell P, et al. Increase of GKLF messenger RNA and protein expression during progression of breast cancer. Cancer Res 2000; 60:6488–95.
Pandya AY, Talley LI, Frost AR, et al. Nuclear localization of KLF4 is associated with an aggressive phenotype in early-stage breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10:2709–19.
Chen C, Bhalala HV, Vessella RL, Dong JT . KLF5 is frequently deleted and down-regulated but rarely mutated in prostate cancer. Prostate 2003; 55:81–8.
Chen C, Bhalala HV, Qiao H, Dong JT . A possible tumor suppressor role of the KLF5 transcription factor in human breast cancer. Oncogene 2002; 21:6567–72.
Bateman NW, Tan D, Pestell RG, Black JD, Black AR . Intestinal tumor progression is associated with altered function of KLF5. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:12093–101.
Acknowledgements
This work was in part supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (DK52230, DK64399 and CA84197). Vincent W.Yang is the recipient of a Georgia Cancer Coalition Distinguished Cancer Clinician Scientist Award. W. Brian. Dalton is a member of the Medical Scientist Training Program of Emory University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GHALEB, A., NANDAN, M., CHANCHEVALAP, S. et al. Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5: the yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation. Cell Res 15, 92–96 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7290271
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7290271
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Circ_0020256 induces fibroblast activation to drive cholangiocarcinoma development via recruitment of EIF4A3 protein to stabilize KLF4 mRNA
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Krüppel-Like Factor 4 and Its Pharmacological Potential in Parkinson’s Disease: a Comprehensive Review
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
MicroRNA-375 repression of Kruppel-like factor 5 improves angiogenesis in diabetic critical limb ischemia
Angiogenesis (2023)
-
Prognostic significance of KLF4 in solid tumours: an updated meta-analysis
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
“Cutting the Mustard” with Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: An Overview and Applications in Healthcare Paradigm
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2022)