Abstract
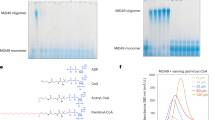
Myosin light chain kinases (MLCK) phosphorylate the regulatory light chain of myosin II in thick filaments and bind to F-actin-containing thin filaments with high affinity. The ability of short myosin light chain kinase (S-MLCK) to bind F-actin is structurally attributed to the DFRXXL regions in its N-terminus. The long myosin light chain kinase (L-MLCK) has two additional DFRXXL motifs and six Ig-like modules in its N-terminal extension. The six Ig-like modules are capable of binding to stress fibers independently. Our results from the imaging analysis demonstrated that the first two intact Ig-like modules (2Ig) in N-terminal extension of L-MLCK is the minimal binding module required for microfilament binding. Binding assay confirmed that F-actin was able to bind 2Ig. Stoichiometries of 2Ig peptide were similar for myofilament or pure F-actin. The binding affinities were slightly lower than 5DFRXXL peptide as reported previously. Similar to DFRXXL peptides, the 2Ig peptide also caused efficient F-actin bundle formation in vitro. In the living cell, over-expression of 2Ig fragment increased “spike”-like protrusion formation with over-bundled F-actin. Our results suggest that L-MLCK may act as a potent F-actin bundling protein via its DFRXXL region and the 2Ig region, implying that L-MLCK plays a role in cytoskeleton organization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kamm KE, Stull JT . The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1985; 25:593–620.
Hartshorne DJ . In: Johnson LR, eds. Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Raven Press: New York 1987:423–482.
Stull JT, Lin PJ, Krueger JK, Trewhella J, Zhi G . Myosin light chain kinase: functional domains and structural motifs. Acta Physiol Scand 1998; 164:471–482.
Kamm KE, and Stull JT . Dedicated myosin light chain kinases with diverse cellular functions. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:4527–4530.
Schoenwaelder SM, Burridge K . Bidirectional signaling between the cytoskeleton and integrins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1999; 11:274–286.
Bresnick AR . Molecular mechanisms of nonmuscle myosin-II regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1999; 11:26–33.
Sato M, Tani E, Fujikawa H, Kaibuchi K . Involvement of Rho-kinase-mediated phosphorylation of myosin light chain in enhancement of cerebral vasospasm. Circ Res 2000; 87:195–200.
van Nieuw Amerongen GP, van Delft S, Vermeer MA, Collard JG, van Hinsbergh VW . Activation of RhoA by thrombin in endothelial hyperpermeability: role of Rho kinase and protein tyrosine kinases. Circ Res 2000; 87:335–340.
Jung C, Chylinski TM, Pimenta A, Ortiz D, Shea TB . Neurofilament transport is dependent on actin and myosin. J Neurosci 2004; 24:9486–9496.
Clayburgh DR, Rosen S, Witkowski ED, et al. A differentiation-dependent splice variant of myosin light chain kinase, MLCK1, regulates epithelial tight junction permeability. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:55506–55513.
Tran QK, Watanabe H, Zhang XX, Takahashi T, Ohno R . Involvement of myosin light-chain kinase in chloride-sensitive Ca2+ influx in porcine aortic endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 1999; 44:623–631.
Szaszi K, Kurashima K, Kapus A, et al. RhoA and rho kinase regulate the epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3. Role of myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:28599–28606.
Aromolaran AS, Albert AP, and Large WA . Evidence for myosin light chain kinase mediating noradrenaline-evoked cation current in rabbit portal vein myocytes. J Physiol 2000; 524:853–863.
Ammit AJ, Armour CL, Black JL . Smooth-Muscle Myosin Light-Chain Kinase Content Is Increased in Human Sensitized Airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 161:257–263.
Birukov KG, Schavocky JP, Shirinsky VP, et al. Organization of the genetic locus for chicken myosin light chain kinase is complex: multiple proteins are encoded and exhibit differential expression and localization. J Cell Biochem 1998; 70:402–413.
Watterson DM, Schavocky JP, Guo L, et al. Analysis of the kinase-related protein gene found at human chromosome 3q21 in a multi-gene cluster: organization, expression, alternative splicing, and polymorphic marker. J Cell Biochem 1999; 75:481–491.
Smith AF, Bigsby RM, Word RA, Herring NT . A 310-bp minimal promoter mediates smooth muscle cell-specific expression of telokin. Am J Physiol 1998; 274:C1188–1195.
Blue EK, Goeckeler ZM, Jin Y, et al. 220- and 130-kDa MLCKs have distinct tissue distributions and intracellular localization patterns. Am J Physiol 2002; 282:C451–460.
Herring BP, Dixon S, Gallagher PJ . Smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase expression in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 2000; 279:C1656–1664.
Smith L, Su X, Lin P, Zhi G, Stull JT . Identification of a novel actin binding motif in smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem 1999; 274:29433–29438.
Lin P, Luby-Phelps K, Stull JT . Properties of filament-bound myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem 1999; 274:5987–5994.
Smith L, Stull JT . Myosin light chain kinase binding to actin filaments. FEBS Lett 2000; 480:298–300.
Smith L, Parizi-Robinson M, Zhu MS, et al. Properties of long myosin light chain kinase binding to F-actin in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 2002; 277:35597–35604.
Poperechnaya A, Varlamova O, Lin PJ, Stull JT, Bresnick AR . Localization and activity of myosin light chain kinase isoforms during the cell. J Cell Biol 2000; 151:697–708.
Kudryashov DS, Chibalina MV, Birukov KG, et al. Unique sequence of a high molecular weight myosin light chain kinase is involved in interaction with actin cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett 1999; 463:67–71.
Pollard TD, Goldberg I, and Schwarz WH . Nucleotide exchange, structure, and mechanical properties of filaments assembled from ATP-actin and ADP-actin. J Biol Chem 1992; 267:20339–20345.
Zhu MS, Pan Y, Chen HQ, et al. Induction of SARS-nucleoprotein-speicfic immune response by use of DNA Vaccine. Immunol Lett 2004; 92:237–243.
Shirinsky VP, Vorotnikov AV, Birukov KG, et al. A kinase-related protein stabilizes unphosphorylated smooth muscle myosin minifilaments in the presence of ATP. J Biol Chem 1993; 268:16578–16583.
Shin JH, Gardel ML, Mahadevan L, Matsudaira P, Weitz DA . Relating microstructure to rheology of a bundled and cross-linked F-actin network in vitro. PNAS 2004; 101:9636–9641.
Yang CX, Wei DM, Chen C, Yu WP, Zhu MS . 5DFRXXL region of long myosin light chain kinase causes F-actin bundle formation. Chin Sci Bull 2005; 50: 2044–2050.
Mogilner A, Rubinstein B . The physics of filopodial protrusion. Biophysics Journal 2005; 89:782–795.
Yamashiro S, Yamakita Y, Ono S, Matsumura F . Fascin, an actin-bundling protein, induces membrane protrusions and increases cell motility of epithelial cells. Mol Biol Chem 1998; 9:993–1006.
Kudryashov DS, Chibalina MV, Birukov KG, et al. Unique sequence of a high molecular weight myosin light chain kinase is involved in interaction with actin cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett 1999; 463:67–71.
Hayakawa K, Okagaki T, Higashi-Fujime S, Kohama K . Bundling of actin filaments by myosin light chain kinase from smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994; 199:786–791.
Hayakawa K, Okagaki T, Ye LH, et al. Characterization of the myosin light chain kinase from smooth muscle as an actin-binding protein that assembles actin filaments in vitro. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1999; 1450:12–14.
Kudryashov DS, Stepanova OV, Vilitkevich EL, et al. Myosin light chain kinase (210 kDa) is a potential cytoskeleton integrator through its unique N-terminal domain. Exp Cell Res 2004; 298:407–417.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr James Stull and Dr Kristine Kamm for their generous help and instructive suggestions, Dr Qing Shun Zhao for valuable discussions on the manuscripts, Dr Jiong Chen for editing the manuscript, Min Yan Yu for cell culture help and Peng Yu Gu for technical assistance on confocal microscopy. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30470852) and the National Gongguan Project of China (21001BA710B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Chen, H., Chen, C. et al. Microfilament-binding properties of N-terminal extension of the isoform of smooth muscle long myosin light chain kinase. Cell Res 16, 367–376 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7310047
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7310047
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vasopressin and the regulation of aquaporin-2
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2013)
-
Cytoskeletal protein kinases: titin and its relations in mechanosensing
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2011)