Abstract
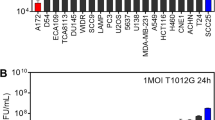
Recombinant strains of herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) harboring mutations in the infected cell product (ICP)34.5 region lose their neurovirulence and replicate more efficiently in dividing tumor cells than stationary cells, becoming replication-selective oncolytic agents. Additional mutation of the ICP6 gene, which encodes ribonucleotide reductase, further impairs the ability of HSV-1 mutants to replicate in normal cells, enhancing tumor selectivity. The present study investigated the effect of HSV-G207, a recombinant HSV-1 lacking ICP34.5 and ICP6, against epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) in vitro and in vivo in a mouse xenograft model. To assess the selectivity of multimutated HSV-G207 against malignant cells, HSV-G207 and wild-type HSV-F were comparatively tested against normal human peritoneal mesothelial cells and EOC cells in vitro. HSV-G207 infected both EOC cells and mesothelial cells; however, unlike EOC cells, mesothelial cells provided a poor substrate for replication of HSV-G207. In contrast to wild-type HSV-F, HSV-G207 exerted a potent oncolytic effect on EOC cells but spared normal mesothelial cells in vitro. Primary EOC cells were more sensitive to the virus than established EOC cell lines. A single intraperitoneal injection of HSV-G207 resulted in a significant reduction in tumor volume and tumor spread in vivo. HSV-G207 was shown to penetrate deeply within tumor nodules and caused no apparent intraperitoneal toxicity. Oncolytic therapy with multimutated replication-restricted HSV may offer a novel approach in the treatment of EOC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coukos, G., Makrigiannakis, A., Montas, S. et al. Multi-attenuated herpes simplex virus-1 mutant G207 exerts cytotoxicity against epithelial ovarian cancer but not normal mesothelium and is suitable for intraperitoneal oncolytic therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 7, 275–283 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700130
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700130
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IL-12 Expressing oncolytic herpes simplex virus promotes anti-tumor activity and immunologic control of metastatic ovarian cancer in mice
Journal of Ovarian Research (2016)
-
Carrier cell-based delivery of replication-competent HSV-1 mutants enhances antitumor effect for ovarian cancer
Cancer Gene Therapy (2011)
-
Comparison of intravenous versus intraperitoneal administration of oncolytic herpes simplex virus 1 for peritoneal carcinomatosis in mice
Cancer Gene Therapy (2009)
-
Molecular analysis of human cancer cells infected by an oncolytic HSV-1 reveals multiple upregulated cellular genes and a role for SOCS1 in virus replication
Cancer Gene Therapy (2008)
-
An oncolytic virus derived from type 2 herpes simplex virus has potent therapeutic effect against metastatic ovarian cancer
Cancer Gene Therapy (2007)