Abstract
Aim:
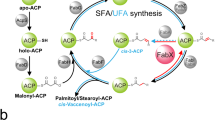
To investigate the inhibition features of the natural product juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) against the three key enzymes from Helicobacter pylori (cystathionine γ-synthase [HpCGS], malonyl-CoA:acyl carrier protein transacylase [HpFabD], and β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase [HpFabZ]).
Methods:
An enzyme inhibition assay against HpCGS was carried out by using a continuous coupled spectrophotometric assay approach. The inhibition assay of HpFabD was performed based on the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase-coupled system, while the inhibition assay for HpFabZ was monitored by detecting the decrease in absorbance at 260 nm with crotonoyl-CoA conversion to β-hydroxybutyryl-CoA. The juglone/FabZ complex crystal was obtained by soaking juglone into the HpFabZ crystal, and the X-ray crystal structure of the complex was analyzed by molecular replacement approach.
Results:
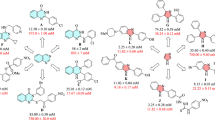
Juglone was shown to potently inhibit HpCGS, HpFabD, and HpFabZ with the half maximal inhibitory concentration IC50 values of 7.0±0.7, 20±1, and 30±4 μmol/L, respectively. An inhibition-type study indicated that juglone was a non-competitive inhibitor of HpCGS against O-succinyl-L-homoserine (Ki=αKi=24 μmol/L), an uncompetitive inhibitor of HpFabD against malonyl-CoA (αKi=7.4 μmol/L), and a competitive inhibitor of HpFabZ against crotonoyl-CoA (Ki=6.8 μmol/L). Moreover, the crystal structure of the HpFabZ/juglone complex further revealed the essential binding pattern of juglone against HpFabZ at the atomic level.
Conclusion:
HpCGS, HpFabD, and HpFabZ are potential targets of juglone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- IC50:
-
the half maximal inhibitory concentration
- K i :
-
the dissociation constant for inhibitor binding
- CoA:
-
coenzyme A
- ACP:
-
acyl carrier protein transacylase
- PDB:
-
Protein Data Bank
- HO-HxoDH:
-
D-2-Hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase
References
Dubreuil JD, Giudice GD, Rappuoli R . Helicobacter pylori interactions with host serum and extracellular matrix proteins: potential role in the infectious process. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2002; 66: 617–29.
Cover TL, Blaser MJ . Helicobacter pylori infection, a paradigm for chronic mucosal inflammation: pathogenesis and implications for eradication and prevention. Adv Intern Med 1996; 41: 85–117.
Cameron EA, Powell KU, Baldwin L, Jones P, Bell GD, Williams SG . Helicobacter pylori: antibiotic resistance and eradication rates in Suffolk, UK, 1991 2001. J Med Microbiol 2004; 53: 535–8.
Paulsen MT, Ljungman M . The natural toxin juglone causes degradation of p53 and induces rapid H2AX phosphorylation and cell death in human fibroblasts. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2005; 209: 1–9.
Inbaraj JJ, Chignell CF . Cytotoxic action of juglone and plumbagin: a mechanistic study using HaCaT keratinocytes. Chem Res Toxicol 2004; 17: 55–62.
Rippmann JF, Hobbie S, Daiber C, Guilliard B, Bauer M, Birk J, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent proline isomerization catalyzed by Pin1 is essential for tumor cell survival and entry into mitosis. Cell Growth Differ 2000; 11: 409–16.
Chao SH, Greenleaf AL, Price DH . Juglone, an inhibitor of the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1, also directly blocks transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: 767–73.
Varga Z, Bene L, Pieri C, Damjanovich S, Gaspar R . The effect of juglone on the membrane potential and whole-cell K+ currents of human lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 218: 828–32.
Hennig L, Christner C, Kipping M, Schelbert B, Rucknagel KP, Grabley S, et al. Selective inactivation of parvulin-like peptidyl-prolylcis/trans isomerases by juglone. Biochemistry 1998; 37: 5953–60.
Alice MC, Tannis MJ, Charles DH . Antimicrobial activity of juglone. Phytotherapy Research 1990; 4: 11–4.
Clausen T, Huber R, Prade L, Wahl MC, Messerschmidt A . Crystal structure of Escherichia coli cystathionine gamma-synthase at 1.5 A resolution. EMBO J 1998; 17: 6827–38.
Soda K . Microbial sulfur amino acids: an overview. Methods Enzymol 1987; 143: 453 9.
Aitken SM, Kim DH, Kirsch JF . Escherichia coli cystathionine gamma-synthase does not obey ping-pong kinetics. Novel continuous assays for the elimination and substitution reactions. Biochemistry 2003; 42: 11297–306.
Wahl MC, Huber R, Prade L, Marinkovic S, Messerschmidt A, Clausen T . Cloning, purification, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of cystathionine gamma-synthase from E coli. FEBS Lett 1997; 414: 492–6.
Salama NR, Shepherd B, Falkow S . Global transposon mutagenesis and essential gene analysis of Helicobacter pylori. J Bacteriol 2004; 186: 7926–35.
Campbell JW, Cronan JE . Bacterial fatty acid biosynthesis: targets for antibacterial drug discovery. Annu Rev Microbiol 2001; 55: 305–32.
White SW, Zheng J, Zhang YM, Rock CO . The structure biology of type II fatty acid biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochemistry 2005; 74: 791–831.
Magnuson K, Jackowski S, Rock CO, Cronan JE . Regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev 1993; 57: 522–42.
Williamson IP, Wakil SJ . Studies on the mechanism of fatty acid synthesis. XVII. Preparation and general properties of acetyl coenzyme A and malonyl coenzyme A-acyl carrier protein transacylases. J Biol Chem 1966; 241: 2326–32.
Ruch FE, Vagelos PR . The isolation and general properties of Escherichia coli malonyl coenzyme A-acyl carrier protein transacylase. J Biol Chem 1973; 248: 8086–94.
Verwoert II, Verbree EC, van der Linden KH, Nijkamp HJ, Stuitje AR . Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Escherichia coli fabD gene, encoding malonyl coenzyme A-acyl carrier protein transacylase. J Bacteriol 1992; 174: 2851–7.
Kutchma AJ, Hoang TT, Schweizer HP . Characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa fatty acid biosynthetic gene cluster: purification of acyl carrier protein (ACP) and malonyl-coenzyme A:ACP transacylase (FabD). J Bacteriol 1999; 181: 5498–504.
Mohan S, Kelly TM, Eveland SS, Raetz CR, Anderson MS . An Escherichia coli gene (FabZ) encoding (3R)-hydroxymyristoyl acyl carrier protein dehydrase. Relation to fabA and suppression of mutations in lipid A biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 32896–903.
Heath RJ, Rock CO . Roles of the FabA and FabZ beta-hydroxyacylacyl carrier protein dehydratases in Escherichia coli fatty acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 27795–801.
Pillai S, Rajagopal C, Kapoor M, Kumar G, Gupta A, Surolia N . Functional characterization of beta-ketoacyl-ACP reductase (FabG) from Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 303: 387–92.
Sharma SK, Kapoor M, Ramya TN, Kumar S, Kumar G, Modak R, et al. Identification, characterization, and inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase (FabZ). J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 45661–71.
Kong YH, Wu DL, Bai HY, Han C, Chen J, Chen LL, et al. Enzymatic characterization and inhibitor discovery of a new cys-tathionine γ-synthase (CGS) from Helicobacter pylori. J Biochem (Tokyo) 2008; 143: 59–68.
Liu WZ, Han C, Hu LH, Chen KX, Shen X, Jiang HL . Characterization and inhibitor discovery of one novel malonyl-CoA: acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT) from Helicobacter pylori. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 697–702.
Liu WZ, Luo C, Han C, Peng SY, Yang Y, Yue J, et al. A new beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase (FabZ) from Helicobacter pylori: molecular cloning, enzymatic characterization, and structural modeling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 333: 1078–86.
Zhang L, Liu WZ, Hu TC, Du L, Luo C, Chen KX, et al. Structural basis for catalytic and inhibitory mechanisms of beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase (FabZ). J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 5370–9.
Chen LL, Gui CS, Luo XM, Yang QG, Gunther S, Scandella E, et al. Cinanserin is an inhibitor of the 3C-like proteinase of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and strongly reduces virus replication in vitro. J Virol 2005; 79: 7095–103.
Otwinowski Z, Minor W . Methods in Enzymology 1997; 276: 307–26.
Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve, et al. Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 1998; 54: 905–21.
Emsley P, Cowtan K . Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2004; 60: 2126–32.
Silver LL . Multi-targeting by monotherapeutic antibacterials. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007; 6: 41–55.
Inatsu S, Ohsaki A, Nagata K . Idebenone acts against growth of Helicobacter pylori by inhibiting its respiration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006; 50: 2237–9.
Park BS, Lee HK, Lee SE, Piao XL, Takeoka GR, Wong RY, et al. Antibacterial activity of Tabebuia impetiginosa Martius ex DC (Taheebo) against Helicobacter pylori. J Ethnopharmacol 2006; 105: 255–62.
Tasdemir D, Lack G, Brun R, Ruedi P, Scapozza L, Perozzo R . Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum fatty acid biosynthesis: evaluation of FabG, FabZ, and FabI as drug targets for flavonoids. J Med Chem 2006; 49: 3345–53.
Wang J, Soisson SM, Young K, Shoop W, Kodali S, Galgoci A, et al. Platensimycin is a selective FabF inhibitor with potent antibiotic properties. Nature 2006; 441: 358–61.
Delanoue WL . The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. San Carlos, CA: DelanoScientific, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30525024, 20721003, and 90713046).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Yh., Zhang, L., Yang, Zy. et al. Natural product juglone targets three key enzymes from Helicobacter pylori: inhibition assay with crystal structure characterization. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29, 870–876 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00808.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00808.x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A comprehensive review on ethnobotanical, medicinal and nutritional potential of walnut (Juglans regia L.)
Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy (2022)
-
Two-weeks repeated-dose oral toxicity study of Pediococcus acidilactici J9 in a mice model
BMC Microbiology (2020)
-
A new anti-Helicobacter pylori juglone from Reynoutria japonica
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2019)
-
Theoretical investigation of the radical scavenging activity of shikonin and acylshikonin derivatives
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2012)
-
Emodin targets the β-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase from Helicobacter pylori: enzymatic inhibition assay with crystal structural and thermodynamic characterization
BMC Microbiology (2009)